- Introduction to Data Science Careers
- Why Choose Data Science?
- Career Opportunities in Data Science
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Essential Skills
- Education and Certifications
- Building a Portfolio
- Conclusion
Introduction to Data Science Careers
Data science has rapidly become one of the most dynamic and fast-growing fields in today’s job market. As industries across the globe generate massive amounts of data from social media and finance to healthcare and manufacturing the need for professionals who can collect, manage, analyze, and interpret this data has grown exponentially. Data scientists play a pivotal role in transforming raw data into meaningful insights that guide strategic decision-making and solve complex problems. This multidisciplinary career combines expertise in technology, mathematics, and business with strong communication skills. Data scientists, through Data Science Training, not only develop and apply algorithms but also translate technical findings into actionable recommendations for diverse stakeholders. Their work impacts various sectors, including government policy development, healthcare innovations, financial risk assessment, marketing strategies, and educational improvements. The growing reliance on data-driven decisions has resulted in a high demand for skilled data science professionals worldwide. This demand translates into competitive salaries and numerous job opportunities, making data science an attractive and rewarding career choice. For those passionate about data and eager to tackle challenging problems, data science offers continuous learning, innovation, and the chance to make a tangible impact on industries and society.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Why Choose Data Science?
Choosing data science as a career offers numerous compelling benefits. Firstly, the demand for skilled data scientists far exceeds the supply, creating a significant talent gap. This imbalance provides strong job security and gives professionals greater leverage when negotiating salaries and benefits. Secondly, data science roles often involve working on impactful and meaningful projects. Whether it’s advancing healthcare through predictive analytics, improving climate models, or optimizing business strategies, data scientists contribute to solutions that can affect lives and industries worldwide, highlighting the Role of Citizen Data Scientists in Today’s Business. Thirdly, the work itself is intellectually stimulating. It requires a blend of creativity, logical reasoning, and analytical skills, keeping daily tasks challenging and engaging. Fourthly, data science is a versatile field. Skills acquired in one industry, such as finance or retail, are often transferable to others, allowing professionals to explore diverse sectors without restarting their career path.
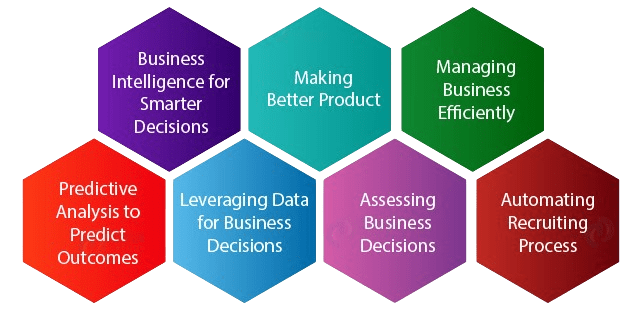
Lastly, data scientists are well-compensated, with competitive salaries reflecting the high demand and specialized skill set. Moreover, there are abundant career growth opportunities, including pathways to senior technical roles or leadership positions like Chief Data Officer or Head of Analytics. Overall, a career in data science offers both professional fulfillment and financial reward, making it an attractive choice for many aspiring tech professionals.
Career Opportunities in Data Science
- Data Scientist: Designs and builds models to analyze complex data, extract insights, and support decision-making. Requires strong statistical, programming, and communication skills.
- Data Analyst: Focuses on interpreting data, creating visualizations, and generating reports to help businesses understand trends and performance.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Specializes in building and deploying machine learning models into production systems. Requires strong software engineering and algorithm development skills.
- Data Engineer: Develops and maintains data pipelines and architecture, ensuring data is clean, available, and optimized for analysis and machine learning Top Reasons To Learn Python.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: Translates data into actionable insights for business strategy using tools like Tableau, Power BI, or SQL.
- AI Research Scientist: Works on cutting-edge research in artificial intelligence, including deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. Often requires advanced degrees.
- Statistician or Quantitative Analyst: Applies statistical methods to analyze data and solve problems in fields such as finance, healthcare, and government.
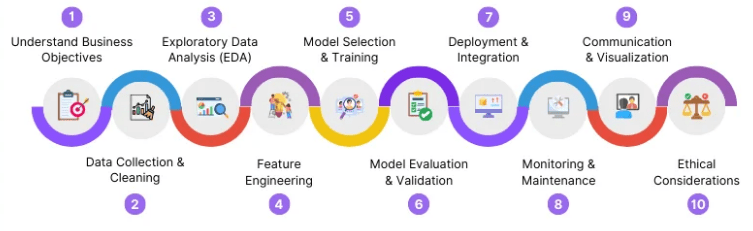
- Data Collection and Acquisition: Gathering relevant data from various sources such as databases, APIs, or third-party providers to build a comprehensive dataset for analysis.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Ensuring data quality by handling missing values, correcting inconsistencies, removing duplicates, and converting data into usable formats.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Analyzing data patterns, trends, and distributions using visualizations and statistics as part of Data Science Training to understand the dataset and guide model development.
