
- What is a Data Analyst?
- Why Data Analyst
- Understanding the Role of a Data Analyst
- Job Description of Data Analyst
- Roles and Responsibilities of a Data Analyst
- Skills Required for Data Analyst
- Conclusion
A Data Analyst plays a critical role in interpreting and analyzing data to provide actionable insights for decision-making. Their primary responsibilities include collecting, processing, and cleaning data from various sources, ensuring its accuracy and consistency. Data analysts use tools like Excel, SQL, and Tableau to create reports, dashboards, and visualizations that highlight trends, patterns, and key metrics. They work closely with business teams to understand their data needs and help identify opportunities for improvement, a key aspect of Data Science Training. Data analysts also perform statistical analysis and hypothesis testing to make data-driven recommendations. Additionally, they ensure data is accessible and user-friendly for stakeholders and may assist in setting up data collection systems. A key aspect of their role is transforming raw data into a form that is easy to interpret, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize performance.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is a Data analyst?
A statistics analyst is an expert who collects, processes and translates statistics to assist companies in making knowledgeable enterprise decisions. They examine big datasets to become aware of trends, patterns, and correlations that offer insights into enterprise overall performance and possibilities for improvement. Data analysts use statistical techniques, data visualization tools, and programming languages like SQL, Python, Hadoop, and R to clean, organize, and analyze data effectively, while also learning to Discover the Best AI Tools for 2025 Writing and Editing. Their function regularly entails growing reports, dashboards, and displays to speak findings to stakeholders in a clean and actionable way.
Data analysts paint throughout diverse industries, including finance, healthcare, marketing, and e-trade, assisting organizations in optimizing operations, beautifying client experiences, and pressure strategic decision-making. By remodeling uncooked statistics into significant insights, statistics analysts play a vital function in enhancing performance and riding enterprise success.
Why Data Analyst
- High Demand: Data analysts are in high demand across various industries as organizations rely more on data-driven decision-making.
- Versatile Career: Data analysis skills are applicable in diverse sectors like finance, healthcare, marketing, and technology, offering a wide range of career opportunities.
- Problem-Solving: Data analysts play a key role in identifying trends and patterns in data, solving complex business challenges, and improving processes.
- Career Growth: With the increasing importance of data, data analysts have excellent career advancement opportunities, where techniques like Interpolation are essential.
- Impactful Work: By interpreting data, analysts provide actionable insights that directly influence business strategies and outcomes.
- Skill Development: The role helps develop a strong foundation in analytical thinking, programming, and data visualization tools.
- Good Compensation: Data analysts typically enjoy competitive salaries and benefits, making it an attractive career choice.
- Continuous Learning: The evolving nature of data technology ensures that data analysts are constantly learning and staying at the forefront of new tools and techniques.
- The tremendous quantity of statistics created daily has widespread enterprise value. Data analysts are essential to unlocking this value. Their obligations fluctuate primarily based on the sector, including comparing purchaser statistics for e-trade or affected person statistics for pharmaceuticals. They put together statistics so that Data Scientists can assemble progressive systems.
- Healthcare is one of the sectors that has benefitted the most from data evaluation methodologies. Patients’ records generated with the assistance of scientific businesses are in quintillion bytes, making them a key area of focus in Data Science Training.
- The Data Analyst’s obligations are extracting the records from records warehouses and preparing them for evaluation. At first, the extracted records are within the uncooked shape, on which operations, manipulation, and visualization will yield inconsistent results. To establish the records, data analysts carry out diverse strategies to prepare them for use.
- Data Analysts seek and extract applicable statistics for their companies. After extracting statistics, they carry out exploratory statistics evaluation to apprehend it and make it in a based shape for Data Scientists to construct Machine Learning Models.
- Once the records are prepared, they are given to Data Scientists for manipulation, visualization, and predictive analytics. The evaluation of records using records scientists inside the healthcare quarter enables the collection of records associated with drug requirements, ventilators, and different facilities. It additionally allows control of doctors` availability, vacant rooms, emergency wards, and more.
- Data Collection: Data analysts are responsible for gathering data from various sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, and external APIs, ensuring that the data is relevant and accurate.
- Data Cleaning: They clean and preprocess data by identifying and correcting errors, handling missing values, and removing duplicates to ensure high-quality data for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Data analysts apply statistical methods and tools to explore and analyze datasets, identifying trends, patterns, and correlations that can provide valuable insights for the business.
- Data Visualization: They create visualizations like charts, graphs, and dashboards to simplify data, aiding informed decisions in Data Science in Retail Industry.
- Reporting: Data analysts generate regular reports that summarize findings, highlight key metrics, and provide actionable recommendations to support business strategies.
