
These Network security Interview Questions have been designed specially to get you acquainted with the nature of questions you may encounter during your interview for the subject of Network security . As per my experience good interviewers hardly plan to ask any particular question during your interview, normally questions start with some basic concept of the subject and later they continue based on further discussion and what you answer.we are going to cover top 100 Network security Interview questions along with their detailed answers. We will be covering Network security scenario based interview questions, Network security interview questions for freshers as well as Network security interview questions and answers for experienced.
1. What is the role of a firewall in network security?
Ans:
Firewalls act as barriers between a private network and external networks, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. They provide a crucial defense against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats, playing a pivotal role in securing network perimeters.
2. Explain the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption
Ans:
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption | Key Types | Single Key: Uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption. | >Key Pair: Uses a pair of public and private keys for encryption and decryption, respectively. | Key Distribution | Challenging: Secure key distribution is crucial as the same key is used for both parties. | Easier: Public keys can be distributed openly, while private keys remain confidential. | Computational Cost | Computational Cost | Higher: Generally slower and demands more computational resources. |
|---|
3. What is a VPN (Virtual Private Network) and how does it enhance network security?
Ans:
A VPN establishes a secure, encrypted connection over an untrusted network, such as the internet. By encrypting data in transit, VPNs ensure confidentiality and integrity, safeguarding sensitive information from potential eavesdropping and tampering.
4. Describe the concept of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and their importance in network security.
Ans:
- IDS monitors network or system activities, identifying and responding to suspicious behavior or security policy violations.
- By providing real-time alerts, IDS contributes to the early detection of potential cyber threats, helping organizations proactively defend against attacks.
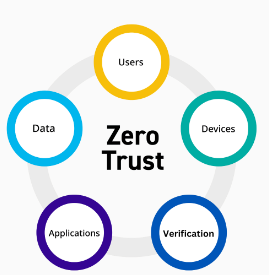
5. Explain the concept of Zero Trust Security.
Ans:
- Zero Trust Security assumes that no entity, whether internal or external, should be trusted by default.
- It mandates strict verification for anyone trying to access resources, regardless of their location or network connection.
- This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within a network.
6. What role does a Proxy Server play in enhancing network security?
Ans:
Proxy Servers act as intermediaries between client devices and the internet, forwarding requests and responses. By doing so, they provide anonymity, content filtering, and an additional layer of security by concealing the user’s IP address and protecting against malicious content.
7. How does a Denial of Service (DoS) attack differ from a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack?
Ans:
In a DoS attack, a single source overwhelms a target system or network, causing a disruption in services. DDoS attacks involve multiple, coordinated sources, amplifying the impact and making it challenging to mitigate. Both aim to render a network or service unavailable temporarily or permanently.
8. Examine the importance of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
Ans:
- SIEM systems collect and analyze log data from various sources within a network, offering a holistic view of security events.
- By correlating information and providing real-time alerts, SIEM systems assist in detecting and responding to security incidents promptly, enhancing overall network security posture.
9. What are the key characteristics of a secure wireless network?
Ans:
- SIEM systems collect and analyze log data from various sources within a network, offering a holistic view of security events.
- By correlating information and providing real-time alerts, SIEM systems assist in detecting and responding to security incidents promptly, enhancing overall network security posture.
10. How does SSL/TLS contribute to securing communication over the internet?
Ans:
- SSL/TLS protocols encrypt data during transmission, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of information exchanged between web browsers and servers.
- This cryptographic protection prevents eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks, enhancing the overall security of online communication.
11. Explain the concept of VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and their role in network security.
Ans:
VLANs segment a physical network into multiple logical networks, improving performance and reducing the risk of unauthorized access. By isolating broadcast domains, VLANs enhance network security by limiting the scope of potential attacks and minimizing the impact of security incidents.
12. Discuss the significance of Network Access Control (NAC) in network security.
Ans:
NAC verifies the compliance of devices attempting to connect to a network, ensuring they meet security policies before granting access. By enforcing endpoint security measures, NAC helps prevent the spread of malware and unauthorized access, bolstering the overall security of the network.
13. What are the challenges associated with securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices in a network?
Ans:
- IoT devices often have limited security features and may pose vulnerabilities if not properly configured.
- Securing IoT devices requires implementing robust authentication, encryption, and monitoring mechanisms to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and potential exploitation
14. Examine the role of a Network Proxy in enhancing privacy and security.
Ans:
- A Network Proxy acts as an intermediary between client devices and the internet, forwarding requests and responses.
