
Cybersecurity is a collective name for a collection of procedures, tools, and methods used to guard computer networks, data, and information from theft, damage, and illegal access. With the growing reliance on digital platforms and the interconnectedness of contemporary systems, it is an essential subject in the field of information technology. Ensuring the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of data and systems are the main objectives of cybersecurity.
1. Explain Cybersecurity.
Ans:
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, damage, or theft. It involves implementing measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and resources in the digital realm. Cybersecurity includes various strategies, technologies, and best practices to safeguard against a wide range of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, ransomware, and unauthorized access.
2. How do IDS and IPS vary from one another?
Ans:
IDS (Intrusion Detection System): IDS monitors network or system activities for suspicious patterns or security policy violations. When it detects such activity, it generates alerts to notify administrators.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System): IPS, on the other hand, not only detects but also takes automated actions to prevent or block potentially malicious activities. It can dynamically respond to threats by blocking traffic, modifying firewall rules, or taking other predefined actions.
3. Describe a Botnet.
Ans:
A botnet is a network of compromised computers, often referred to as “bots” or “zombies,” that are controlled by a single entity, the “botmaster.” These compromised computers can be infected with malware, allowing the botmaster to remotely control them.
4. What are the common Cyber Attacks?
Ans:
Phishing: Phishing is a fraudulent practice of sending spam emails by impersonating legitimate sources.
Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering attacks can take many forms and can be carried out anywhere human collaboration is required.
Ransomware: Ransomware is a documented encryption program that uses the special cryptographic calculations to encrypt the records in a targeted framework.
Cryptocurrency Hijacking: As a cdigital currencies and mining become more popular, so do cybercriminals. They have found an advantage in cryptocurrency mining, which involves the complex calculations to mine virtual currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, and Litecoin.
5. Define DNS.
Ans:
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates the domain names into the IP addresses that browsers use to load the web pages. Every device connected to the Internet has its own IP address, which other devices use to identify it in a simple language, can say that DNS Defines the Service of a network.
6. What are elements of cyber security?
Ans:
- Application Security
- Information Security
- Network Security
- Disaster Recovery Planning
- Operational Security
- End User Education
7. What is Firewall?
Ans:
A firewall is the hardware or software-based network security device that monitors all the incoming and outgoing traffic and accepts, denies, or drops that particular traffic based on the defined set of security rules.
8. What is social engineering attack?
Ans:
Social engineering is the act of manipulating individuals to take actions that may or may not be in the best interests of the “target”. This may include obtaining information, obtaining access, or obtaining a goal to perform a particular action. It has the ability to manipulate and deceive people. A phone call accompanied by a survey or quick internet search can bring up the dates of birthdays and anniversaries and arm with that information. This information is enough to create the password attack list.
9. What is VPN?
Ans:
VPN stands for a Virtual Private Network. A virtual private network (VPN) is the technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over an insecure network like the Internet. A virtual private network is the method of extending a private network using a public network such as the Internet. The name only indicates that it is a virtual “private network”. A user may be part of a local area network at a remote location. Create a secure connection using a tunnelling protocol.
10. What are the different sources of malware?
Ans:
Worms: A worm is basically the type of malicious malware that spreads rapidly from one computer to the another via email and file sharing. Worms do not require a host software or code to execute.
Spyware: Spyware is basically the type of malicious malware that runs in the background of a computer, steals all sensitive data, and reports this data to remote attackers.
Ransomware: Ransomware is used as a malware to extort money from the users for ransom by gaining unauthorized access to the sensitive user information and demanding payment to delete or return that information from the user.
Virus: A virus is the type of malicious malware that comes as an attachment with a file or program. Viruses usually spread from one program to another program, and they will run only when the host file gets executed.
11. What is the difference between active and passive cyber attacks?
Ans:
| Aspect | Active Attacks | Passive Attacks | |
| Objective |
Disrupt, damage, manipulate |
Gather information | |
| Example | Malware, DDoS, ransomware | Eavesdropping, scanning | |
| Interaction | Direct interference | Observing and collecting | |
| Detection |
Easily detected |
Harder to detect |
12. Define encryption and decryption.
Ans:
Encryption is a process of transforming an ordinary message (plaintext) into a meaningless message (ciphertext). Decryption is a process of transforming a meaningless message (ciphertext) into its original form (plaintext). The main difference between the covert writing and covert writing is that it converts the message into a cryptic format that cannot be deciphered unless the message is decrypted. Covert writing, on the other hand, is reconstructing an original message from encrypted information.