- Collaboration: They work closely with various departments, such as marketing, finance, and IT, to understand their data needs and ensure that analytics efforts align with organizational goals.
- Continuous Improvement: Data analysts continuously refine data collection, analysis, and reporting processes to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and the overall value of data-driven decision-making.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
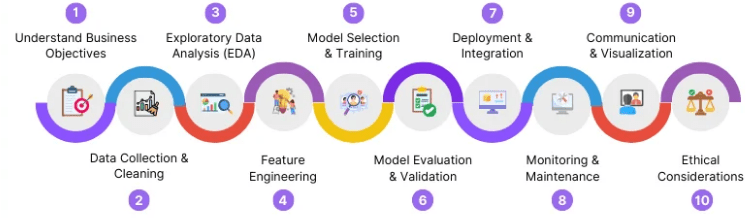
Understanding the Role of a Data Analyst
Job Description of Data Analyst
This weblog on Data Analyst roles and duties provides an overview of job postings for Data Analyst positions by various companies on online job portals, highlighting key requirements. A typical Data Analyst job often requires a bachelor’s degree in fields like computer science or data analytics. Strong written and verbal communication skills are essential, as analysts must present data insights clearly to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Knowledge of software engineering methods is also important for developing efficient data processing systems, helping to better understand What is Data and how it can be utilized. Experience with database technologies and managing large-scale databases is crucial to ensure data integrity and accessibility. Data Analysts are responsible for converting raw data into actionable insights that businesses can use to address problems and improve operations. They are also tasked with creating, deploying, and maintaining innovative data analytics solutions. Throughout an organization, data is continuously collected and analyzed to support decision-making processes, helping both team members and management make informed, data-driven choices.
Want to Pursue a Data Science Master’s Degree? Enroll For Data Science Masters Course Today!
Roles and Responsibilities of a Data Analyst
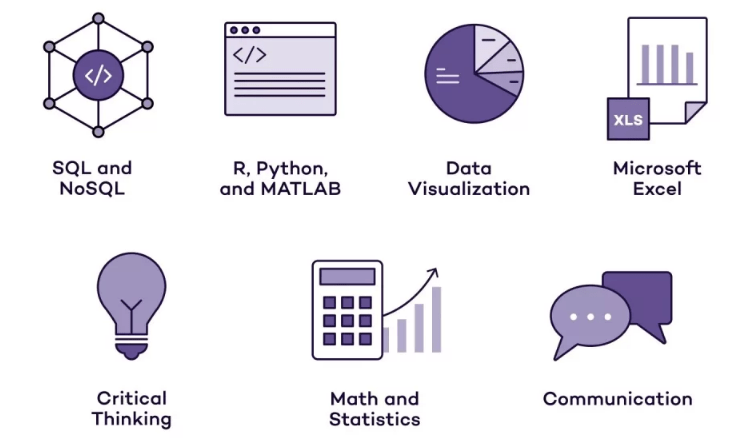
Skills Required for Data Analyst
A Data Analyst requires a diverse set of technical and soft skills to excel in the role. Technical proficiency is crucial, with expertise in tools like SQL, Excel, and data visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI for creating reports and dashboards. Strong knowledge of statistical analysis and the ability to interpret data using methods such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing is essential. Programming skills in languages like Python or R are also valuable for automating data processes and conducting advanced analysis, key elements of Understanding Data Science and Data Analytics in 2025. Understanding database management and experience with tools like Hadoop or NoSQL databases can be beneficial for handling large datasets. In addition to technical skills, strong problem-solving abilities and the capacity to think analytically are key to interpreting data effectively and making actionable recommendations. Communication skills are also vital, as Data Analysts must present complex insights in a clear and understandable manner to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. A detail-oriented mindset and the ability to manage multiple tasks are also essential for success in this role.
Go Through These Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
In conclusion, facts analysts are critical in reworking uncooked facts into significant insights that force commercial enterprise selections and improvements. Leveraging statistical strategies, facts visualization gear, and analytical capabilities, they assist businesses in perceiving trends, optimizing processes, and beautifying average performance. Data analysts are crucial in numerous industries, including finance, healthcare, marketing, and technology, wherein data-driven decision-making is essential for success, and their skills are a key component of Data Science Training. Despite demanding situations inclusive of facts, significant troubles, and the need for non-stop learning, the call for professional facts and analysts keeps growing. As organizations increasingly depend upon facts, the function of a facts analyst remains crucial in ensuring correct, informed, and strategic decision-making. A Data Analyst is chargeable for translating uncooked facts into applicable insights that force commercial enterprise selections. Data Analysts help companies optimize operations and enhance performance by using statistical evaluation, programming, facts visualization, and database management capabilities.