- By doing so, it provides anonymity, content filtering, and an additional layer of security by concealing the user’s IP address and protecting against malicious content.
15. How does Network Segmentation contribute to network security?
Ans:
Network Segmentation divides a large network into smaller, isolated segments, reducing the potential impact of security incidents. This approach limits lateral movement for attackers, making it more challenging for them to traverse the network and minimizing the scope of potential breaches.
16. What is the role of a Network Gateway in enhancing security?
Ans:
- A Network Gateway serves as a point of entry and exit between different networks, enforcing security policies and providing a barrier against unauthorized access.
- By inspecting and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic, network gateways play a crucial role in preventing malicious activities and ensuring the overall integrity of the network.
17. Explain the concept of Honeypots and their significance in network security.
Ans:
- Honeypots are decoy systems designed to attract attackers, diverting their attention from critical network assets.
- By closely monitoring interactions with the honeypot, security professionals can gather valuable information about potential threats, tactics, and vulnerabilities, enhancing their ability to proactively defend against cyber attacks.
18. Explain the concept of DNS Security and its significance in network protection.
Ans:
- Involves measures to protect the Domain Name System from cyber threats.
- Mitigates risks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
- Ensures the integrity and authenticity of DNS data.
- Reduces the risk of domain hijacking and unauthorized redirection.
- Enhances the overall security of network communications.
19. Examine the importance of Security Patch Management in network security.
Ans:
- Security Patch Management involves regularly updating software and systems to address known vulnerabilities.
- By staying current with patches, organizations can close potential security loopholes, reducing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors and maintaining a resilient defense against evolving cyber threats.
20. Discuss the role of a Security Operations Center (SOC) in network security.
Ans:
- Monitors, detects, and responds to security incidents.
- Conducts real-time analysis of security alerts and logs.
- Collaborates with incident response teams for swift actions.
- Implements threat intelligence for proactive defense.
- Enhances overall incident detection and response capabilities.
21. What measures can be taken to secure Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications?
Ans:
- Encrypted VoIP traffic to ensure confidentiality.
- Implements strong authentication for VoIP devices.
- Regularly updates and patches VoIP systems for security.
- Monitors for unusual or unauthorized VoIP activities.
- Ensures network segmentation to isolate VoIP traffic.
22. What is the role of a Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) in cybersecurity?
Ans:
NIDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activities or patterns indicative of a cyber attack. By analyzing packets and comparing against predefined signatures or behaviors, it detects unauthorized access or potential threats, enabling timely response to mitigate security risk
23. What are the key considerations in securing wireless networks, and how can these challenges be addressed?
Ans:
- Implements strong encryption protocols for wireless communication.
- Utilizes robust authentication mechanisms for connected devices.
- Enforces proper access controls to mitigate unauthorized access.
- Regularly monitors wireless networks for potential security threats.
- Addresses challenges to ensure the confidentiality of transmitted data.
24. Explain the concept of a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack and methods to prevent it.
Ans:
- A MitM attack occurs when an attacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties.
- Implementing encryption (like SSL/TLS), using secure protocols, and employing strong authentication mechanisms are effective measures to thwart MitM attacks, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
25. How does Endpoint Security contribute to overall network protection?
Ans:
Endpoint Security focuses on securing individual devices (endpoints) connected to a network. Employing antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems on endpoints mitigates the risk of malware infections and unauthorized access, bolstering the overall security posture of the network.
26. Discuss the role of a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system in incident response.
Ans:
SIEM systems collect and analyze log data, providing a centralized view of security events. In incident response, SIEM tools facilitate rapid detection, analysis, and response to security incidents, aiding in understanding the scope and impact of a breach for effective mitigation.
27. How does Biometric Authentication contribute to network security?
Ans:
- Utilizes unique biological traits for user identification.
- Enhances security by providing strong user authentication.
- Reduces the risk of unauthorized access through stolen credentials.
- Biometric data, when encrypted, adds an extra layer of protection.
- Addresses challenges related to password vulnerabilities.
28. What is the purpose of Network Address Translation (NAT) in network security?
Ans:
NAT translates private IP addresses within a local network to a single public IP address, acting as a barrier between internal and external networks. This enhances security by hiding internal network details, making it challenging for attackers to directly target specific devices.
29. How does a Denial of Service (DoS) attack differ from a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack?
Ans:
- In a DoS attack, a single source overwhelms a target system or network, causing a disruption in services.
