
- Introduction
- Definition and Importance
- How AI Models Process Prompts
- Types of Prompting Techniques
- Role-based Prompting
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting
- Zero-shot vs. Few-shot Prompting
- Examples of Effective Prompts
- Common Mistakes in Prompt Engineering
- Tools for Prompt Optimization
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, simply knowing how to use AI tools is no longer enough how you communicate with these tools defines the quality of your outcomes. This is where prompt engineering comes in. Prompt engineering is the practice of designing, refining, and optimizing prompts carefully constructed instructions or queries that guide AI systems to generate accurate, relevant, and valuable responses. As the interface between human intent and machine execution, prompts are the linchpin for achieving meaningful interactions with AI. With models like GPT, DALL·E, and other advanced AI systems becoming integral across industries from software development and marketing to education, healthcare, Data Science Training, and creative arts—the ability to engineer precise prompts has become a critical skill. Whether you’re asking a model to summarize a report, compose a poem, analyze a dataset, or generate code, the structure, context, and clarity of your prompt significantly influence the quality of the AI’s output. As AI continues to permeate every facet of modern life, mastering the art of prompt engineering will empower you to unlock the full creative and analytical capabilities of intelligent systems boosting efficiency, innovation, and impact across your work.
Eager to Acquire Your Data Science Certification? View The Data Science Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Definition and Importance
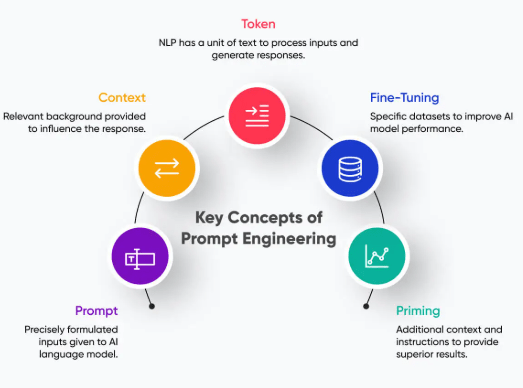
- Prompt Engineering is the strategic process of crafting clear, precise, and effective prompts to guide AI models in generating accurate, coherent, and contextually relevant responses. In essence, prompts serve as instructions or queries that shape how an AI system interprets a user’s intent and processes a request.
- The quality of these prompts directly influences the performance of the model, making prompt engineering a crucial element in unlocking the full potential of AI technologies.
- Effective prompt engineering is essential for optimizing model output, minimizing ambiguity, and ensuring clear, goal-oriented communication between humans and machines. By carefully structuring prompts, users can significantly improve the reliability, relevance, and accuracy of the responses generated by Artificial Intelligence systems.
- This technique plays a pivotal role across a wide range of applications, including text generation, conversational AI, image creation, code development, language translation, and data analysis.
- As artificial intelligence continues to evolve and integrate more deeply into everyday workflows and innovative solutions, mastering the art of prompt engineering becomes increasingly critical.
- It not only enhances productivity and efficiency but also fuels creativity, personalization, and problem-solving in AI-driven environments. Whether you’re a developer, data scientist, educator, marketer, or content creator, the ability to design high-quality prompts is a powerful skill that transforms how you interact with intelligent systems.
How AI Models Process Prompts
AI models process prompts through Natural Language Processing(NLP) and deep learning techniques. When a prompt is submitted, the model:
- Tokenizing the Input: Breaks the prompt into smaller units called tokens (words or subwords).
- Contextualizes the Tokens: Analyzes token relationships using attention mechanisms (in models like GPT).
- Generates a Response: Based on the prompt and the model’s pre-trained knowledge, it generates the most probable sequence of words or output in Natural Language Processing.
- Refines with Iterations: With larger models, feedback and adjustments further refine the accuracy and relevance of the output.
- Understanding how AI interprets prompts helps in designing clearer and more effective instructions.
Types of Prompting Techniques
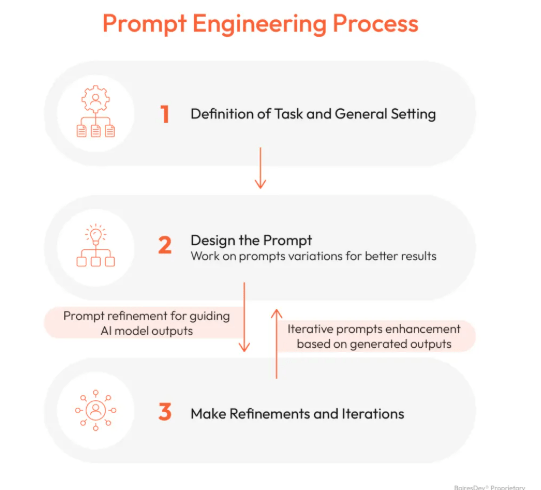
There are several effective prompting techniques used to fine-tune AI outputs and enhance the quality, relevance, and precision of the generated responses. Direct prompting involves providing straightforward and unambiguous instructions, such as “Summarize the article in 3 sentences,” which allows the AI to quickly understand the expected output format. Contextual prompting adds necessary background information or user perspective to shape the response appropriately for instance, “As a data scientist through Data science Training, explain the concept of regression analysis” helps the AI tailor the explanation to a specific audience. Conditional prompting introduces specific criteria, limitations, or requirements to narrow the scope of the response, like “List 5 healthy recipes under 300 calories,” guiding the AI to consider constraints in its generation process. Guided prompting leverages step-by-step directions or strategic keywords to steer the AI in a particular direction, such as “Explain blockchain technology in simple terms for beginners,” ensuring clarity and accessibility in the output. Mastering and applying the proper prompting technique based on the task at hand ensures more accurate, goal-oriented, and contextually appropriate responses—maximizing the efficiency and usefulness of AI-driven interactions.
