
- Introduction
- Definition of Data Science
- Definition of Business Analytics
- Skill Sets Compared
- Tools and Technologies Used
- Career Opportunities
- Salary Comparison
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, both Data Science and Business Analytics play essential roles in helping organizations make informed decisions. While both fields focus on leveraging data to extract valuable insights, they differ significantly in their approach, focus, and applications. Data Science is more technical, involving advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and programming to build predictive models and uncover hidden patterns within large, complex datasets. It often deals with big data, utilizing cloud computing and AI technologies to solve intricate problems. Business Analytics, on the other hand, centers on interpreting data to drive strategic business decisions, as emphasized in Data Science Training. It emphasizes analyzing structured data, generating reports, and visualizing insights to help stakeholders improve operations, marketing, and overall business performance. With the rapid growth of big data and AI, both fields have seen increased demand and evolving tools that enable more effective data processing and analysis. This article explores the definitions, key differences, necessary skill sets, popular tools, career opportunities, and salary comparisons between Data Science and Business Analytics. Understanding these aspects will help you choose the right path based on your interests, strengths, and career goals, whether you are inclined toward the technical side of data or the business-oriented application of analytics.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Definition of Data Science
Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that combines mathematics, statistics, computer science, and domain knowledge to extract meaningful insights from structured and unstructured data. It involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing large volumes of data to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships that can inform decision-making. The primary goal of Data Science is to transform raw data into actionable intelligence using various techniques such as statistical analysis, machine learning, data mining, and predictive modeling, as seen in A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist. At its core, Data Science relies heavily on programming languages like Python and R, as well as tools and frameworks that support data manipulation, visualization, and algorithm development. Data scientists often work with big data technologies such as Hadoop and Spark to manage vast datasets that traditional databases cannot handle efficiently. Additionally, cloud computing platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide scalable infrastructure for data storage and processing.
Data Science applications span multiple industries, including finance, healthcare, marketing, and technology, where it helps optimize operations, improve customer experiences, detect fraud, and enable innovations like autonomous systems and personalized recommendations. The field demands strong analytical skills, proficiency in coding, and the ability to translate complex data findings into understandable insights. As data continues to grow exponentially, Data Science remains a critical discipline for driving innovation and competitive advantage in today’s digital economy.
Definition of Business Analytics
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Business Analytics focuses on leveraging data to support and enhance strategic and operational decision-making within organizations.
- Analytical Techniques: It employs various analytical approaches, including descriptive (what happened), diagnostic (why it happened), predictive (what might happen), and prescriptive analytics (what should be done).
- Business-Oriented Focus: The primary aim is to address real-world business challenges and drive growth, efficiency, and profitability through data-driven insights.
- Structured Data Use: Business Analytics primarily works with structured data collected from sources like ERP systems, CRM platforms, offering clarity and actionable metrics, supported by Top Python Libraries For Data Science.
- Tools and Software: Common tools include Excel for basic analysis, SQL for database queries, and visualization platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik for interactive reporting.
- Communication of Insights: A key aspect of Business Analytics is presenting data findings in a way that is understandable and useful for business leaders, helping guide decisions.
- Wide Industry Application: It is widely used across sectors such as finance, marketing, healthcare, retail, and logistics to improve operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and increase competitiveness.
- Programming Skills: Data Science requires strong programming abilities in languages like Python, R, and SQL for data processing, analysis, and machine learning. Business Analytics often uses SQL and Excel, with less emphasis on advanced coding.
- Statistical and Mathematical Knowledge: Data scientists need in-depth knowledge of statistics, probability, and mathematics to build models and perform complex analysis. Business analysts require a foundational understanding to interpret data and trends effectively.
- Machine Learning Expertise: Data Science heavily involves designing and applying machine learning algorithms for tasks like prediction and classification, which are key topics in Data Science Training.
- Data Handling and Processing: Data scientists are trained to handle large, unstructured, and real-time data using tools like Hadoop, Spark, and cloud platforms. Business analysts usually work with structured data in spreadsheets or business systems.
- Visualization and Reporting: Both roles need visualization skills. Business analysts use tools like Tableau and Power BI, while data scientists may use Python libraries such as Matplotlib and Seaborn.
- Domain Knowledge: Business analysts often require deep domain expertise to align data insights with business strategies. Data scientists benefit from domain knowledge but focus more on technical aspects.
- Communication Skills: Both roles must convey insights to non-technical stakeholders, but business analysts generally place a greater emphasis on communication and storytelling with data.
- Data Scientist: Data scientists analyze large datasets, build predictive models, and use machine learning to solve complex problems. They are employed across industries like tech, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
- Business Analyst: Business analysts focus on interpreting data to improve business processes, strategy, and performance. They work in sectors such as finance, retail, consulting, and manufacturing.
- Data Analyst: In Business Analytics, data analysts support decision-making, while in Data Science, they often serve as a stepping stone to more advanced roles.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Emerging from Data Science, this role designs machine learning systems, showing Why Data Science Matters & How It Powers Business Value.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: BI analysts gather and analyze business data using tools like Power BI and Tableau. They help organizations make data-informed decisions and are more aligned with Business Analytics.