- DDoS attacks involve multiple, coordinated sources, amplifying the impact and making it challenging to mitigate. Both aim to render a network or service unavailable temporarily or permanently.
30. What are the key characteristics of a secure wireless network?
Ans:
Secure wireless networks implement encryption protocols, strong authentication mechanisms, and proper access controls. Additionally, regular monitoring and updates to address vulnerabilities contribute to the overall security of wireless networks, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
31. Explain the concept of a Security Token and its role in Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Ans:
- Security tokens generate one-time passcodes for authentication.
- Adds an additional layer of security beyond passwords.
- Can be hardware-based (tokens) or software-based (mobile apps).
- Enhances security by requiring possession of the physical token.
- A crucial component in achieving secure MFA implementations.
32. Discuss the concept of Network Forensics and its role in investigating security incidents.
Ans:
Network Forensics involves analyzing network traffic to uncover evidence of security incidents. By reconstructing events and identifying attack vectors, forensic analysts contribute to understanding the timeline and impact of breaches, aiding in incident response and future prevention.
33. How does a Security Token enhance authentication in network access?
Ans:
- Security Tokens generate dynamic, time-sensitive codes for authentication.
- By introducing a second factor, they strengthen access controls, making it harder for attackers to compromise user credentials.
- Security Tokens provide an additional layer of defense, especially in remote or cloud-based environments.
34. Explain the principle of Least Privilege and its application in network security.
Ans:
Least Privilege restricts user access to the minimum necessary for their job function. Implementing this principle reduces the attack surface, limiting the impact of compromised accounts and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches within a network.
35. Discuss the challenges associated with securing Industrial Control Systems (ICS) in critical infrastructure.
Ans:
- Legacy systems often lack built-in security features.
- Disruption concerns due to limited maintenance windows.
- Balancing security measures without compromising operational efficiency.
- Necessitates robust authentication mechanisms for authorized access.
- Regular assessments to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
36. What is the role of a Network Proxy in enhancing privacy and security?
Ans:
A Network Proxy acts as an intermediary between client devices and the internet, forwarding requests and responses. By doing so, it provides anonymity, content filtering, and an additional layer of security by concealing the user’s IP address and protecting against malicious content.
37. How does Network Segmentation contribute to network security?
Ans:
- Network Segmentation divides a large network into smaller, isolated segments, reducing the potential impact of security incidents.
- This approach limits lateral movement for attackers, making it more challenging for them to traverse the network and minimizing the scope of potential breaches.
38. Discuss the principles behind the concept of Defense in Depth.
Ans:
- Defense in Depth involves implementing multiple layers of security mechanisms to protect against a variety of threats.
- This approach includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, creating a robust defense strategy that can withstand diverse cyber threats.
39. What role does Endpoint Security play in overall network protection?
Ans:
- Protects individual devices (endpoints) from security threats.
- Enforces security policies on devices connected to the network.
- Prevents malware infections and data breaches at the endpoint.
- Enhances overall network security by securing individual access points.
- Involves antivirus software, firewalls, and device encryption.
40. Explain the concept of Honeypots and their significance in network security.
Ans:
Honeypots are decoy systems designed to attract attackers, diverting their attention from critical network assets.
By closely monitoring interactions with the honeypot, security professionals can gather valuable information about potential threats, tactics, and vulnerabilities, enhancing their ability to proactively defend against cyber attacks.
41. Discuss the challenges and considerations in securing data in transit over networks.
Ans:
- Encrypts data to ensure confidentiality during transmission.
- Implements secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL.
- Regularly updates cryptographic protocols to address vulnerabilities.
- Ensures secure key management for encryption/decryption.
- Balances security and performance for efficient data transfer.
42. Examine the importance of Security Patch Management in network security.
Ans:
- Security Patch Management involves regularly updating software and systems to address known vulnerabilities.
- By staying current with patches, organizations can close potential security loopholes, reducing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors and maintaining a resilient defense against evolving cyber threats.
43. Discuss the challenges associated with securing Cloud-based networks.
Ans:
Cloud-based networks introduce unique security challenges, including data privacy concerns, shared responsibility models, and the need for secure authentication and authorization mechanisms. Securing cloud environments requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses these challenges, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services.
44. Explain the principles of Risk Assessment in the context of network security.
Ans:
- Identifies potential security risks and vulnerabilities.
- Assesses the potential impact of identified risks.
- Prioritizes risks based on their severity and likelihood.
- Guides the implementation of effective risk mitigation strategies.
- Ongoing process to adapt to evolving threat landscapes.
