There may be not much a difference, but big data vs data science has always instigated the minds of many and put them into a dilemma. Today, we will reveal the real difference between these two terms in an elaborative manner which will help you understand the core concepts behind them and how they differ from each other. First of all, data science is an evolutionary extension of statistics that deals with large datasets with the help of computer science technologies. Many confuse Data science with absolutely wrong machine learning. Although machine learning is a subset of Data science, they are not the same.
On the other hand, big data deals with the vast collection of heterogeneous data from different sources and is not available in standard database formats that we are aware of. This implies that the data won’t be tabulated into a table or chart or graph.
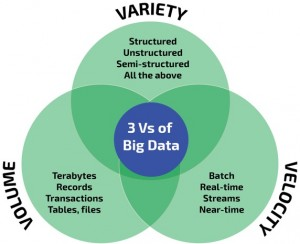
Big data classifies data into unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data.
- Unstructured data – social networks, emails, blogs, digital images, and contents
- Semi-structured data – XML files, text files, etc.
- Structured data – RDBMS, OLTP, and other structured formats.
While structured data is quite simple to understand, unstructured data required customised modelling techniques to extract information from the data which is done by the help of computer tools, statistics, and other data science approaches.
Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data — both structured and unstructured.
Data science, also known as data-driven science, is an interdisciplinary field about scientific methods, processes, and systems to extract knowledge or insights from data in various forms, either structured or unstructured, similar to data mining.

In the digital era that we live in, data has become the biggest and most valuable asset for most organisations. Data is rapidly transforming the way we live and communicate, and it is by collecting, sorting and studying this data, that organisations across the world are looking for ways to impact their bottom lines.
When working with all terminology related to data, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the different scope of work related to it. In this article, we’ll discuss the differences between Big Data and Data Science. Though these terms are interlinked and often used interchangeably, there’s a vast underlying difference between them in all aspects.
Difference between Big Data & Data Science
1. Concept
Data Science
It is the umbrella term that encompasses most things related to data — from the generation of data to data cleansing, visualizing, mining to analytics and deals with both raw data and structured data (information). The science encompasses statistics, programming, mathematics, problem-solving, to name a few.
Big Data
Analytics of Big Data is all about examining raw data to support decision making in the fields of business intelligence. Algorithmic processes, when applied will derive operational visions for multifaceted business solutions. In short, it needs to be inspected, transformed, cleansed and modelled into information.
2. Applications
Data Science
Digital advertisement: You will notice that whenever you open any website supported by advertisements, the advertisements are related to browsing history! Data science algorithms and machine learning are used by every digital marketing domain like Google Ad Sense or Media.Net to personalize the ads you see.
Internet search: Sometimes when you search for a term or run a query in your browser in both the normal mode and incognito mode, it will surprise you how the search results are different in the two browser windows. That is because we live in a sort of filter bubble, where when we are logged into our accounts, based on the browsing history of that account, the search results are filtered. .
Big Data
Gaming sector: A single frame of your favourite online game can require 100mb of data to render. Imagine how much Big Data is generated from the server in a single gaming session online.
Healthcare sector: Hospitals and Healthcare service providers store big data to analyse in order to perform tasks like track and optimise patient influx, track the use of equipment and medicines in the facilities, organise patient information, etc.
3. Job Responsibilities
Data Science
The major responsibility of data science can be captured in two words – exploratory analysis. As the term suggests, the science explores and analysis the data, with a combination of machine learning algorithms. The analysis can either predict an outcome – such as the US housing market crash of 2009 with the help anomalies and trends, both hidden and obvious.
Big Data
Big Data is large is more than one terabyte and unstructured as it is captured from multiple sources. Future solutions are dependent on the data and the structure,
The behaviour and structure for future solutions and how they can be delivered by applying different technologies like Spark, Hadoop, etc. based on the requirements.
4. Skills Required
Data Science
To become a Data Scientist, you should have excellent:
- analytical skills
- data management skills
- programming skills
- technical skills
- sound knowledge of database system
Big Data
As an aspiring big data analytics professional, it is necessary to develop proficiency:
Programming languages skills in statistics and mathematics are required.
- Data wrangling skills
- Data visualisation,
- Machine learning skills, and
- Communication skills.
5. Pay Scales
Data Science
A Data Scientist can earn an average salary of about is ₹7,08,012 per annum.
Big Data
An average Big Data Analytics professional can earn Rs. 7,24,280 per annum
6. Career Options
Data Science
Data Scientists are fast becoming the backbone of the companies they work for, as it is their ability to read data that helps companies achieve success. Here are some of the career options that you can explore:
Data/Infrastructure/Enterprise Architects are tasked with building solutions for design analytics, tracking applications behaviour, and overseeing business systems.
Big Data
With billions of bytes of data being produced across the world, it should come as no surprise that there are several career options available to Big Data Analysts. Some of the options you can explore are:
Big Data Engineers are responsible for building designs, followed by testing and maintaining the design along with solution analysts.
Big Data Analysts are well-versed in Hadoop and other technologies. They are responsible for finding information from the huge data sets which statisticians and scientists can use.
7. Basis of Formation
Data Science
In the field of Data Science, scientific applications are used. These applications help the data scientist to extract information or unearth trends hidden in Big and other data.
The field is related to filtering data followed by preparing it for analysis.
Apps and tools are used to filter patterns and develop working models and solutions.
Big Data
Big Data is usually captured by the high volume of Internet traffic.
Users behavioural patterns and preferences are captured via electronic devices, AV feeds, online forums, and other digital media
Comparison of Big data Vs Data Science
| Basis | Data Science | Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Skewed towards the scientific approach of interpreting the data and retrieves the information from a given data set | Revolves around the huge volumes of data which cannot be handled using the conventional data analysis method |
| Concept | Obtained with big data is heterogeneous that indicates a diversified data set which has to be per-cleaned and sorted before running analytics on them | Scientific techniques to process data, extract information and interpret results which help in the decision-making process |
| Formation | Internet users/ traffic, live feeds, and data generated from system logs | Data filtering, preparation, and analysis |
| Application areas | Internet search, digital advertisements, text-to-speech recognition, risk detection, and other activities | Telecommunication, financial service, health and sports, research and development, and security and law enforcement |
| Approach | Uses mathematics and statistics extensively along with programming skills to develop a model to test the hypothesis and make decisions in the business | Used by businesses to track their presence in the market which helps them develop agility and gain a competitive advantage over others |