Excited to Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Role-based Prompting
Role-based prompting assigns the AI a specific persona or Role, guiding it to respond with expertise or empathy. For example:
- Technical Role: “You are a software engineer. Explain how REST APIs work.”
- Creative Role: “You are a travel blogger. Write a blog post about visiting Paris.”
- Support Role: “You are a customer service agent. Handle a complaint about a late delivery.” This technique helps the model adopt the appropriate tone, language, and knowledge level, making the output more credible and relevant.
Interested in Pursuing Data Science Master’s Program? Enroll For Data Science Master Course Today!
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting is a technique where the prompt guides the AI through a step-by-step reasoning process, improving accuracy and coherence. For example:
- Without CoT: “What is 27 times 14?” → The AI gives a direct answer without explanation.
- With CoT: “First, multiply 27 by 10, then multiply 27 by 4, and add the results.” → The AI breaks down the calculation into clear, logical steps.
- Encourages the AI to “think out loud,” mimicking human reasoning.
- Enhances transparency in how answers are derived.
- Reduces the chance of logical errors in complex problem-solving in Data Science.
- Improves performance on tasks requiring multi-step solutions, such as math problems, logical puzzles, and decision-making scenarios.
- Zero-shot: “Translate ‘Hello’ to French.”
- Few-shot: “Translate the following to French: ‘Hello’ → ‘Bonjour’; ‘Goodbye’ → ‘Au revoir’; ‘Thank you’ → ?”
- Creative Writing: “Write a 200-word story about a time traveler visiting ancient Egypt.”
- Data Analysis: “Explain the concept of linear regression in simple terms with an example.”
- Marketing Content: “Generate five catchy taglines for a sustainable clothing brand.”
- Effective prompts typically include clear instructions, context, and output expectations, guiding the AI to produce high-quality responses.
- Prompt Perfect: Helps you optimize prompts for large language models.
- OpenAI Playground: Allows you to test and refine prompts in a controlled environment.
- Prompt Base: Offers a marketplace of pre-tested, effective prompts.
- Lang Chain: A framework for building complex prompt chains for AI applications.
- These tools help streamline prompt experimentation and improve accuracy.
Benefits of Chain-of-Thought Prompting:
By prompting the AI to explain its reasoning process, CoT prompting not only delivers more reliable results but also builds user trust in the output, making it an essential technique in prompt engineering.
Zero-shot vs. Few-shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting involves asking the AI to perform a task without providing examples, while few-shot prompting includes one or more examples for context.
Few-shot prompting improves accuracy by giving the model a reference for the desired output style or format. It is ideal for fine-tuning the AI’s responses when precision is required.
Preparing for a Data Science Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer
Limitations of AI Tools in Excel
Crafting clear and specific prompts ensures better results. Here are some practical examples:
Common Mistakes in Prompt Engineering
Ineffective prompting can significantly impact the quality of AI-generated outputs, often resulting in responses that are ambiguous, irrelevant, or misaligned with the user’s intent. One of the most common mistakes is using vague or unclear prompts, such as “Explain it,” without providing a specific subject or direction, leaving the model to guess the context. Another frequent issue is the lack of context, like asking “Summarize the article” without actually including the article or any relevant details, which limits the model’s ability to produce an accurate or meaningful summary. Additionally, overly complex instructions that contain too many details or conflicting elements can confuse the AI and Machine learning Trends lead to fragmented or inaccurate responses. Inconsistent formatting is another pitfall—when prompts are phrased inconsistently or structured irregularly, the model may struggle to understand the intended pattern, resulting in varied or off-target outputs. To avoid these mistakes, it is essential to craft prompts that are specific, clearly worded, and contextually rich, ensuring the AI has enough guidance to produce relevant, coherent, and goal-oriented responses.
Tools for Prompt Optimization
Conclusion
Prompt engineering stands at the forefront of effective human-AI collaboration. As AI systems become increasingly integrated into professional, academic, and creative workflows, the ability to craft well-structured, context-rich prompts becomes more than just a technical skill it becomes a strategic advantage. From improving the accuracy of generated content to tailoring AI responses for specific roles or tasks, prompt engineering empowers users to unlock deeper levels of precision, relevance, and innovation. By understanding how AI models process language and leveraging techniques like role-based prompting, chain-of-thought reasoning, and few-shot learning especially within the context of Data Science Training users can fine-tune their interactions with AI to achieve highly targeted results. Avoiding common mistakes and utilizing prompt optimization tools further enhances this process, ensuring consistency and clarity. Ultimately, mastering prompt engineering is key to maximizing the potential of AI technologies. Whether you’re generating content, solving complex problems, or building AI-driven applications, well-crafted prompts bridge the gap between human intent and machine output—enabling more meaningful, intelligent, and impactful outcomes.


