- Introduction to AI and Robotics
- Role of AI in Robotics
- Machine Learning in Robotics
- NLP for Human-Robot Interaction
- AI-Powered Robot Decision Making
- Applications of AI in Robotics
- Challenges in AI Robotics Development
- Conclusion
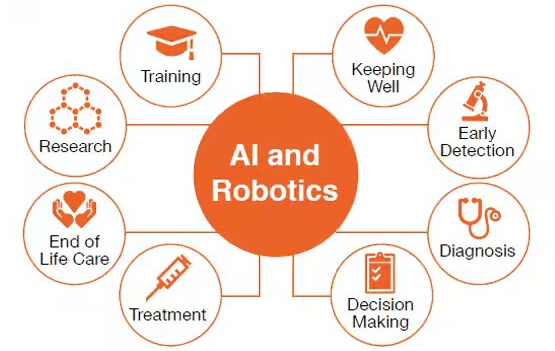
Introduction to AI and Robotics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics are two rapidly evolving fields that, when combined, have the potential to revolutionize industries and daily life. AI involves the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making. Robotics, on the other hand, focuses on designing and building machines that can perform tasks either autonomously or with minimal human input. When AI is integrated with robotics, it allows robots to analyze data, learn from their experiences, and make intelligent decisions in real time, with Data Science Training playing a key role in developing the skills necessary for effective data analysis and decision-making. This synergy enhances the adaptability and efficiency of robots in complex and dynamic environments. Applications of AI-powered robotics span across numerous sectors, including healthcare, where robots assist in surgeries and patient care; manufacturing, where they improve precision and productivity; and hazardous industries like mining or disaster response, where they can operate safely in dangerous conditions. The convergence of AI and robotics is paving the way for a more automated, efficient, and intelligent future across all aspects of life.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Role of AI in Robotics
AI plays a critical role in enhancing the capabilities of robots by enabling them to perceive, understand, and interact with the environment intelligently. Some of the key roles of AI in robotics include:
- Autonomy: AI enables robots to make decisions independently without requiring constant human input. Robots can adapt their actions based on environmental feedback through machine learning algorithms, optimizing their performance over time.
- Perception: AI technologies like computer vision and sensors allow robots to perceive the world around them. By processing visual, auditory, or tactile data, robots can understand their surroundings, recognize objects, while techniques like Excel Sheet Protection can be used to secure sensitive data during the analysis process.
- Learning and Adaptation: Through machine learning, AI allows robots to learn from their mistakes and successes. For example, a robot might initially struggle to pick up an object, but with feedback and experience, it becomes better at this task over time.
- Interaction: AI enables robots to interact naturally and effectively with humans and other machines. This can include understanding natural language, interpreting gestures, or responding to human commands.
- Problem Solving: AI-powered robots can analyze complex problems and find optimal solutions. This is crucial in tasks that involve decision-making, route planning, or process optimization.
- Motion Planning: Robots use ML algorithms to learn optimal paths for moving through environments. For example, in autonomous vehicles, ML models help the robot understand obstacles and plan safe driving routes.
- Object Recognition: Using supervised learning, robots can be trained to recognize various objects in their environment. For instance, a robot in a warehouse can learn to distinguish between different items and sort them accordingly.
- Sensor Data Processing: Robots rely on sensor data (e.g., camera feeds, temperature sensors, proximity sensors) to make decisions, and understanding What is Data Analysis is crucial for processing and interpreting this data effectively.
- Robotic Control: Reinforcement learning (RL) controls robotic actions. In RL, robots receive feedback (rewards or penalties) for their actions, which helps them learn the most effective ways to achieve a desired result.
- Grasping and Manipulation: Using deep learning techniques, robots can be trained to understand how to grasp and manipulate objects in various conditions. This is particularly important in tasks like packaging, assembly, or handling delicate items.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Machine learning enables robots to interact more naturally with humans. By using natural language processing (NLP) and gesture recognition, robots can understand and respond to verbal commands, body language, or facial expressions.
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI-powered robots, such as self-driving cars, use sensors, computer vision, and reinforcement learning to navigate and make decisions in real time.
- Agriculture: AI-driven robots are used for planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops. These robots help improve yield and reduce labor costs.
- Service Industry: AI-powered robots are increasingly used in the service industry for tasks like cleaning, delivery, and customer service, with SQL Stored Procedures playing a key role in managing and automating database operations for efficient service delivery.
- Healthcare: AI-powered robots are used for surgery (e.g., robotic-assisted surgery), patient care (e.g., robotic nursing assistants), and rehabilitation (e.g., exoskeletons for mobility support).
- Manufacturing and Automation: Industrial robots with AI capabilities are used for tasks such as assembly, welding, and quality control, improving efficiency, accuracy, and safety in manufacturing processes.
- Data and Training Requirements: Robots require large amounts of data to learn and make decisions. Gathering and processing this data can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Real-Time Decision Making: Robots must make decisions in real-time, which requires powerful AI algorithms and computing capabilities.
