
- Introduction to UI/UX
- UI vs UX Explained
- Design Process Overview
- User Research Techniques
- Creating Personas
- Wireframing Basics
- Designing UI Elements
- Prototyping Techniques
- Conclusion
Introduction to UI/UX
In today’s digital era, every product interaction counts. UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are core disciplines in product design that determine how people engage with digital products. While UI focuses on aesthetics and layout, UX emphasizes the journey and satisfaction of the user. Together, they form the backbone of effective digital design, shaping the way users interact, feel, and return to a product.Good UI/UX design goes beyond just visuals. It ensures accessibility, usability, efficiency, and emotional satisfaction. Whether you’re building a simple website or a complex app, the success of your digital product heavily relies on how well the UI and UX are integrated.UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) design are two essential disciplines in creating effective, engaging digital products. While they are often grouped together, they focus on different yet closely connected aspects of the design process. User Interface (UI) Design Process Overview deals with the look and feel of a product. It includes everything a user sees and interacts with such as buttons, icons, spacing, colors, typography, and overall visual layout. The goal of UI Design Process is to create aesthetically pleasing and consistent interfaces that make interaction easy and intuitive.User Experience (UX) design, on the other hand, focuses on the overall experience a person has when using a product or service. It considers the user’s journey, goals, pain points, and behaviors. UX design is about solving problems, improving usability, and ensuring the product meets the needs of real users through thoughtful design decisions, user research, and testing.Together, UI and UX form the foundation of any digital product from websites and apps to software platforms. Good UI/UX design ensures that products are not only functional and accessible, but also enjoyable to use.In today’s digital-first world, companies recognize that successful design goes beyond just appearance. A beautiful product that frustrates users will quickly fail. That’s why UI/UX Training plays a key role in business growth, customer retention, and user satisfaction.Whether you’re a beginner exploring the field or a developer collaborating with designers,Wireframing Basics, understanding the fundamentals of UI and UX helps you contribute to better product outcomes. As technology evolves, so does the importance of designing experiences that are user-centered, efficient, and human-friendly.
Ready to Get Certified in UI/UX Design? Explore the Program Now UI/UX Design Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
UI vs UX Explained
Though often confused or used interchangeably, UI and UX have distinct roles:
- UI (User Interface): Pertains to the visual and interactive elements users engage with such as buttons, icons, menus, and layouts.
- UX (User Experience): Involves the overall experience, including ease of navigation, clarity of information, and user satisfaction.
- Empathize & Discover: Understand business goals, user problems, and market opportunities.
- Research: Gather insights through interviews, surveys, and data analysis.
- Define: Synthesize findings into user needs and product goals.
- Ideate: Generate design ideas and user flows.
- Wireframe: Build skeletal layouts to visualize structure and flow.
- Prototype: Create clickable models that simulate real interactions.
- Test: Validate the experience through usability tests.
- Deliver & Iterate: Collaborate with developers and refine based on feedback.
- Name, age, occupation.
- Goals and frustrations.
- Background and environment.
- Technology proficiency.
- Preferred platforms.
- Name: Priya Mehta, 29, Digital Marketer.
- Goals: Monitor ad performance on the go.
- Challenges: Needs fast, mobile-friendly dashboards.
- Preferences: Minimalist interfaces, responsive designs.
- Low-Fidelity: Simple sketches to explore ideas.
- High-Fidelity: Detailed structure with near-final content.
- Buttons: Clear calls-to-action with feedback states.
- Forms: Simple inputs with validation and hints.
- Icons: Intuitive symbols for faster recognition.
- Navigation: Logical menus and hierarchies.
- Typography: Readable, consistent fonts with hierarchy.
- Color: Strategic use of contrast and brand identity.
- Paper Prototypes : Quick sketches for initial ideas.
- Low-Fidelity Digital: Clickable wireframes for testing structure.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes : Fully designed, interactive screens simulating the end product.
Think of UI as the paint and UX as the blueprint. A beautifully designed website (UI) may still frustrate users if it’s hard to navigate (UX). Similarly, a seamless journey can be undermined by clunky, unattractive visuals. Successful digital products harmonize both.
Design Process Overview
The UI/UX Design Process Overview is iterative, user-centered, and collaborative. Here’s a typical flow:
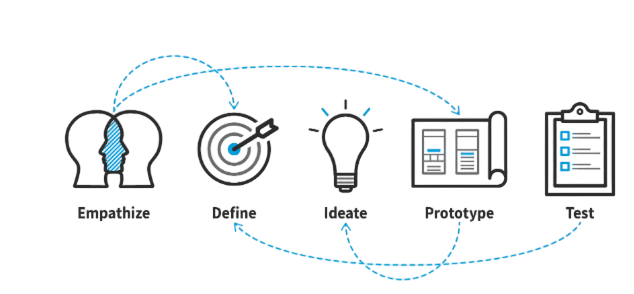
Design is cyclical; each stage can prompt a return to previous ones based on insights.
