- An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- A Synopsis of Human Intelligence
- Essential Distinctions Between Human and Artificial Intelligence
- What Is AI Unable to Do Without Human Help?
- Will Human Intelligence Be Replaced by Artificial Intelligence in Employment?
- How Can AI and Human Intelligence Work Together?
- Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized many industries. From healthcare and finance to education and entertainment, AI is making strides and transforming the way we live and work. However, as AI continues to evolve, it raises important questions about the relationship between human and machine intelligence. How do AI and human intelligence differ? Can one replace the other, particularly in terms of employment? And can AI and human intelligence work together for optimal results? In this article, we will explore these questions, starting with an introduction to AI and a synopsis of human intelligence, as often discussed in Data Science Training. We will then dive into the key distinctions between human and artificial intelligence, discuss what AI cannot do without human help, and examine whether AI will replace human intelligence in the workplace. Finally, we will consider the possibilities for AI and human intelligence to collaborate.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and carry out tasks that typically require human cognitive abilities. These tasks include reasoning, decision-making, speech recognition, language translation, and visual perception. The primary goal of AI is to create systems that replicate human thinking and continuously improve as they process more data. AI can be categorized into two main types: Narrow AI (Weak AI) and General AI (Strong AI), a distinction often discussed in Top Data Science Programming Languages. Narrow AI is designed to perform specific tasks or functions, such as chatbots, recommendation systems (like those used by Netflix or Amazon), and facial recognition software. While narrow AI excels at its designated tasks, it is limited to those functions and cannot go beyond its programmed capabilities. On the other hand, General AI is an advanced form that aims to replicate human-like intelligence across a broad range of tasks, with the ability to learn and adapt, similar to humans.
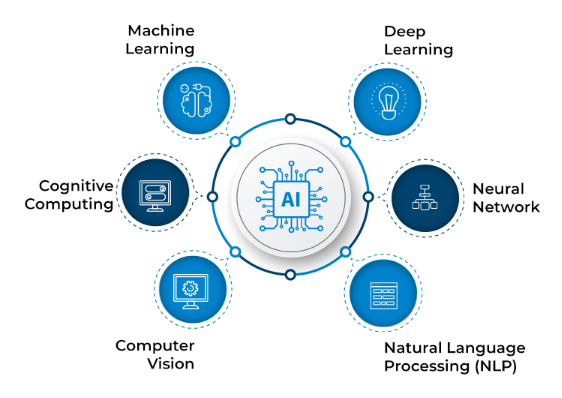
However, General AI remains a theoretical concept and has not yet been realized. AI encompasses technologies like machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and neural networks. Machine learning allows AI systems to learn from data and enhance their performance independently. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, leverages intricate neural networks to analyze vast datasets and make predictions or decisions.
A Synopsis of Human Intelligence
Human intelligence is the ability of the human brain to reason, learn, comprehend complex ideas, adapt to new situations, solve problems, and think abstractly. Unlike AI, which is built using algorithms, human intelligence is a product of biology and evolution, deeply embedded in the structure and functioning of the human brain.The main features of human intelligence include:
- Consciousness and Self-awareness: Humans can be aware of themselves, their surroundings, and their thoughts. This self-awareness allows humans to reflect, question their actions, and make decisions based on experience and emotional context.
- Emotions: Emotions play a crucial role in human intelligence. Feelings such as empathy, joy, fear, and sadness influence decision-making, problem-solving, and social interactions insights that are often reflected in A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist. Emotional intelligence is a key aspect of human reasoning.
- Learning and Adaptability: Humans can learn from their environment, experiences, and interactions. This learning process is not restricted to a particular domain; humans can apply knowledge across various situations and adapt to new challenges.
- Creativity and Critical Thinking: Humans can generate novel ideas, think outside the box, and approach problems from multiple angles. Human intelligence involves logical reasoning and creative thinking, allowing humans to solve problems innovatively.
- Human Intelligence: One of the most significant differences is that humans possess consciousness and self-awareness. Humans think and reflect on their thoughts, question their beliefs, and have a sense of individuality. Consciousness allows humans to engage in deep introspection and make decisions based on personal experiences and emotions.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI, by contrast, lacks consciousness and self-awareness. It can analyze data, recognize patterns, and generate responses, but it does not “understand” the information in a human-like way. It does not have emotions or subjective experiences topics often highlighted in Data Science Training. AI performs tasks based on programming and algorithms without the ability to think independently or reflect on its actions.
- Human Intelligence: Emotions profoundly influence human decision-making. Human intelligence integrates emotional responses with rational thinking to guide behavior and interactions. For instance, empathy allows humans to understand the feelings and perspectives of others, leading to more effective social communication and relationships.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI does not possess emotional intelligence. Although AI can simulate emotions through facial recognition or sentiment analysis, it does not truly experience emotions. AI can process and recognize patterns in human behavior but cannot feel or empathize with others.