13. What is block cipher?
Ans:
Block Cipher Converts the plaintext to ciphertext using one block of plaintext at time. Use 64-bit or 64-bit or greater. The complexity of the block ciphers is simple. The algorithm modes used in the block ciphers are ECB (Electronic Code Book) and CBC (Cipher Block Chaining).
14. What are the black hat hackers and white hat hackers?
Ans:
White Hat Hacker: A white hat hacker is a certified hacker who works for governments and organizations by conducting penetration tests and identifying cybersecurity gaps.
Black Hat Hackers: They are often called the crackers. Black hat hackers can gain unauthorized access to the system and destroy important data. The attack method uses the common hacking techniques learned earlier.
16. Difference between plaintext and cleartext?
Ans:
The plaintext is not encrypted at all and cannot be considered as encrypted and Clear text is the text sent or stored that has not been encrypted and was not intended to be encrypted. So don’t need to decrypt to see plaintext. In its simplest form.
17. What is block cipher?
Ans:
Block Cipher Converts the plaintext to ciphertext using one block of plaintext at time. Use 64-bit or 64-bit or greater. The complexity of the block ciphers is simple. The algorithm modes used in the block ciphers are ECB (Electronic Code Book) and CBC (Cipher Block Chaining).
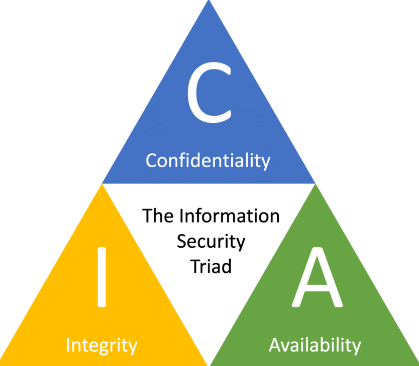
18. What is the CIA triangle?
Ans:
When it comes to network security, the CIA Triad is one of the most important models developed to guide the information security policy within an organization. CIA stands for:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
19. What is a Three-way handshake?
Ans:
TCP uses the three-way handshake to establish reliable connections. The connection is a full-duplex, with synchronization (SYN) and acknowledgment (ACK) on both sides. The exchange of these four flags is done in the three steps: SYN, SYN to ACK, and ACK.
20. How can identified theft be prevented?
Ans:
- Use a strong password and don’t share PIN with anyone on or off the phone.
- Use two-factor notifications for email. Protect all the devices with one password.
- Do not install software from the Internet. Do not post confidential information on social media.
- When entering the password with the payment gateway, check its authenticity.
- Limit the personal data run. Get in the habit of changing the PIN and password regularly.
21. What are the common Hashing functions?
Ans:
The hash function is the function that converts the specific numerical key or alphanumeric key into the small practical integer value. The mapped integer value is used as an index for hash tables. Simply put, a hash function maps any valid number or string to a small integer that can be used as an index into a hash table. The types of Hash functions are :
- Division Method
- Mid Square Method
- Folding Method
- Multiplication Method
22. What is two-factor authentication?
Ans:
Two-factor authentication refers to using any two independent methods from the variety of authentication methods. Two-factor authentication is used to ensure users have access to secure the systems and to enhance security. Two-factor authentication was first implemented for laptops due to basic security needs of mobile computing. Two-factor authentication makes it difficult for unauthorized users to use mobile devices to access secure data and systems.
23. What does XSS stand for?
Ans:
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is the vulnerability in web applications that allows the third parties to execute scripts on behalf of web application in the user’s browser. Cross-site scripting is one of the most prevalent security vulnerabilities on Internet today. Exploiting XSS against users can have the variety of consequences, including the Account compromise, account deletion, privilege escalation, malware infection, etc.
24. What is Shoulder Surfing?
Ans:
- A shoulder surfing attack describes the situation in which an attacker can physically look at a device’s screen or keyboard and enter a password to obtain personal information.
- Used to access malware. Similar things can happen from the nosy people, leading to invasion of privacy.
