
- Introduction to Motivation Theories
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
- Goal-Setting Theory
- Self-Determination Theory
- Reinforcement Theory
- Impact on Employee Performance
- Conclusion
Introduction to Motivation Theories
Motivation theories are psychological frameworks that explain why individuals behave in certain ways and what drives them to achieve specific goals. Understanding these theories is essential in the workplace, as motivation plays a crucial role in improving employee performance, job satisfaction, and overall productivity. Motivation theories, such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, and McClelland’s Theory of Needs, provide valuable insights into what encourages people to perform at their best. By applying these theories, organizations can create environments that nurture motivation, leading to increased employee engagement, reduced absenteeism, and lower turnover rates, supported by insights from Data Science Training. For example, addressing employees’ basic and psychological needs can help foster a more committed and efficient workforce. Motivated employees are not only more productive but also more innovative and resilient, contributing positively to the company’s goals. When organizations understand the underlying factors of employee behavior, they are better equipped to design strategies that support motivation and retention. This, in turn, leads to long-term success and a strong organizational culture where employees feel valued and driven to contribute meaningfully.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is one of the most recognized motivation theories, developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow. The theory proposes that human needs are structured in a five-tier pyramid, starting with basic physical needs and progressing to higher-level psychological and self-fulfillment needs, much like the differences explored in Data Mining Vs. Machine Learning. The five levels include physiological needs (such as wages, salaries, and basic benefits), safety needs (including job security and a safe working environment), social needs (like a sense of belonging, teamwork, and good relationships), esteem needs (respect, recognition, and achievements), and finally, self-actualization needs (personal growth, creativity, and realizing one’s potential). In the workplace, employers can apply Maslow’s theory by first ensuring that employees’ basic needs, such as fair compensation and job security, are met.
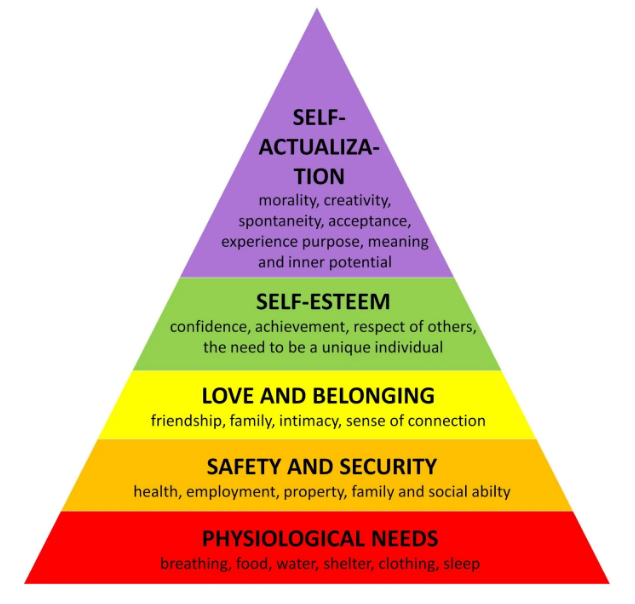
Once these foundational needs are satisfied, organizations can focus on promoting a positive social environment, recognizing achievements, and providing opportunities for professional and personal development. When all levels of needs are addressed, employees are more likely to feel valued, motivated, and fully engaged in their roles. This comprehensive approach helps improve productivity, morale, and long-term employee retention within the organization.
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
- Introduction to the Theory: Developed by Frederick Herzberg, the Two-Factor Theory explains what causes job satisfaction and dissatisfaction. It divides motivational factors into two categories: hygiene factors and motivators.
- Hygiene Factors: These are elements related to the work environment. They do not lead to higher motivation but can cause dissatisfaction if missing. Examples include salary, company policies, job security, supervision, and working conditions.
- Motivators: These factors relate to the nature of the work itself and can significantly boost employee motivation and satisfaction. Key motivators include achievement, recognition, responsibility, personal growth, and meaningful work.
- Dual Influence: Herzberg emphasized that satisfaction and dissatisfaction are not opposites, a concept that can also be explored in Data Science Training to understand employee sentiment through data analysis.
- Application in the Workplace: Employers should ensure hygiene factors are adequately managed to prevent dissatisfaction, while also actively promoting motivators to encourage engagement and productivity.
- Job Enrichment: Herzberg suggested enhancing jobs by increasing responsibility, offering growth opportunities, and recognizing achievements to boost motivation.
- Organizational Benefit: When both factor sets are properly addressed, organizations see improved employee morale, lower turnover, and increased performance.
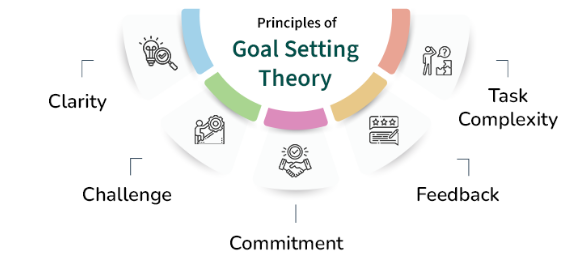
- Theory Overview: Introduced by Edwin Locke, Goal-Setting Theory highlights that setting precise, ambitious goals combined with regular feedback leads to increased motivation and improved performance.