- Human Intelligence: Humans excel at generalizing knowledge and applying it across various domains. For example, they can learn to solve a math problem and then apply similar problem-solving strategies to a completely different situation, such as managing personal finances or navigating a new job.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI, particularly narrow AI, is highly specialized and excels at specific tasks but struggles with generalization, a concept often discussed in Reasons You Should Learn R, Python, & Hadoop. For example, an AI trained to recognize objects in images may not be able to understand or perform tasks in other domains, such as natural language processing, without significant retraining or reprogramming.
- Human Intelligence: Humans have an innate ability to create new ideas, art, music, and solutions to problems. Creativity in humans is driven by reason and emotion, enabling humans to think innovatively and approach issues from multiple perspectives. Humans can combine unrelated concepts to generate novel ideas.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI can generate outputs that resemble human creativity, such as composing music or producing art. However, these outputs are based on patterns and data derived from human-created content. AI cannot generate truly original ideas that are disconnected from previous data. Its creativity is limited to the scope of its training.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Innovation: Combining AI’s computational power with human creativity and emotional intelligence leads to improved decision-making, problem-solving, and productivity across industries.
- Decision Support Systems: AI processes large datasets quickly and offers insights or suggestions (e.g., in healthcare), while humans make the final decisions using their expertise and empathy.
- Augmenting Creativity: In fields like design, advertising, and entertainment, AI can assist in idea generation and optimization, but humans provide the emotional depth and original creative direction.
- Human-AI Collaboration in Education: AI can personalize learning through adaptive resources and feedback, but teachers remain essential for nurturing critical thinking, offering emotional support, and guiding complex understanding a balance also reflected in Why Python Is Essential for Data Analysis & Data Science.
- Workplace Automation and Assistance: AI can handle repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and customer support, allowing employees to focus on strategic, interpersonal, and high-level creative work.
- Scientific Research and Innovation: AI accelerates scientific discovery by analyzing complex datasets, modeling simulations, and identifying patterns or correlations that may not be immediately apparent to humans, while researchers provide the critical thinking and ethical oversight needed to guide breakthroughs.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Essential Distinctions Between Human and Artificial Intelligence
Consciousness and Self-Awareness
Emotional Intelligence
Generalization and Flexibility
Creativity and Innovation
What Is AI Unable to Do Without Human Help?
Despite significant advancements in Artificial Intelligence, there are still many areas where AI falls short without human involvement. One major limitation is understanding context. AI systems often struggle to interpret nuanced or dynamic situations, especially when faced with incomplete information or unexpected scenarios. While AI excels in structured, rule-based environments, it lacks the flexibility and intuitive grasp of broader context that humans naturally possess, which is essential for making informed decisions in complex and ever-changing situations. Another key limitation lies in dealing with ethical dilemmas, a topic that contrasts with the technical focus of What is Normality Test in Minitab. AI lacks the moral reasoning and ethical judgment that humans use to navigate complex issues involving fairness, justice, and right or wrong. While developers can program AI to follow certain ethical frameworks, those guidelines are created and interpreted by humans. In real-world situations, where ethical decisions are often subjective and nuanced, human input remains essential. Additionally, AI lacks emotional understanding and empathy. Although it can mimic human-like responses through data analysis and pattern recognition, AI does not genuinely experience emotions. Human interactions, especially in fields like counseling, healthcare, or customer service, often rely on empathy, compassion, and emotional intelligence qualities that AI cannot authentically replicate.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science by Enrolling in Our Data Science Masters Course.
Will Human Intelligence Be Replaced by Artificial Intelligence in Employment?
Automation of Routine Tasks
AI has already begun to automate many tasks in industries such as manufacturing, data entry, customer service, and logistics. Functions that require consistency, precision, and efficiency are well-suited for AI, and as technology advances, we can expect these tasks to become increasingly automated.
Human-Centric Roles
Jobs that require emotional intelligence, creativity, complex problem-solving, and human interaction such as those in healthcare, education, and leadership are less likely to be replaced by AI, a perspective emphasized in the Role of Citizen Data Scientists in Today’s Business.
New Opportunities
AI’s growth will also create job opportunities in AI development, data science, and robotics. Humans will still play a critical role in designing, training, and overseeing AI systems. The future of work will likely involve a partnership between humans and AI, complementing each other’s strengths.
How Can AI and Human Intelligence Work Together?
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
In conclusion, while AI and human intelligence share certain similarities, their capabilities, origins, and limitations are fundamentally distinct. AI excels at performing specific tasks quickly and with precision, making it invaluable in roles that demand computational power. However, it lacks the emotional intelligence, creativity, and ability to generalize that characterize human thought. Humans possess the unique ability to adapt to new and diverse situations, something AI still struggles with. Rather than replacing humans, AI is better positioned to complement human intelligence, particularly in areas that benefit from both computational prowess and human insight, as emphasized in Data Science Training. This collaboration will become increasingly important as the future of work unfolds, with AI enhancing human potential, supporting creativity, and enabling innovation. Together, AI and humans can drive progress and innovation across industries, leveraging the strengths of each to create more efficient, creative, and impactful solutions. This symbiotic relationship will shape a future where technology and human ingenuity work hand-in-hand.




