
- Introduction to Strategy Implementation
- Significance of Strategy Execution
- Implementation Steps
- Establishing Clear Goals
- Resource Allocation
- Allocation of Roles and Responsibilities
- Monitoring and Control
- Communication and Stakeholder Involvement
- Risk Management
- Measuring Success and KPIs
- Challenges in Implementing Strategy
- Effective Execution Best Practices
Detailed Guide to Strategy Implementation
Introduction to Strategy Implementation
Strategy implementation involves implementing an organization’s strategic plan by converting broad goals into actionable tasks. It is about aligning resources, processes, and people to meet the desired results. Although developing a strategy is crucial, its implementation is also critical, as it decides whether the organization can effectively attain its objectives. The implementation action needs open communication, coordination, and tracking to ensure that the intended results are achieved. It also means adjusting to problems, making dynamic changes, and aligning all parties.. For more details on how project management principles can aid in strategy implementation, consider exploring PMP Training.
Significance of Execution of Strategy
The successful execution of strategy is essential for organizations to attain their long-term objectives. Without effective implementation, even an excellent plan will not succeed. Execution guarantees that the vision and mission of an organization are realized in tangible forms. It also assists firms in:
- Gain a Competitive Edge: Properly implementing their strategies allows organizations to beat the competition and effectively fulfill market needs.
- Maintain Organizational Alignment: Implementation creates a situation where all departments, teams, and employees work towards the same goals.
- Maximize Resource Utilization: With the proper distribution of resources, organizations can maximize productivity and reduce waste.
- Hold People Accountable: By establishing clear roles and responsibilities, organizations can monitor progress and make people accountable for outcomes.
- Drive Sustained Growth: Regular monitoring and improvisation during the implementation process fuel sustained business growth.
Become a Project Management expert by enrolling in this PMP Training Online Course today.
Critical Steps in Implementation
Strategy implementation typically involves a few well-delineated steps, such as
Defining Goals: Creating objective and quantifiable goals per the larger strategy.
- Action Plan Development: Segmenting the strategy into mini-tasks or actions that can be managed.
- Delegating Tasks: Identifying and assigning key persons to perform respective tasks.
- Allocating Resources: Ensuring the appropriate financial, human, and technological resources exist.
- Communicating the Plan: Informing all interested parties to obtain their alignment.For more information on useful resources, check out What are Project Management Tools.
- Monitoring Progress: Periodically tracking the implementation process through performance reviews.
- Adjusting as Needed: Making in-the-moment adjustments in response to difficulties or altered conditions.
These steps are the basis for a systematic and systematic implementation process.
Advance your Project Management career by joining this PMP Training Online Course now.
Setting Clear Objectives
Clear and measurable goals are the foundations of effective strategy implementation. Well-stated goals assist the organization in the following ways:
- Establish a Clear Direction: Detail what the company wants to achieve.
- Enable Measurement of Performance: Set KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to gauge progress.
- Enhance Team Concentration: Streamline all the departments toward the common objectives.