45. How does a Security Token enhance authentication in network access?
Ans:
Security Tokens generate dynamic, time-sensitive codes for authentication. By introducing a second factor, they strengthen access controls, making it harder for attackers to compromise user credentials. Security Tokens provide an additional layer of defense, especially in remote or cloud-based environments.
46. What is the significance of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems in network security?
Ans:
- Aggregates and analyzes log data from diverse sources.
- Provides real-time threat detection and alerts.
- Enables comprehensive visibility into security events.
- Facilitates rapid incident response and investigation.
47. What is the purpose of Network Address Translation (NAT) in network security?
Ans:
NAT translates private IP addresses within a local network to a single public IP address, acting as a barrier between internal and external networks. This enhances security by hiding internal network details, making it challenging for attackers to directly target specific devices.
48. Discuss the challenges associated with implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) in a network.
Ans:
While MFA enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification, challenges include user resistance, implementation complexity, and potential usability issues. Balancing security and user experience is crucial in overcoming these challenges for successful MFA deployment.
49. Examine the importance of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates in web security.
Ans:
- SSL certificates establish secure, encrypted connections between web browsers and servers, ensuring data confidentiality.
- They verify the legitimacy of websites, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks. Regularly updating SSL certificates is vital for maintaining robust web security and protecting against emerging vulnerabilities.
50. What are the key considerations in securing a wireless network, and how can these challenges be addressed?
Ans:
- Securing a wireless network involves implementing strong encryption, using WPA3 protocols, and configuring robust authentication mechanisms.
- Additionally, regular monitoring for unauthorized access and firmware updates on wireless devices are crucial.
- Addressing these challenges ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over wireless networks, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
51. Explain the concept of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) and its role in network security.
Ans:
- Establishes encrypted connections over untrusted networks.
- Ensures confidentiality and integrity of transmitted data.
- Facilitates secure communication for remote access.
- Mitigates the risk of eavesdropping and data interception.
- Enhances overall privacy and security of network communications.
52. What is a protocol defined as?
Ans:
A protocol is a set of guidelines and customs that control how data is sent between connected devices. To provide standardized communication, it specifies how data is prepared, transferred, received, and acknowledged. Protocols create the foundation for smooth system-to-system communication, enabling effective and error-free data transfer over a network. They are essential to the correct operation and interoperability of different networking components.
53. Could you enumerate the OSI model’s several layers?
Ans:
- Physical Layer: Describes the hardware properties and deals with the actual connections between devices.
- Data Link Layer: Oversees error detection and correction while ensuring the dependable transfer of data frames between devices connected to the same network.
- Network Layer: This layer facilitates end-to-end communication by concentrating on the logical addressing and packet routing between various networks.
- Transport Layer: Controls flow control and retransmission, and guarantees dependable, error-checked, and systematic data transfer between devices.
- The session layer allows synchronization and data sharing across programs by managing and creating sessions, or connections.
- Presentation Layer: Manages data compression, encryption, and formatting while translating information between the application layer and the lower levels.
- Application Layer: Enables data interchange and communication between software entities by directly providing network services to end users and apps.
54. Could you describe what pipelining is all about?
Ans:
Pipelining is a processing technique where multiple tasks are overlapped in a sequential manner to improve overall efficiency and throughput. In computing, it involves breaking down a task into smaller stages and allowing each stage to operate concurrently, reducing idle time and increasing the overall speed of execution.
55. What distinguishes switches from hubs?
Ans:
- Switches are different from hubs in that they forward data selectively depending on MAC addresses while operating at the OSI model’s data connection layer. By transferring data exclusively to the designated receiver, switches may effectively regulate network traffic and lessen congestion.
- Hubs on the other hand, operate at the physical layer and broadcast data to all connected devices, lacking the ability to make intelligent forwarding decisions. Switches offer improved performance and security compared to hubs in modern networking environments.
56. Which OSI model layers are referred to as network support layers?
Ans:
The OSI model layers referred to as network support layers are the Physical layer and the Data Link layer. These layers focus on the physical and data link aspects of network communication, including the transmission of raw data over the physical medium (Physical layer) and the framing and addressing of data at the link layer (Data Link layer). They provide the foundational support for higher-layer protocols and ensure the reliable transmission of data within the network.
57. In the context of networking, what does RIP stand for?
Ans:
In networking, RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol. It is a dynamic routing protocol used to convey information about network routes among routers. RIP helps routers make informed decisions about the most efficient paths for data transmission within a network.