25. What is meant by System Hardening?
Ans:
The attack surface includes all the flaws and vulnerabilities that a hacker could use to gain access to the system, such as default passwords, improperly configured firewalls, etc. The idea of system hardening is to make the system more secure by reducing the attack surface present in a design of the system. System hardening is a process of reducing the system’s attack surface, thereby making it much more robust and secure. This is an integral part of the system security practices.
26. Differentiate between spear phishing and phishing?
Ans:
Phishing: This is the type of email attack in which an attacker fraudulently attempts to discover the user’s sensitive information through electronic communications, pretending to be from the relevant and trusted organization. The emails are carefully crafted by attackers, targeted to specific groups, and clicking links installs malicious code on the computer.
Spear phishing: Spear phishing is the type of email attack that targets a specific individual or organisation. In Spear, a phishing attacker tricks the target into clicking a malicious link and installing the malicious code, allowing the attacker to obtain sensitive information from a target’s system or network.
27. What is Perfect Forward Secrecy?
Ans:
- Perfect Forward Secrecy is the style of encryption that creates the temporary exchange of secret keys between server and client.
- It is primarily used to call the apps, websites, and messaging apps where user privacy is paramount.
- A new session key is generated every time the user performs an action. This keeps data uncompromised and safe from the attackers.
28. What is ransomware?
Ans:
Ransomware is the type of malware that encrypts data to make it inaccessible to the computer users. Cybercriminals use it to extort money from the individuals and organizations that hacked data and hold data hostage until the ransom is paid.
29. How to prevent MITM?
Ans:
- A Strong WEP/WAP Encryption on the Access Points
- A Strong Router Login Credentials
- Use the Virtual Private Network
30. What is Public Key Infrastructure?
Ans:
A Public Key Infrastructure, or PKI, is the governing authority behind the issuance of the digital certificates. Protect sensitive data and give the users and systems unique identities. Therefore, communication security is more ensured. The public key infrastructure uses the keys in public-private key pairs to provide security. Public keys are vulnerable to attacks, so maintaining public keys requires a healthy infrastructure.
31. What are the steps involved in hacking a server or network?
Ans:
- Access the web server.
- Use anonymous FTP to access this network to gather more information and scan ports.
- Pay attention to the file sizes, open ports, and processes running on the system.
- Run a few simple commands on a web server like “clear cache” or “delete all files” to highlight the data stored by the server behind these programs.
- Connect to the other sites on the same network, such as Facebook and Twitter, so that you can check the deleted data. Access server using the conversion channel.
- Access the internal network resources and data to gather more information.
32. What is Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDoS)?
Ans:
A denial of service (DoS) is the cyber attack against an individual computer or website aimed at denying service to the intended users. Its purpose is to interfere with an organization’s network operations by denying access. Denial of service is usually achieved by flooding the target machine or resource with excessive requests, overloading the system, and preventing some or all legitimate requests from being satisfied.
33. What is a proxy firewall?
Ans:
The proxy firewall monitors the application-level information using the firewall proxy server. A proxy firewall server creates and runs the process on the firewall that mirrors services as if they are running on the end host.
The application layer has several protocols such as HTTP (a protocol for sending and receiving web pages) and SMTP (a protocol for the e-mail messages on the Internet). A proxy server like a Web Proxy Server is like the process that mirrors behavior of the HTTP service.
34. Explain SSL Encryption.
Ans:
Data sent between online browsers and servers is secured using Secure Socket Layer, or SSL. SSL secures the connection between the web server and the browser, protecting any information sent between them from prying eyes. Protocols for a secure socket layer: Protocol for SSL recording.
35. How to avoid ARP poisoning?
Ans:
Static ARP Tables: Verifying the correct mapping of MAC addresses to IP addresses, half the problem is solved. This is doable but costly to administer. ARP tables to record all the associations and each network change are manually updated in tables.
Switch Security: Most Ethernet switches have the features that help mitigate the ARP poisoning attacks. Also known as a Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI), these features help validate the ARP messages and drop packets that indicate any kind of malicious activity.
Physical Security: A very simple way to mitigate the ARP poisoning attacks is to control the physical space of the organization. ARP messages are only routed within the local network. Therefore, the attacker may have a physical proximity to the victim’s network.