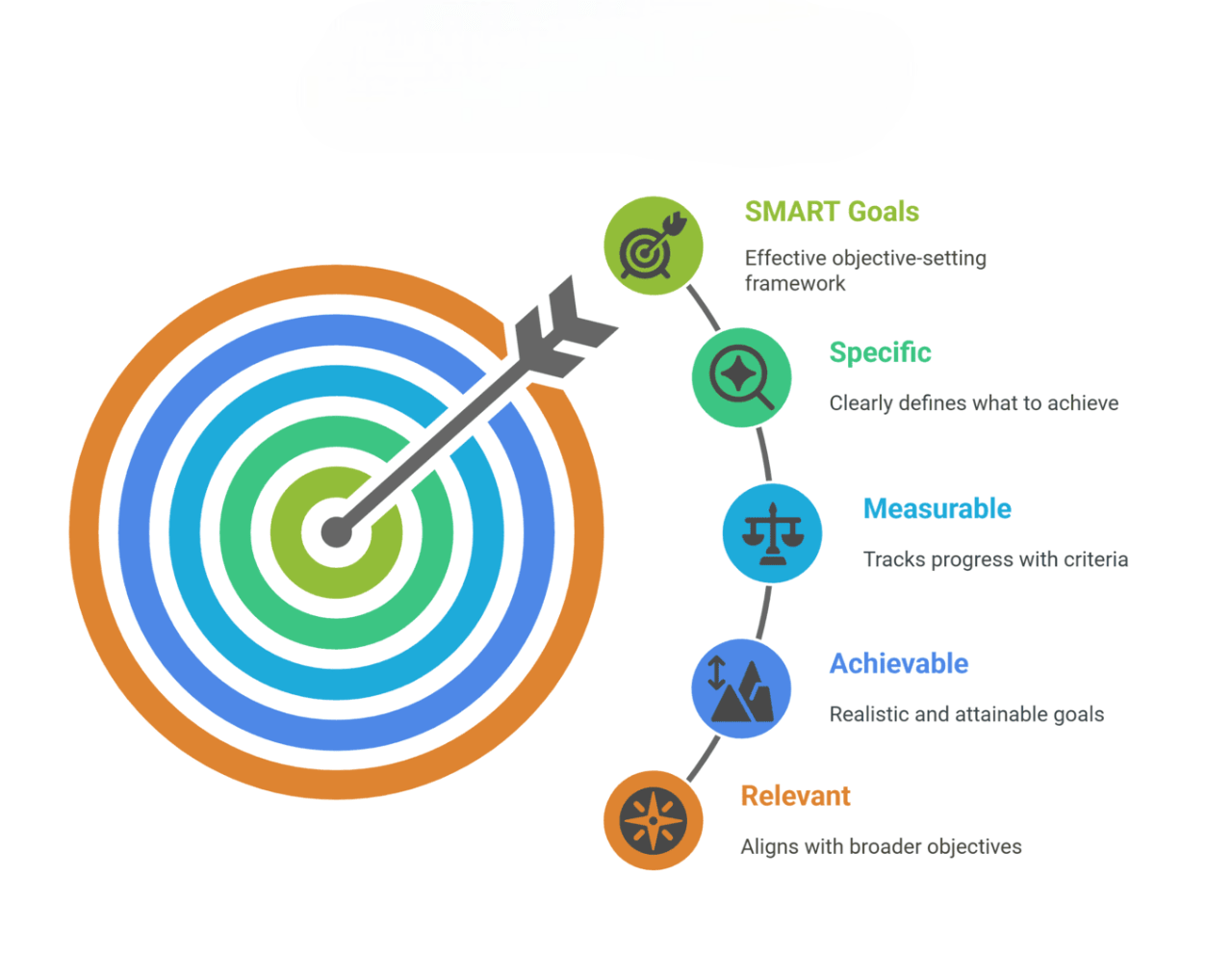
- Specific: Clearly outline desired results.
- Measurable: Set metrics to evaluate success.
- Achievable: Plan realistic and attainable goals.
- Relevant: Fits within the overall strategy of the organization.
- Time-bound: Set timelines for reaching the objectives.
Reasonable goals need to adhere to the SMART model:
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation entails deploying the financial, human, and technological resources required to implement the strategy. Efficient allocation provides the organization with the abilities necessary to meet its objectives. For a better understanding of adaptive methods, explore What is Agile. Significant considerations in resource allocation are…
- Budgeting: Providing adequate funds for projects, technology, and workforce needs.
- Human Resources: Allocating competent human capital with the appropriate expertise to tasks.
- Technology and Tools: Equipping employees with the tools and technology to facilitate the execution process.
- Time Management: Allowing adequate time for each task to avoid hasty or poor implementation.
- Effective use of resources maximizes productivity and facilitates smooth execution.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
A practical definition of roles and responsibilities makes it easier to hold individuals or teams accountable and ensures smooth execution. Providing individuals or teams with particular responsibilities encourages clarity and effectiveness. PMP Training can help improve the understanding of these key aspects in project management. Essential steps in this process are…
- Identifying Key Stakeholders: Determining who will own, lead, manage, and execute different strategy elements.
- Establishing Accountability: Creating definitive ownership of responsibilities and deliverables.
- Ensuring Collaboration: Promoting cross-functional collaboration by allocating shared responsibilities when needed.