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring the safety and reliability of AI-powered robots is crucial, particularly in environments where human interaction is involved, and Python for Data Science is often used to analyze and model data to improve the performance and safety of these robots.
- Cost and Accessibility: The development and deployment of advanced AI-powered robots can be expensive, limiting their accessibility to larger companies and industries.
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: The use of AI-powered robots raises important ethical and legal questions, particularly regarding privacy, accountability, and decision-making.
- Integration with Existing Systems: One of the challenges in deploying AI-powered robots is ensuring they can integrate seamlessly with existing systems and workflows.
Machine Learning in Robotics
Machine learning (ML) is one of the key subfields of AI that has significantly impacted the development of intelligent robots. In robotics, ML enables robots to improve their performance by learning from data without being explicitly programmed for every task. Some ways in which ML is used in robotics include:
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
NLP for Human-Robot Interaction
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a key area of AI that focuses on enabling machines to understand and generate human language. In the field of robotics, NLP significantly enhances human-robot interaction (HRI) by allowing robots to interpret and respond to verbal communication. With NLP, robots can process spoken commands and execute corresponding actions, such as turning on lights, fetching items, or navigating through spaces based on simple instructions, often utilizing algorithms like the Boyer Moore Algorithm for efficient pattern matching in text processing. This ability to understand voice commands makes robots more intuitive and user-friendly in everyday applications. Moreover, robots equipped with NLP can engage in more natural, dynamic conversations, making them valuable in customer service, healthcare, and other environments where real-time, human-like communication is needed.
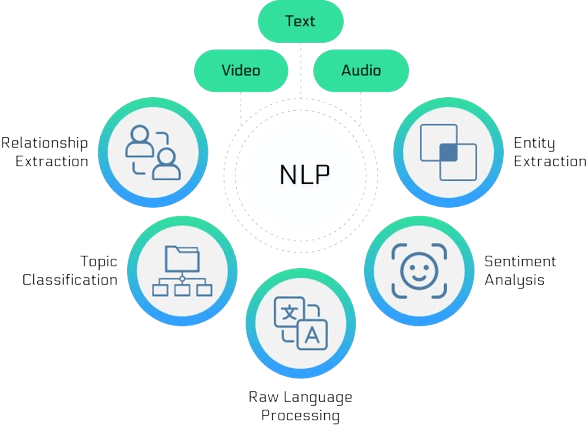
Additionally, sentiment analysis through NLP enables robots to detect the emotional tone in a conversation, allowing them to tailor their responses to match the user’s mood. This level of emotional awareness enhances the robot’s ability to provide personalized support, whether in assisting elderly individuals, offering emotional support, or delivering customer service, improving overall user satisfaction and interaction.
AI-Powered Robot Decision Making
AI-powered robots are capable of making decisions based on the data they gather from their surroundings and interactions. By using advanced AI algorithms, these robots can evaluate various possible outcomes and select the most optimal course of action to achieve the best results. One way they do this is through decision trees, which help robots map out potential actions and their corresponding consequences. Additionally, AI planning algorithms enable robots to organize and plan complex, multi-step tasks to reach their objectives efficiently, and Data Science Training provides the foundational knowledge needed to optimize these algorithms. These capabilities allow robots to operate with a high level of autonomy and precision. AI also provides robots with the ability to understand the context of a situation, enabling them to make informed decisions tailored to specific circumstances. For example, in a warehouse, a robot may prioritize retrieving an item based on its urgency or the proximity of other ongoing tasks, optimizing its workflow. Thanks to AI-powered decision-making, robots can function autonomously in dynamic, real-time environments, adapting to changing conditions without needing constant human oversight. This autonomy makes them highly effective in applications ranging from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and beyond.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science by Enrolling in Our Data Science Masters Course.
Applications of AI in Robotics
AI has enabled robots to perform a wide range of tasks across different sectors, including:
Challenges in AI Robotics Development
Despite the advancements in AI and robotics, several challenges still need to be addressed:
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
The integration of AI and robotics has already made a significant impact on industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, transforming the way tasks are performed and improving overall efficiency. As AI technology continues to advance, robots are becoming more intelligent and capable of performing increasingly complex tasks with greater autonomy. This progress is enabling robots to take on roles that were once thought to be solely within human capability, from assisting in surgeries to managing warehouse inventories. However, challenges such as data requirements, real-time decision-making, safety, and ethical concerns still need to be addressed, and Data Science Training can help equip professionals with the skills to tackle these issues effectively. Ensuring that AI-powered robots operate safely, make ethical decisions, and are reliable in diverse environments remains a key focus of ongoing research. Additionally, legal and social considerations, including privacy and accountability, must be taken into account as robots become more integrated into everyday life. Despite these challenges, the future of AI and robotics holds immense potential. With continued innovation and development, robots will play an even more significant role in shaping the future of industries, enhancing productivity, improving safety, and contributing to better quality of life for individuals across the globe.