36. What is penetration testing?
Ans:
- Penetration testing is done to find the vulnerabilities, malicious content, flaws, and risks.
- It’s done to make an organization’s security system defend the IT infrastructure.
- It is an official procedure that can be deemed helpful and not a harmful attempt.
- It is part of an ethical hacking process that specifically focuses only on penetrating information systems.
37. What are the risks associated with public Wi-Fi?
Ans:
- Malware, Viruses, and Worms
- Rogue Networks
- Unencrypted Connections
- Network Snooping
- Log-in Credential Vulnerability
- System Update Alerts
- Session Hijacking
38. Difference between Diffie-Hellman and RSA?
Ans:
Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithm: It is the key exchange protocol that allows the two parties to communicate over the public channel and establish a shared secret without sending it over the Internet. DH allows the two people to use a public key to encrypt and decrypt conversations or data using a symmetric cryptography.
RSA: It is the type of asymmetric encryption that uses two different linked keys. RSA encryption allows the messages to be encrypted with both public and private keys. The opposite key used to encrypt messages is used to decrypt messages.
39. Explain session hijacking.
Ans:
Session hijacking is the security attack on user sessions over the protected network. The most common method of session hijacking is called the IP spoofing, where an attacker uses the source-routed IP packets to inject commands into active communication between two nodes on the network, allowing an authenticated impersonation of one of the users. The types of the session hijacking are :
- Packet Sniffing
- CSRF (Cross-site Request Forgery)
- Cross-site Scripting
- IP spoofing
40. Explain honeypot and its types.
Ans:
A honeypot is the networked system that acts as a trap for cyber attackers to detect and investigate hacker tactics and types of the attacks. Acting as a potential target on the Internet, it notifies defenders of unauthorized access to the information systems. Honeypots are classified based on deployment and intruder involvement.
41. What is Null Session?
Ans:
The system administrators do not consider this type of attack when implementing the network security measures. This can have unimaginable consequences, as this type of attack allows the hackers to obtain all information they need to access the system remotely. This type of attack is difficult to execute if a customer is using the newer version of the operating system.
42. What is IP blocklisting?
Ans:
- IP blacklisting is the method used to block unauthorized or malicious IP addresses from the accessing network.
- A blacklist is the list of ranges or individual IP addresses to the block.
43. What are the classification of honeypots?
Ans:
Research honeypots: Used by the researchers to analyze hacking attacks and find the different ways to prevent them.
Production Honeypots: Production honeypots are deployed with the servers on the production network. These honeypots act as the front-end trap for attackers composed of false information, giving administrators time to fix all the vulnerabilities in the real systems.
44. What are Polymorphic viruses?
Ans:
“Poly” refers to the many and “morphic” refers to shape. Thus, polymorphic viruses, as the name suggests, are complex computer viruses that change shape as they spread in order to avoid detection by the antivirus programs. This is the self-encrypting virus that combines the mutation engine with the self-propagating code.
45. What is an Eavesdropping Attack?
Ans:
- Eavesdropping occurs when the hacker intercepts, deletes or modifies a data sent between the two devices.
- Eavesdropping, also known as sniffing or snooping, relies on the unsecured network communications to access the data sent between devices.
46. What is a man-in-the-middle attack?
Ans:
This is the type of cyber attack in which the attacker stays between two to carry out a mission. The type of function it can perform is to modify the communication between the two parties so that both parties feel like they are communicating over the secure network.
47. What is traceroute?
Ans:
- Traceroute is the widely used command line tool available on almost all the operating systems.
- A complete route to the destination address is displayed. It also shows time (or delay) between the intermediate routers.
48. Difference between HIDS and NIDS?
Ans:
HIDS: This intrusion detection system sees the host itself as the whole world. It can be a computer (PC) or a server that can act as the standalone system and analyze and monitor its own internals. It works by looking at files/data coming in and out of the host.
NIDS: This system is responsible for the installation points across the network and can operate in the mixed and hybrid environments. Alerts are triggered when something malicious or the anomalous is detected in the network, cloud, or other mixed environments.
49. What is RSA?
Ans:
The RSA algorithm is the asymmetric encryption algorithm. Asymmetric means that it actually works with the two different keys like Public and Private Keys. As the name suggests, a public key is shared with everyone and a private key remains secret.