- Empowering Decision-Makers: Empowering decision rights to key people for quicker implementation.
Well-defined roles and responsibilities avoid confusion, duplication of efforts, and delays.
Monitoring and Control
Monitoring and control are necessary to monitor progress, assess performance, and make the required adjustments. This includes:
Setting Performance Indicators: Employing KPIs and benchmarks to gauge success.
- Regular Reviews: Performing frequent performance reviews to assess progress.
- Identifying Deviations: Identifying differences between intended and actual results.
- Corrective Actions: Making changes to realign with strategic objectives.
Effective monitoring enables organizations to detect and correct inefficiencies promptly, keeping the strategy on track.
Are you getting ready for your PMP interview? Check out our blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers!
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Good communication is essential to implement the strategy. It keeps all stakeholders aligned and informed about their roles. Some essential communication strategies are
- Clear Messaging: Communicate the strategy’s objectives, advantages, and expectations.
- Regular Updates: Share regular updates on progress to inform stakeholders.
- Open Feedback Channels: Foster employee and stakeholder feedback to detect potential problems.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve stakeholders early to gain their buy-in and support.
- Risk management is necessary during strategy implementation to identify possible problems and minimize their effects. This includes:
- Identifying Risks: Identifying possible hurdles or threats that may impact the implementation.
- Assessing Risk Impact: Determining the probability and severity of every risk.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: Establishing contingency plans to minimize the effects of possible risks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Constantly reviewing risks and making changes accordingly.
- Successful risk management guarantees business continuity and minimizes the likelihood of project failure.
- Measuring success via Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is necessary to assess the effectiveness of strategy implementation.To learn more about how to plan for product success, explore What is a Product Roadmap Typical KPIs are
- Financial Metrics: Revenue growth, profit margins, and cost savings.
- Operational Efficiency: Productivity rates, process efficiency, and resource utilization.
- Customer Satisfaction: Feedback scores, retention rates, and Net Promoter Score (NPS).
- Employee Engagement: Staff satisfaction and retention metrics.
- Periodic measurement of these KPIs assists organizations in determining their progress, areas for improvement, and strategic alignment.
- Inadequate Communication: Miscommunication may cause confusion and misalignment.
- Inadequate Resources: Inadequate funding, trained staff, or technology may inhibit execution.
- Resistance to Change: Employees can resist changes, causing delays in implementation. To understand how different methodologies can help manage change, check out Scrum vs Kanban.
- Ineffective Leadership: Poor leadership can lead to inadequate direction and poor coordination.
- Poor Monitoring and Control: Lack of monitoring progress results in deviations from the initial strategy.
- Aligning with Organizational Goals: All the implementation efforts should be aligned with the overall strategic goals.
- Developing a Step-by-Step Action Plan: Divide the strategy into concrete, actionable steps.
- Ensuring Leadership: Get effective leaders on board to monitor and propel the implementation process.
- Encouraging Collaboration: Invite cross-functional collaboration for smoother implementation.
- Employing Technology and Tools: Utilize project management tools and data analysis for improved monitoring and decision-making.
- Continuous Improvement: Periodically review and adjust the implementation process for optimal performance.
Effective communication fosters trust, enhances morale, and facilitates smooth coordination.
Risk Management
Measuring Success and KPIs
Challenges in Implementing Strategy
During strategy implementation, organizations are likely to encounter several challenges, such as:
Solving these issues proactively guarantees more efficient execution.
Best Practices to Ensure Effective Execution
To ensure effective strategy execution, organizations should adopt best practices, including
By following these best practices, organizations can implement their strategies effectively and efficiently.
Conclusion
Strategy implementation is a multidimensional but unavoidable process that transforms strategic plans into tangible realities. It involves meticulous planning, resource mobilization, compelling communication, and constant follow-up. PMP Training can help enhance these skills by providing essential knowledge for managing complex projects. Organizations can guarantee the effective implementation of their strategies by establishing viable objectives, involving stakeholders, and gauging success based on KPIs. Mitigating challenges through risk management and adaptive leadership is vital in propelling sustainable business growth and attaining long-term goals.