58. What elements can affect a network’s performance?.
Ans:
Several elements can impact a network’s performance, including bandwidth limitations, network congestion, latency, packet loss, and the overall health of network devices. These factors collectively influence the speed, reliability, and efficiency of data transmission within the network.
59. In what ways are wired and wireless LANs different?
Ans:
Wired LANs utilize physical cables for connectivity, offering reliable and high-speed data transfer. In contrast, wireless LANs rely on radio waves for communication, providing greater flexibility and mobility but potentially lower data transfer speeds compared to wired counterparts.
60. In IP packets, what function does TCP serve?
Ans:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) in IP packets serves the crucial role of ensuring reliable and ordered communication.
- It manages the segmentation, acknowledgment, and retransmission of data segments, ensuring that data is delivered accurately and in the correct order between devices in a network.
61. Can you name the different kinds of mistakes that can happen when sending data across a network?
Ans:
Various kinds of faults that may occur when sending data transmission across a network include noise, which is random interference affecting signal quality; attenuation, the loss of signal strength over distance; distortion, which alters the signal’s waveform; and interference, where signals from other sources disrupt communication, impacting data integrity.
62. What does ALOHA mean in networking?
Ans:
- In networking, ALOHA refers to a network protocol developed for efficient communication between multiple users and a central computer.
- It allows users to transmit data over a shared communication channel, but it introduces the possibility of collisions when two or more users attempt to transmit simultaneously.
- ALOHA laid the foundation for multiple access protocols in computer networks.
63. What methods are commonly used for user authentication?
Ans:
User authentication methods include passwords, biometrics, smart cards, and two-factor authentication. These methods verify the identity of users accessing a system or network.
64. Could you explain what IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) is in network security?
Ans:
IPS, or Intrusion Prevention System, is a network security technology that actively monitors and analyzes network traffic for potential security threats. It aims to detect and prevent unauthorized access or malicious activities in real-time.
65. What potential consequences might an organization face due to a network security attack?
Ans:
The potential consequences of a network security attack for an organization can include data breaches, financial losses, damage to reputation, legal ramifications, and disruptions to normal business operations.
These consequences can have long-lasting and severe impacts on the affected organization.
66. Why are Administrator Privileges necessary when attempting to install a download?
Ans:
Administrator Privileges refer to elevated permissions that allow users to make system-wide changes. They are required during installations to modify system files and settings, ensuring that the user has the necessary control to make changes to the system.
67. What is network encryption, and how does it function to secure data transmission?
Ans:
- Network encryption involves encoding data to prevent unauthorized access during transmission.
- It works by converting plaintext into ciphertext using encryption algorithms.
- This safeguards sensitive information from being intercepted or manipulated by unauthorized parties.
68. Can you define the CIA Triad in the context of information security?
Ans:
The CIA Triad in information security stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It is a foundational concept emphasizing the need to protect data from unauthorized access (Confidentiality), maintain data accuracy and consistency (Integrity), and ensure data accessibility when needed (Availability).
69. What is a UTM (Unified Threat Management) firewall?
Ans:
A UTM (Unified Threat Management) firewall integrates multiple security features into a single device or service. It typically includes functions such as firewall, antivirus, intrusion detection and prevention, VPN, and content filtering to provide comprehensive security.
70. How would you describe Stateful Inspection in the realm of network security?
Ans:
- With the use of context-based decision-making and connection state monitoring, Stateful Inspection is a firewall technique.
- It improves security by comprehending the communication context and monitoring the status of network connections, permitting or prohibiting traffic depending on the state information.
71.Why does Active FTP encounter issues with network firewalls?
Ans:
Active FTP encounters issues with network firewalls because it involves two separate data connections, which can create challenges for firewalls configured to allow only specific types of connections. Passive FTP is often used as an alternative to overcome these firewall compatibility issues.
72. What is the meaning of a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack?
Ans:
DDoS attack is when a target system or network is overloaded with traffic from several infected machines, disrupting regular operations. Making the target inaccessible to its intended consumers is the aim.
73. Describe ransomware.
Ans:
Malicious malware known as ransomware encrypts user files or the system as a whole, making it impossible for users to access them. Attackers offer to provide the decryption key and provide access to the victim’s data in return for a ransom, typically in cryptocurrency.
74. How is ransomware implemented?
Ans:
- Ransomware is typically implemented through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or compromised websites.
- Once a user interacts with the infected content, the ransomware is activated, encrypting files on the victim’s device or network.