50. What is Risk, Vulnerability and Threat in network?
Ans:
Cyber threats are malicious acts aimed at stealing or corrupting data or destroying the digital networks and systems. A threat can also be defined as the possibility of successful cyberattack to gain unethical access to the sensitive data on a system.
Vulnerabilities in cybersecurity are deficiencies in a system’s designs, security procedures, internal controls, etc. that can be exploited by the cybercriminals. In very rare cases, cyber vulnerabilities are the result of cyberattacks rather than a network misconfiguration.
Cyber risk is a potential result of loss or damage to assets or data caused by cyber threats. It can’t eliminate a risk completely, but can manage it to a level that meets the organization’s risk tolerance. Therefore, the goal is not to build the system without risk but to keep risk as low as possible.
51. What is Forward Secrecy and how does it work?
Ans:
Forward secrecy is the feature of some key agreement protocols that guarantees that session keys will remain secure even if a server’s private key is compromised. Perfect forward secrecy, also known as a PFS, is the term used to describe this. The “Diffie-Hellman key exchange” algorithm is employed to achieve this.
52. Difference between vulnerability and exploit?
Ans:
Vulnerability: A vulnerability is the error in the design or implementation of the system that can be exploited to cause unexpected or undesirable behaviour. There are many ways the computer can become vulnerable to security threats. A common vulnerability is for the attackers to exploit system security vulnerabilities to gain access to the systems without proper authentication.
Exploit: Exploits are tools that can be used to exploit vulnerabilities. They are created using the vulnerabilities. Exploits are often patched by software vendors as soon as they are released. They take a form of software or code that helps them control computers and steal network data.
53. What are the HTTP response codes?
Ans:
HTTP response codes display whether the particular HTTP request has been completed.
- 1xx (Informational) – The request has been received, and the process is continuing.
- 2xx (Success) – The request was successfully received and accepted.
- 3xx (Redirection) – Further action must be taken to complete it.
- 4xx (Client Error) – Request cannot be fulfilled or incorrect syntax.
- 5xx (Server Error) – The server fails to fulfill the request.
54. What is the use of Traceroute?
Ans:
A Traceroute is the network diagnostic tool, used for tracking the pathway of an IP network from source to the destination. It records the period of each hop the packet makes while its route to the destination.
55. What is needed for DNS monitoring?
Ans:
- DNS (Domain Name System) is the service that is used for converting the user-friendly domain names into the computer-friendly IP address. It allows the websites under a particular domain name that is simple to remember.
- DNS monitoring is nothing but monitoring the DNS records to ensure it routes traffic properly to websites, electronic communication, services, and more.
56. What is the difference between hashing and salting?
Ans:
Hashing is the majorly used for authentication and is a one-way function where data is planned to the fixed-length value.
Salting is an extra step for hashing, where it adds additional value to the passwords that change hash value created.
57. What is cognitive security?
Ans:
Cognitive security is one of the applications of the AI technologies that is used explicitly for identifying threats and protecting physical and digital systems based on the human understanding processes. Self-learning security systems use pattern recognition, natural language processing, and data mining to mimic the human brain.
58. How to prevent ‘Man-in-the-Middle Attack’?
Ans:
- Having stronger WAP/WEP Encryption on the wireless access points avoids unauthorized users.
- Use a VPN for a secure environment to protect sensitive information. It uses key-based encryption.
- Public key pair-based authentication must be used in the various layers of a stack for ensuring whether communicating the right things are not.
- HTTPS must be employed for securely communicating over the HTTP through public-private key exchange.
59. What are various types of system hardening:? .
Ans:
- Database hardening
- Operating system hardening
- Application hardening
- Server hardening
- Network hardening
60. What is the use of Patch Management?
Ans:
The purpose of the patch management is to keep updating the various systems in the network and protect them against the malware and hacking attacks.
Many enterprise patch management tools manage patching processes by installing or deploying agents on the target computer, and they provide a link between the centralized patch servers and computers to be patched.
61. What are common methods of authentication for network security?
Ans:
Biometrics: It is a known and registered physical attribute of a user specifically used for verifying identity.
Token: A token is used for the accessing systems. It makes it difficult for hackers to access accounts that have long credentials.