- Data Engineer: Common in Data Science, data engineers build and maintain data pipelines, databases, and architecture to support analytics and modeling.
- Product or Strategy Analyst: Often from a Business Analytics background, these professionals use data insights to shape product development, market strategy, and business growth initiatives.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
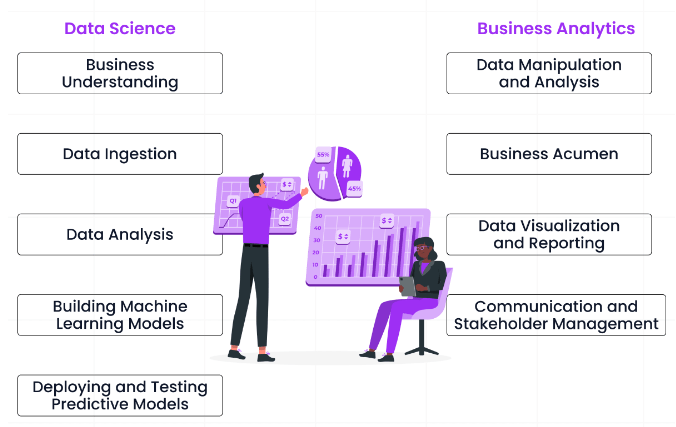
Skill Sets Compared
Tools and Technologies Used
Data Science and Business Analytics utilize different sets of tools and technologies, reflecting their distinct focuses and requirements. In Data Science, the emphasis is on handling large datasets, building models, and performing complex analyses. Common programming languages include Python and R, which offer extensive libraries for machine learning, data manipulation, and visualization. Tools like Jupyter Notebooks, Apache Spark, and Hadoop are frequently used for big data processing and distributed computing. Data scientists also rely on specialized machine learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, and PyTorch to develop predictive models. Additionally, SQL is essential for querying databases, while cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide scalable infrastructure for data storage and computation, boosting Python Career Opportunities. In contrast, Business Analytics focuses more on interpreting data to support business decisions, often using tools designed for data visualization and reporting. Excel remains a fundamental tool for many analysts, alongside SQL for database querying. Business intelligence platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView are popular for creating interactive dashboards and visual reports that communicate insights effectively to stakeholders. Analysts also use statistical software like SAS and SPSS for more advanced analysis. While some programming knowledge can be beneficial, Business Analytics tools prioritize user-friendly interfaces and integration with business systems. Together, these tools reflect the technical depth of Data Science and the decision-oriented nature of Business Analytics, catering to different skill sets and professional goals.
Looking to Master Data Science? Discover the Data Science Masters Course Available at ACTE Now!
Career Opportunities
Salary Comparison
When comparing salaries in Data Science and Business Analytics, it’s important to consider the differences in technical expertise, demand, and industry trends. Generally, Data Science roles tend to offer higher salaries due to the specialized skills required, such as advanced programming, machine learning, and statistical modeling. Data scientists often command salaries ranging from $90,000 to $150,000 annually for mid-level positions, with experienced professionals and those in leadership or specialized roles earning upwards of $180,000 or more, especially in tech hubs or industries like finance, healthcare, and tech. On the other hand, Business Analytics roles typically have a slightly lower salary range but still offer competitive compensation, often requiring skills like What is Logistic Regression. Entry to mid-level business analysts can expect salaries between $60,000 and $100,000, with experienced analysts and managers earning up to $120,000 or more. Business analytics salaries vary based on factors such as industry, company size, and geographic location. Roles that combine analytics with strategic decision-making, like business intelligence managers, tend to see higher pay. Overall, while Data Science often offers higher financial rewards due to its technical nature and demand, Business Analytics provides solid earning potential with less emphasis on programming skills. Both fields offer opportunities for salary growth as professionals gain experience and take on more responsibility. Ultimately, salary should be weighed alongside personal interest and skill alignment when choosing a career path.
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Data Science and Business Analytics are two closely related fields with distinct focuses, skill sets, and career paths. Data Science is a highly technical discipline centered around extracting insights from large and complex datasets using advanced techniques such as machine learning, statistical modeling, and programming. It requires a strong foundation in mathematics, computer science, and coding languages like Python or R. Data scientists build predictive models and algorithms to uncover patterns and make data-driven predictions, often working with big data and unstructured data sources. In contrast, Business Analytics emphasizes using data to inform and improve business decisions. While it involves data analysis, it focuses more on interpreting results and communicating insights to stakeholders, as emphasized in Data Science Training. Business analysts typically use tools like Excel, SQL, Tableau, and business intelligence platforms to analyze structured data and generate reports. The role requires a strong understanding of business processes, critical thinking, and communication skills to translate data findings into actionable strategies. Educationally, Data Science often demands more technical coursework, including programming and statistics, whereas Business Analytics programs tend to integrate business concepts with data analysis. Career roles in Data Science include data scientist, machine learning engineer, and data engineer. Business Analytics roles include business analyst, data analyst, and operations analyst. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prefer technical, algorithm-driven work or business-focused, decision-making roles. Both offer robust career opportunities, but aligning your strengths and interests with the field’s demands is key to success.