75. Could you list a few distinct kinds of ransomware?
Ans:
Some distinct types of ransomware include WannaCry, CryptoLocker, Locky, and Ryuk. Each variant may have unique characteristics, encryption methods, or targeted vulnerabilities.
76. What Is Malware?
Ans:
Malware, an acronym for malicious software, is any program that is intentionally created to do harm, exploit, or compromise networks, user data, or computer systems. It includes a broad spectrum of dangers, including trojans, worms, viruses, and ransomware.
77. In networking, what is access control?
Ans:
The process of controlling and limiting user access to resources, systems, or information is known as access control in networking. It entails creating and implementing rules to control who has access to what areas of a network, maintaining security, and thwarting illegal access.
78. In networking, what is application security?
Ans:
- Application security in networking refers to putting safeguards in place to shield software programmes from dangers and weaknesses.
- This entails using authentication techniques to prevent unwanted access, updating often, and adhering to secure code standards.
79. What kinds of phishing assaults are there?
Ans:
- Phishing attacks can take many different forms, such as spear phishing, in which attackers target particular people or organizations, and vishing, in which targets are tricked via voice contact.
- Other forms include pharming, which sends people to phony websites in order to obtain sensitive data, and smishing, which uses SMS texts.
80. What varieties of VPNs are there?
Ans:
- There are several types of virtual private networks (VPNs), such as site-to-site VPNs that link whole networks together via the internet and remote access VPNs that let users connect to a private network from a distance.
- There are also IPsec VPNs, which utilize IPsec protocols for authentication and encryption, and SSL VPNs, which use SSL/TLS protocols for secure communications.
81. What is the principle behind Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) in enhancing network security?
Ans:
By requesting two forms of identity from users before allowing access, Two-Factor Authentication further strengthens security. Usually, this includes both something the person owns (like a mobile device for receiving authentication codes) and something they know (like a password).
82. Explain the concept of a firewall and how it contributes to network security?
Ans:
- Firewalls are a kind of network security technology that monitor and manage incoming and outgoing network traffic in compliance with pre-established security policies.
- It prevents potential assaults and unauthorized access by acting as a barrier between a trustworthy internal network and a questionable external network.
83. What is the purpose of an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) in network security?
Ans:
An intrusion detection system focuses on system and/or network activity to look for malicious activity or infringements of policies. When it detects suspicious behavior, it helps to identify and respond to security problems by generating alerts or performing specified actions.
84. How does a Virtual Private Network (VPN) enhance the security of data transmitted over a network?
Ans:
- By encrypting data being transferred across a network, a VPN creates a safe tunnel via which devices may communicate.
- Secure communication is ensured and sensitive information is shielded from eavesdropping, especially while using public networks.
85. What role does a Certificate Authority (CA) play in network security, particularly in the context of SSL/TLS?
Ans:
- A Certificate Authority issues digital certificates that verify the legitimacy of entities in a network, ensuring secure communication.
- In SSL/TLS protocols, CAs authenticate the identities of websites, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks and ensuring encrypted connections.
86. How does Network Address Translation (NAT) contribute to network security?
Ans:
NAT hides internal IP addresses by translating them into a single external IP address. This adds a layer of security by obfuscating internal network structures, making it more challenging for external threats to identify and target specific devices.
87. What is the role of a Proxy Server in network security, and how does it function?
Ans:
A mediator between client devices and the internet is a proxy server. Through its barrier function and its inspection and filtering of incoming and outgoing communications, it improves security. Moreover, material caching can enhance speed and lower the possibility of direct assaults.
88. How does a Denial of Service (DoS) attack differ from a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack?
Ans:
In a DoS attack, a single source attempts to overwhelm a target with excessive traffic, disrupting its services.
- In a DoS attack, a single source attempts to overwhelm a target with excessive traffic, disrupting its services.
- A DDoS attack involves multiple sources coordinating simultaneous attacks, making it more challenging to mitigate and potentially causing more severe disruptions.
89. What is the purpose of Network Segmentation, and how does it enhance network security?
Ans:
The technique of splitting a network into distinct areas to control and restrict the spread of potential security threats is known as network segmentation. It lessens the impact of a security breach and enhances network security overall by limiting an attacker’s capacity to move laterally.
90. How can Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems contribute to network security?
Ans:
SIEM systems collect and analyze log data from various network sources to detect and respond to security incidents. They provide real-time monitoring, correlation of events, and alerting, helping organizations identify and mitigate potential security threats promptly.