Transaction Authentication: A one-time pin or password is used in the processing of online transactions through which to verify their identity.
Multi-Factor Authentication: It’s the security system that needs more than one method of authentication.
62. What is the use of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
Ans:
ARP is the protocol specifically used to map the IP network addresses to the physical addresses, such as Ethernet addresses.
It translates the 32-bits addresses to 48-bits addresses and vice versa. This is needed because the most common level of internet protocol(IP) and use today is 32-bits long and MAC addresses are 48-bits long.
63. Difference between Red Team and Blue team?
Ans:
- The red team and blue team refer to cyberwarfare. Many organizations split the security team into the two groups as red team and blue team.
- The red team refers to the attacker who exploits the weaknesses in the organization’s security.
- The blue team refers to the defender who identifies and patches vulnerabilities into the successful breaches.
64. What is Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)?
Ans:
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is the Microsoft protocol specifically designed for the application of data transfer security and encryption between the client devices, users, and virtual network server. It allows the administrators to remotely evaluate and resolve the issues individual subscribers encounter. It supports up to the 64,000 separate data channels with the provision for multipoint transmission.
65. How to reset or remove BIOS password?
Ans:
There are many ways to reset or remove BIOS password:
- By removing CMOS battery
- By using a software
- By using MS-DOS command
- By using the motherboard jumper
- By using the Backdoor BIOS password
66. Difference between false positive and false negative in IDS?
Ans:
- A false positive is considered to be a false alarm and false negative is considered to be the most complicated state.
- A false positive occurs when IDS fires an alarm for a legitimate network activity.
- A false negative occurs when the IDS fails to identify the malicious network traffic.
67. What is active reconnaissance?
Ans:
Active reconnaissance is the kind of computer attack where an intruder engages the target system for collecting the data about vulnerabilities.
The attackers mostly use the port scanning to identify vulnerable ports and exploit the vulnerabilities of services that are associated with the open ports.
68. What are several indicators of compromise(IOC) that organizations should monitor?
Ans:
- Unusual Outbound Network Traffic
- HTML Response Sizes
- Geographical Irregularities
- Increases in the Database Read Volume
- Log-In Red Flags
- Unexpected Patching of Systems
69. What is security misconfiguration?
Ans:
Security misconfiguration is the vulnerability that could happen if the application/network/device is susceptible to attack due to insecure configuration options. It can be as simple as keeping default username/password unchanged.
70. What is Chain of Custody?
Ans:
- Chain of custody refers to probability of data provided as originally acquired and has not been changed before the admission into evidence.
- In legal terms, it’s chronological documentation/paper trail that records the proper sequence of custody, control, analysis, and disposition of electronic or physical evidence.
71. What distinguishes reflected XSS from cached XSS?
Ans:
Reflected XSS (Cross-Site Scripting): In reflected XSS attacks, the malicious script is embedded in a URL, a form, or another input mechanism. When a user interacts with this manipulated input, the script is executed, usually in the context of the user’s browser.
Cached XSS: Cached XSS occurs when a web application stores user inputs in a cache, and subsequent users receive the cached content. If the cached content contains a malicious script, it can affect users who view the cached version of the page, even if the original input was not malicious.
72. What do response codes for HTTP stand for?
Ans:
HTTP response codes indicate the status of a requested HTTP resource. Some common ones include:
- 200 OK: The request was successful.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found.
- 500 Internal Server Error: The server encountered an error.
73. Why is Patch Management used?
Ans:
Patch management is crucial for maintaining the security of software systems. It involves the regular application of updates (patches) to software, operating systems, and applications. Patches often address security vulnerabilities, and timely patching helps prevent exploitation by malicious actors.
74. Is HTTPS or SSL the more secure protocol?
Ans:
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) and SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) serve different purposes. SSL is an older protocol used for securing communication over the internet. HTTPS, on the other hand, is a combination of HTTP and SSL/TLS protocols. In modern terms, it’s more accurate to refer to the use of TLS (Transport Layer Security). TLS is considered more secure than SSL, and HTTPS is the preferred protocol for secure communication on the web.
75. How should data be protected while it’s in transit vs at rest?
Ans:
In Transit: Use encryption protocols such as TLS or SSL when data is being transmitted over networks. This ensures that data remains confidential and secure during transmission.