- Feature Engineering: Creating meaningful features from raw data to improve model performance, including transformation, scaling, and encoding techniques.
- Model Building and Evaluation: Applying machine learning algorithms, training predictive models, and evaluating them using appropriate metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, or RMSE.
- Data Visualization and Communication: Presenting insights using charts, graphs, and dashboards, and effectively communicating findings to stakeholders through reports or presentations.
- Model Deployment and Maintenance: Deploying models into production environments and monitoring their performance over time, making updates as needed to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in computer science, statistics, mathematics, or a related field provides a strong foundation in analytical thinking, programming, and quantitative reasoning.
- Master’s Degree (Optional but Valuable): A master’s in data science, machine learning, or AI can deepen domain expertise and improve job prospects, especially for specialized roles.
- Online Courses and MOOCs: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer affordable, flexible courses on data science, Python, machine learning, and more. These are excellent for self-paced learning.
- Bootcamps: Intensive data science bootcamps provide hands-on, project-based learning on Python Keywords and are ideal for career switchers or fast-track learners.
- Certifications from Tech Giants: Certifications from providers like Google (Professional Data Engineer), IBM (Data Science Professional Certificate), and Microsoft (Azure Data Scientist Associate) add credibility and recognition.
- Specialized Certificates: Earning certificates in tools like Tableau, SQL, Python, R, or cloud platforms like AWS can demonstrate tool-specific expertise.
- Continuous Learning: The data field evolves rapidly, so staying updated through workshops, conferences, and certifications is key to remaining competitive and advancing in your career.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
Roles and Responsibilities
Essential Skills
Success in data science requires a well-rounded blend of technical, analytical, and soft skills. On the technical side, proficiency in programming languages such as Python and R is fundamental, as these are widely used for data manipulation, analysis, and modeling. Knowledge of SQL is essential for querying and managing data stored in relational databases. Familiarity with machine learning libraries and frameworks like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and Keras enables the development of predictive models and deep learning applications. A strong mathematical foundation, especially in statistics, probability, and linear algebra, is critical for understanding data behavior and optimizing model performance, which is essential to grasp What is Data Science. Analytical skills are equally vital. Data scientists must be capable of interpreting large and complex datasets, identifying patterns, and deriving actionable insights that support business objectives. These skills underpin informed decision-making and strategic planning. Soft skills play a significant role in bridging the gap between technical work and business needs. Effective communication helps translate complex findings into clear, actionable recommendations for non-technical stakeholders. Critical thinking enhances problem-solving abilities, while collaboration is key to working within cross-functional teams. Additionally, with many companies adopting cloud infrastructure, knowledge of platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is increasingly important for deploying scalable and efficient data solutions.
Want to Pursue a Data Science Master’s Degree? Enroll For Data Science Masters Course Today!
Education and Certifications
Building a Portfolio
A strong portfolio is essential in the competitive field of data science, as it serves as tangible proof of a candidate’s practical skills and problem-solving ability. While academic qualifications and certifications are valuable, employers often prioritize real-world experience demonstrated through hands-on projects. A well-rounded portfolio should include a diverse range of projects that highlight core competencies such as data cleaning, exploratory data analysis (EDA), machine learning, deep learning, and solving business-relevant problems. Platforms like GitHub and Kaggle are widely used to host and share code, notebooks, and project results, while personal blogs or websites can showcase write-ups and visualizations that explain the insights and methodologies behind each project, highlighting The Importance of Machine Learning for Data Scientists. Common portfolio projects include predictive modeling (e.g., predicting customer churn), recommendation systems, time series forecasting, sentiment analysis, image classification, and other NLP or computer vision tasks. Additionally, participating in hackathons, data science competitions, or contributing to open-source projects not only strengthens technical skills but also demonstrates initiative, collaboration, and community involvement. These experiences help candidates stand out by showing they can apply their knowledge in real-world, high-pressure environments. Overall, a strong, well-documented portfolio is one of the most effective tools for breaking into or advancing in the data science industry.
Go Through These Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data science is a rapidly evolving field that blends statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain expertise to extract valuable insights from data. Whether you’re just starting out or advancing in your career, there are numerous paths and projects that can help you grow your skills from basic data cleaning and visualization to advanced deep learning and big data applications. As industries increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the demand for skilled data professionals continues to rise across sectors such as healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and technology. Success in data science, emphasized during Data Science Training, requires not only technical expertise in tools like Python, SQL, and machine learning frameworks but also the ability to communicate insights effectively and make strategic recommendations Educational backgrounds, certifications, and continuous learning all play a critical role in staying relevant and competitive in this dynamic field. Whether pursuing roles like data analyst, machine learning engineer, or AI researcher, professionals must be adaptable, curious, and committed to solving complex problems. Ultimately, a strong foundation in data handling, critical thinking, and model development paired with real-world project experience can set aspiring data scientists on a rewarding career path. With the right mix of education, practice, and perseverance, data science offers endless opportunities for innovation and impact.