
- Introduction to Data and Information
- What is Data?
- What is Information?
- Key Differences Between Data and Information
- The Interrelation Between Data and Information
- The Function of Data in Decision-Making
- The Function of Information in Business Intelligence
- Conclusion
Introduction to VBA in Excel
Data and information are fundamental components in any data-driven environment, such as business, science, or technology. While they are closely related, they serve distinct roles. Data, in its raw form, consists of facts, figures, or observations that, by themselves, lack context or meaning. It is the unprocessed input that forms the foundation for analysis and interpretation. On the other hand, information is the result of processing, organizing, and structuring data to give it meaning and context, making it useful for decision-making and analysis. In this guide, we will explore the definitions of data and information, focusing on their key differences, a fundamental topic often covered in Data Science Training. We will also highlight their functions in areas like decision-making, business intelligence, and data management. Understanding the distinction between data and information is critical in today’s world, where both play pivotal roles in shaping strategies, driving insights, and improving outcomes. While data provides the raw material for analysis, information enables individuals and organizations to make informed choices and take effective actions. By understanding how data transforms into meaningful information, you can leverage both for better decision-making and success in various fields.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is Data?
Data consists of raw facts, figures, or details that are collected for reference, calculation, or analysis. It can be quantitative (numeric) or qualitative (descriptive), and in its unprocessed form, it lacks context or meaning. Data can take various forms, including numbers, text, images, sounds, or any other type of raw input that is gathered for future processing and analysis. One of the key features of data is that it is raw, often unorganized, and does not provide immediate value until it is processed or analyzed, which is where Techniques for Dimension Reduction can play a crucial role. Additionally, data is objective facts are simply recorded without any inherent judgment or insight, and they do not carry any interpretation until further analysis is applied. Data is also diverse, existing in multiple forms such as text, numbers, audio, and visual content.
For example, a set of numbers like 5, 10, 15, and 20 could be data points; temperature readings recorded at various times throughout the day or survey responses without any analysis also represent raw data. Without context or processing, data is just a collection of isolated elements waiting to be interpreted and converted into useful information.
What is Information?
- Processed Data: Information is data that has been processed, organized, and structured to provide meaning and context.
- Contextual: Unlike raw data, information is relevant and valuable because it is contextualized and interpreted for specific purposes.
- Actionable: Information is useful for decision-making, analysis, and problem-solving, providing insights that can lead to action.
- Clear and Understandable: Information is presented in a clear, understandable format, such as reports, summaries, charts, or graphs, making it easier to comprehend, especially when working with Datasets for Machine Learning.
- Purpose-Driven: Information is generated to serve specific needs, whether it’s for business intelligence, planning, or strategic decision-making.
- Dynamic: Information can evolve over time as new data is processed, offering up-to-date insights for ongoing analysis or decision-making.
- Examples: Information can include sales reports, customer insights, weather forecasts, or market trends that have been derived from raw data.
- Value: Information holds value because it provides clarity, context, and insight, making it more impactful than raw data in guiding actions and strategies.
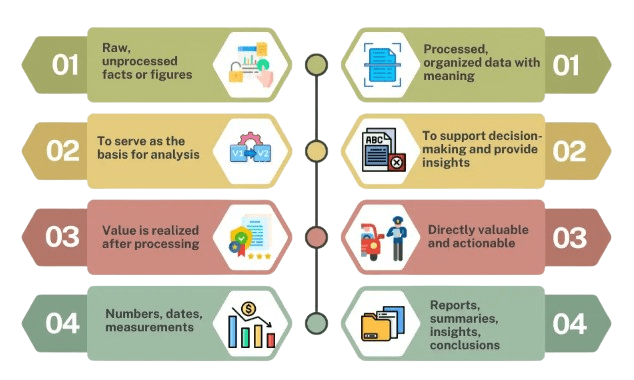
- Definition: Data consists of raw, unprocessed facts and figures, while information is data that has been processed, organized, and given context.
- Context: Data lacks context and meaning by itself, whereas information is meaningful because it is organized and structured in a way that provides context.
- Purpose: Data serves as the raw material for analysis, while information is used to support decision-making, analysis, and problem-solving, which is a critical distinction in understanding the Supervised Learning Workflow and Algorithms.
- Format: Data can exist in various forms such as numbers, text, images, or sounds, while information is typically presented in formats like reports, summaries, or graphs.