At Rest: Implement encryption mechanisms to protect stored data on devices, servers, or databases. This safeguards the data even when it is not actively being transferred.
76. What strategies are employed to stop a brute force attack?
Ans:
To thwart brute force attacks, several strategies are commonly employed. Implementing account lockout policies is a fundamental approach, temporarily locking user accounts after a certain number of unsuccessful login attempts. Introducing CAPTCHA challenges adds an additional layer, distinguishing between human and automated login attempts.
77. Describe the many sorts of data leaks.
Ans:
Data leaks manifest in various forms, each presenting unique challenges. Accidental disclosure occurs when sensitive information is unintentionally shared, posing risks to data integrity.
Malicious insider actions involve employees intentionally leaking data, potentially for personal gain or harm. External hacks result in unauthorized access by external entities, leading to data exposure.
78. How can CSRF attacks be avoided?
Ans:
Preventing Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks requires implementing protective measures. Incorporating anti-CSRF tokens into web applications adds a layer of security, ensuring that each form submission contains a unique token that the server validates to verify the legitimacy of the request.
79. How does port scanning work?
Ans:
Port scanning is a technique used to identify open ports on a target system. TCP Connect Scan involves attempting to establish a full TCP connection with the target’s ports to determine openness.
80. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Ans:
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption employs a pair of public and private keys. Symmetric is faster but requires secure key distribution, whereas asymmetric provides secure key exchange but is computationally more intensive.
81. What is the principle of the “zero-trust” security model?
Ans:
- The zero-trust model operates on the assumption that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default.
- It requires continuous verification of the identity and security posture of all users and devices, even those within the internal network.
81. How does a firewall function in network security?
Ans:
A firewall acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. It examines and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Firewalls can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both.
82. What role does penetration testing play in cybersecurity?
Ans:
- Penetration testing involves simulating cyberattacks to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in a system.
- It goes beyond vulnerability scanning by actively attempting to breach defenses to assess the system’s resilience.
83. Can you explain the concept of multi-factor authentication and its significance?
Ans:
Multi-factor authentication requires users to present two or more authentication factors (e.g., password, fingerprint, or security token) to gain access.
It adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, especially in the case of compromised credentials.
84. What is the role of a Security Information and Event Management system?
Ans:
SIEM systems aggregate and analyze log data from various sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. They provide real-time monitoring, event correlation, and alerting, helping security professionals identify and respond to security incidents effectively.
85. How does end-to-end encryption enhance communication security?
Ans:
End-to-end encryption ensures that data is encrypted on the sender’s device and only decrypted on the recipient’s device, preventing unauthorized access during transit. This method secures communication channels and protects sensitive information from interception.
86. What are the key principles of the CIA triad in cybersecurity?
Ans:
The CIA triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles form the foundation of cybersecurity. Confidentiality ensures that data is only accessible to authorized individuals, integrity safeguards the accuracy and reliability of data, and availability ensures that data and systems are consistently accessible when needed.
87. What is the principle of the least privilege?
Ans:
- The principle of least privilege dictates that individuals or systems should have the minimum level of access or permissions necessary to perform their tasks.
- This minimizes the potential impact of a security breach by limiting the scope of unauthorized access, reducing the risk of data compromise or system manipulation.
88. What is the role of VPN in securing communications?
Ans:
- A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection over a public network, such as the internet.
- It ensures confidentiality and privacy by encrypting data in transit between the user’s device and the VPN server.
- VPNs are commonly used to secure remote connections and protect sensitive data from interception.
89. What is the role of a Security Operations Center (SOC) in cybersecurity?
Ans:
A cybersecurity issue is monitored, detected, responded to, and mitigated by a centralised unit called a SOC. By offering real-time security alert analysis, coordinating responses to security events, and putting measures into place to improve overall security posture, it plays a crucial part in incident response.
90. How does the concept of “defense-in-depth” contribute to a cybersecurity strategy?
Ans:
The implementation of several security control levels is known as defense-in-depth, and it serves as a safeguard against a variety of cyber threats. This strategy acknowledges that no security mechanism is infallible. Organisations may strengthen their defence against cyberattacks by combining intrusion detection systems, firewalls, antivirus software, and other security measures.