To Explore UI/UX in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive UI/UX Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
User Research Techniques
Effective UI/UX begins with knowing your users. Research uncovers behavior, needs, pain points, and expectations.User research is a fundamental part of the UI/UX Training process. It helps designers understand the real needs, behaviors, and challenges of users, Wireframing Basics , ensuring that the final product is both useful and user-friendly. Rather than relying on assumptions, user research allows teams to design based on evidence gathered directly from the people they’re designing for.One common technique is user interviews, which involve one-on-one conversations to explore a user’s experiences, goals, and frustrations. These interviews provide deep, qualitative insights that can shape design decisions early on. Surveys and questionnaires are another widely used method, especially when quick feedback from a large group is needed. They help identify patterns and user preferences at scale.Observational research, such as contextual inquiry, allows designers to watch users interact with a product in real-world settings. This reveals natural behavior and uncovers usability issues that users may not verbalize. Another key method is usability testing, where participants perform tasks while researchers observe. This helps identify confusing areas or design flaws.For projects involving content organization, card sorting helps understand how users expect information to be structured. Lastly, focus groups gather multiple users in a group discussion to capture a range of opinions and attitudes toward a product.By using a mix of these techniques, Design Process Overview designers gain a clearer, more accurate understanding of their users leading to smarter, more user-centered design solutions.
Creating Personas
Personas humanize research data, helping teams empathize with users. A persona summarizes typical user behavior, motivations, and challenges.
Persona Components:
Example Persona:
Personas align design decisions with real user needs.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the UI/UX Design Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Wireframing Basics
Wireframing is a fundamental step in the design process for websites, mobile apps, and other digital products. It involves creating a simple, visual representation of a user interface that outlines the basic structure and layout without focusing on design elements like color, typography, Wireframing Basics or images. Think of a wireframe as a blueprint that helps designers and developers visualize the placement of content, features, and navigation before building the final product.
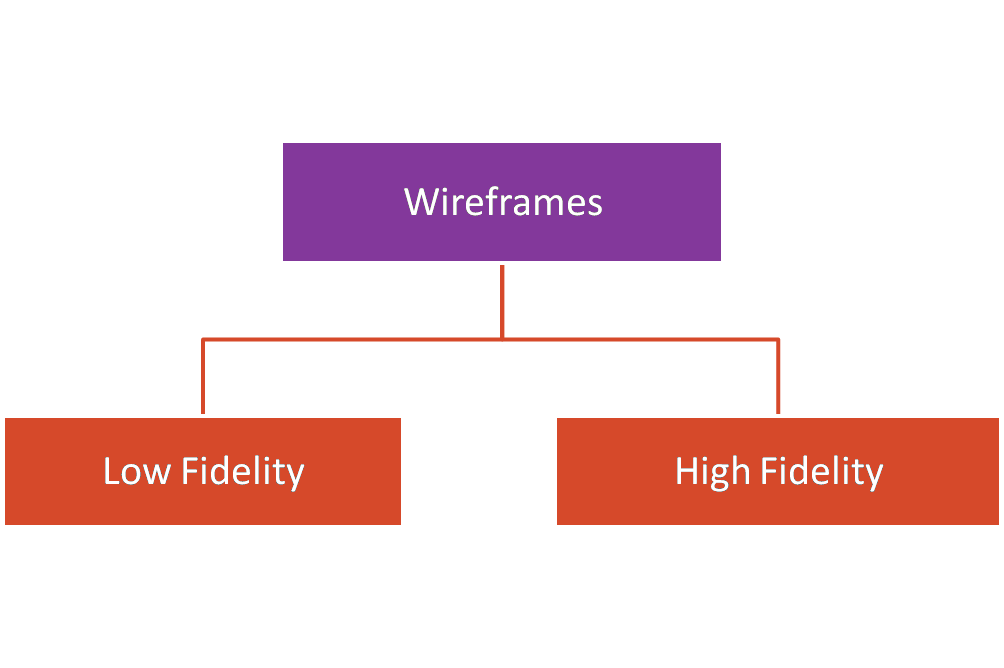
Types of Wireframes:
Wireframes help communicate ideas early and get stakeholder alignment before investing time in final designs.
Designing UI Elements
UI design is about clarity, consistency, and aesthetics. It guides users visually and interactively.
Core UI Components:
Best UI designs utilize spacing, visual hierarchy, and responsive patterns to support both form and function.
Preparing for UI/UX Design Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on UI/UX Design Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Prototyping Techniques
Prototypes are interactive simulations of the final product. They help visualize user flow and catch usability issues early.
Types of Prototypes :
Prototypes are vital for user feedback, internal alignment, and design validation before development.
Conclusion
UI/UX design is a fusion of creativity, empathy, and logic. It brings digital products to life by prioritizing user satisfaction. From research and personas to wireframing and testing, each step is crucial in creating user-friendly interfaces. The process may vary by project, but the user-first mindset must remain constant. By mastering tools like Figma, following best practices, and embracing continuous feedback, designers can build impactful, accessible, and engaging products. Whether you’re new to UI/UX Training or refining your skills, this field promises endless learning, innovation, and the opportunity to positively shape digital experiences.