- Value: Data alone holds limited value and requires further processing to be useful, while information has inherent value as it provides insights and understanding.
- Processing: Data is unprocessed and needs to be structured or analyzed, whereas information is the result of analyzing and organizing data.
- Examples: Data could be raw numbers or survey responses, while information could be sales trends, customer insights, or weather forecasts derived from that data.
- Role in Decision-Making: Data cannot guide decisions on its own because it lacks context, but information helps in making informed decisions by providing relevant insights derived from the data.
- Foundation for Analysis: Data serves as the raw material that decision-makers analyze to gain insights and make informed decisions.
- Identifies Trends and Patterns: By analyzing data, businesses and individuals can identify trends, patterns, and correlations that help forecast future events and outcomes.
- Informs Strategic Planning: Data helps guide strategic decisions, providing factual information that supports long-term planning and goal-setting.
- Reduces Uncertainty: Using data-driven insights helps reduce uncertainty in decision-making by relying on evidence rather than intuition or guesswork, a key principle emphasized in a Comprehensive Data Science Course Syllabus.
- Supports Performance Measurement: Data enables businesses to track performance against key metrics, helping to assess progress and make adjustments when necessary.
- Enhances Accuracy: Data allows for more accurate decision-making by removing subjective biases and providing concrete, measurable information.
- Facilitates Risk Management: By analyzing data, potential risks can be identified early, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate negative impacts.
- Improves Efficiency: Data-driven decisions often lead to more efficient processes, as they are based on facts and metrics that reveal areas for improvement or optimization.
- Data Transformation: Information is derived from raw data through analysis and processing, making it useful for business intelligence (BI) applications that support decision-making.
- Insight Generation: Information helps businesses uncover insights by identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, enabling better strategic decisions.
- Informed Decision-Making: Business intelligence relies on accurate, structured information to guide decisions on marketing, finance, operations, and other key areas, a concept that plays a significant role in shaping your Data Science Career Path.
- Improved Performance: By utilizing information, organizations can assess performance against benchmarks, track progress, and optimize processes for greater efficiency.
- Competitive Advantage: Information derived from BI allows businesses to stay ahead of competitors by identifying market opportunities and responding quickly to changes.
- Predictive Analysis: Information in BI tools helps companies forecast future trends and outcomes, improving planning, risk management, and resource allocation.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Key Differences Between Data and Information
The Interrelation Between Data and Information
Information and data are deeply interconnected, with data serving as the raw material that, when processed, transforms into valuable information. Data, in its unprocessed form, lacks context and meaning, while information is the result of organizing, interpreting, and structuring data in a way that provides clarity and relevance. Both are essential components in effective decision-making processes across various sectors. For example, in a business setting, companies often collect raw data, such as customer preferences, purchase behavior, or survey responses. This raw data, by itself, does not provide actionable insights, which is why it’s crucial to process and analyze it effectively a core concept in Data Science Training. However, when analyzed and organized, it becomes information that can be used to inform decisions. In this case, information could reveal trends or patterns in customer behavior, which can help guide marketing strategies, product development, and customer engagement initiatives. By leveraging both data and information, businesses can make informed choices, develop better strategies, and improve their operations. The relationship between data and information is critical in converting raw facts into meaningful insights that drive progress and success in decision-making.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Data Science? Enroll in the Data Science Masters Course Today!
The Function of Data in Decision-Making
The Function of Information in Business Intelligence
Want to Learn About Data Science? Explore Our Data Science Interview Questions & Answer Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Conclusion
Information and data are closely related concepts, yet they serve different purposes. Data refers to raw, unprocessed facts, figures, or details that by themselves may not have meaningful context. It forms the foundation for any type of analysis but holds limited value until it is processed, structured, and interpreted. Once data is organized and analyzed, it transforms into information something that is understandable, relevant, and useful for decision-making. This transformation is essential in fields like data management, business intelligence, and strategic planning, and is a key focus area in Data Science Training. Understanding the difference between data and information is crucial, as it allows individuals and organizations to use each effectively. Data provides the necessary input, while information delivers the insights needed to guide actions and choices. By mastering how data is converted into meaningful information, companies and individuals can leverage both to improve outcomes, make informed decisions, and gain competitive advantages. Whether in business, research, or everyday activities, recognizing the value of both elements is key to maximizing their potential and driving better results.