- Defined Objectives: When goals are specific and clearly stated, employees have a better understanding of what they need to achieve, minimizing confusion and promoting focus.
- Level of Difficulty: Challenging yet attainable goals drive effort and performance, emphasizing the Importance of Machine Learning for Data Scientists.
- Employee Involvement: Motivation improves when employees are actively involved in setting their goals, as this boosts their sense of ownership and commitment.
- Ongoing Feedback: Consistent and constructive feedback allows employees to track their progress, recognize accomplishments, and adjust strategies as needed.
- Managing Complexity: For goals that involve complicated tasks, it’s important to provide adequate time, training, and support to ensure employees can succeed without becoming overwhelmed.
- Workplace Benefits: Implementing well-structured goal-setting strategies helps align personal goals with organizational aims, enhancing productivity, motivation, and overall company performance.
- Encouraging Good Behavior: Positive reinforcement involves offering rewards, such as recognition, bonuses, or promotions, to reinforce and repeat productive behaviors.
- Discouraging Undesired Actions: Punishment aims to reduce unwanted behavior by introducing consequences, such as warnings or disciplinary action, when standards are not met.
- Withholding Reinforcement: Extinction involves stopping the reinforcement of a behavior, causing it to fade over time for instance, ignoring non-constructive attention-seeking.
- Importance of Consistency: Applying reinforcement fairly helps employees understand acceptable behaviors, similar to how Top Data Science Programming Languages guide effective decisions.
- Prompt Feedback: Providing immediate responses to behavior helps link actions directly with their outcomes, making the learning process more effective.
- Using in the Workplace: Employers can shape employee performance by using a clear, consistent system of rewards and consequences aligned with organizational goals.
- Removing Negative Conditions: Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior by eliminating an unfavorable condition once the desired action is performed, like reducing supervision after consistent good work.
- Introduction to the Theory: Proposed by B.F. Skinner, Reinforcement Theory suggests that behavior is learned and influenced by its outcomes actions followed by rewards are likely to be repeated.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Goal-Setting Theory
Self-Determination Theory (SDT)
Self-Determination Theory (SDT), developed by Edward Deci and Richard Ryan, focuses on the importance of intrinsic motivation and fulfilling three basic psychological needs: autonomy, competence, and relatedness. According to this theory, individuals are most motivated and satisfied when they feel in control of their actions, capable in their roles, and connected to others. In the workplace, employees are more likely to be engaged and productive when they experience these conditions. Autonomy allows workers to make decisions and take ownership of their tasks, while competence is fostered through opportunities to develop and apply skills, similar to the distinctions between Machine Learning Vs Deep Learning. Relatedness involves building meaningful relationships and feeling part of a supportive team or organization. Companies can apply SDT by promoting flexible work environments, providing training and development programs, and cultivating a culture of collaboration and respect. When employees feel empowered, skilled, and socially connected, they are more likely to demonstrate creativity, persistence, and enthusiasm in their work. This intrinsic motivation leads to higher performance and contributes significantly to long-term organizational success, employee satisfaction, and retention. SDT highlights the value of internal drives over external rewards in sustaining motivation and well-being at work.
Looking to Master Data Science? Discover the Data Science Masters Course Available at ACTE Now!
Reinforcement Theory
Impact on Employee Performance
Implementing motivation theories in the workplace has a direct impact on employee performance and overall organizational success. When employees are motivated, they tend to be more productive, committed, and creative in their roles. Motivation encourages collaboration, strengthens teamwork, and leads to a proactive approach in solving problems and suggesting improvements. Employees with a strong sense of motivation often display a solid work ethic and greater dedication to achieving company goals. Additionally, motivated staff are less likely to miss work or leave the organization, which helps reduce absenteeism and turnover rates, much like the consistency seen in A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist. This leads to a more stable and experienced workforce. Motivation also enhances customer satisfaction, as engaged employees are more likely to provide better service and build stronger client relationships. By applying motivation theories such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, or Self-Determination Theory, organizations can create an environment where employees feel valued and empowered. As a result, businesses that prioritize employee motivation often experience improved profitability, stronger retention, and a more effective and united team. In summary, motivated employees are essential for sustainable growth, workplace harmony, and long-term organizational success.
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
Motivation theories are essential as they provide insight into employee behavior and performance. Understanding what drives individuals allows organizations to create a work environment that enhances productivity, engagement, and job satisfaction. Theories such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, and Expectancy Theory offer frameworks for identifying and addressing employee needs. By applying these principles, companies can implement effective motivation strategies, including fair compensation, recognition programs, and clear, meaningful goal-setting. These strategies, informed by insights from Data Science Training, contribute to greater employee commitment, lower turnover, and higher morale. When employees feel valued and motivated, they are more likely to perform at their best and contribute to organizational goals. Moreover, the effective use of motivation theories supports the development of a high-performing and resilient workforce. In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, focusing on employee motivation is not just beneficial, it is necessary for sustainable growth. Organizations that invest in understanding and improving motivation can build a strong organizational culture, retain top talent, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.


