
An organisation’s capacity to identify, address, and mitigate cybersecurity threats can be improved with the help of ArcSight, a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) solution. In order to provide a centralised platform for monitoring and correlating security events in real-time, Micro Focus developed ArcSight, which ingests and analyses massive amounts of data from diverse sources, including logs, network traffic, and security events. Because of its sophisticated analytics and correlation capabilities, security experts can more effectively and proactively respond to cyber threats by identifying and prioritising possible security incidents. By providing a unified and customizable view of security-related activities, supporting compliance management, and promoting quick incident response, ArcSight is essential in bolstering an organisation’s overall cybersecurity posture.
1. What is ArcSight?
Ans:
ArcSight is a security information and event management (SIEM) solution developed by ArcSight, a subsidiary of Micro Focus. It helps organisations analyse and correlate data from various security events to detect and respond to security threats.
2. Explain the main components of ArcSight SIEM.
Ans:
ArcSight SIEM comprises various components, including:
Logger: A centralised log management system.
Connector Framework: Connects various data sources to ArcSight.
ArcSight SmartConnectors:Collect and normalise log data.
ArcSight ESM (Enterprise Security Manager): Correlates and analyses events to identify security threats.
3. What is the purpose of ArcSight Logger?
Ans:
- ArcSight Logger is a centralised log management system that collects, stores, and indexes log data from various sources.
- It provides long-term storage and retrieval of log data for compliance, forensic analysis, and threat detection.
4. How does ArcSight ESM correlate security events?
Ans:
ArcSight ESM correlates security events by analysing data from various sources, applying correlation rules, and identifying patterns or sequences of events that may indicate a security threat. It uses correlation rules to generate meaningful alerts and incidents.
5. Explain the role of ArcSight SmartConnectors.
Ans:
ArcSight SmartConnectors collect log data from diverse sources, normalise it into a common format, and then forward it to ArcSight Logger or ArcSight ESM for analysis. SmartConnectors support a wide range of devices and applications.
6. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Flex Connector framework?
Ans:
The FlexConnector framework is used to create custom connectors for devices that are not supported by out-of-the-box SmartConnectors. It allows organisations to tailor connectors to specific log sources and formats.
7. How does ArcSight help in threat detection?
Ans:
ArcSight aids in threat detection by correlating and analysing security events in real-time. It identifies patterns, anomalies, and suspicious activities across the IT environment, allowing security teams to detect and respond to potential threats promptly.
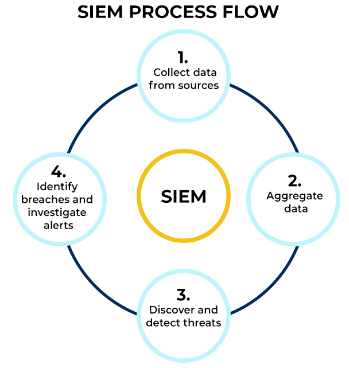
8. Explain process flow of ArcSight SIEM?
Ans:
Process flow of ArcSight SIEM:
Security Event Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and analysis of security events.
Incident Response: Rapid identification and response to security incidents.
Forensic Analysis: Investigation and analysis of historical log data.
Compliance Reporting: Generating reports for regulatory compliance.
9. How does ArcSight handle log data normalisation?
Ans:
ArcSight normalises log data using SmartConnectors, which convert logs from different sources into a standardised format. Normalisation ensures consistent data representation, making it easier to correlate and analyse events.
10. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Active Channel feature?
Ans:
ArcSight Active Channels provide a customizable dashboard within the ArcSight Console. They allow users to create and configure dashboards to monitor specific security events, trends, and key performance indicators.
11. Explain the difference between a rule and a filter in ArcSight ESM.
Ans:
| Feature | Rule | Filter | |
| Purpose |
Finds events and starts acting upon them |
Focuses events for examination | |
| Function | Conditions of function for correlation of events | Standards for choosing an event | |
| Event Selection | Choice of Event Selects particular events to be inclusive | Exclusive: eliminates undesirable occurrences | |
| Trigger Action |
TriggerSets in motion when two events coincide |
does not cause a reaction |
12. How can ArcSight be integrated with other security tools?
Ans:
ArcSight can be integrated with other security tools using various methods, including API integration, custom connectors, and third-party integrations. Common integration points include firewalls, antivirus solutions, and incident response platforms.
13. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Active Lists feature?
Ans:
ArcSight Active Lists are dynamic lists used to store and manage sets of values. They are often used in correlation rules and filters to define conditions based on dynamic lists of entities, such as IP addresses or usernames.
14. Explain the concept of ArcSight dashboards.
Ans:
ArcSight dashboards are visual representations of security data, events, and trends. They provide a graphical overview of the security posture and can be customised to display key metrics, charts, and tables relevant to the organisation’s security needs.
15. How does ArcSight support compliance reporting?
Ans:
- ArcSight supports compliance reporting by providing pre-defined reports and dashboards tailored to various compliance standards, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
- It allows organisations to generate reports demonstrating adherence to regulatory requirements.
16. What is the ArcSight Command Center?
Ans:
The ArcSight Command Center is a centralised management interface for overseeing multiple ArcSight environments. It provides a consolidated view of security events and allows administrators to manage policies and configurations across distributed instances.
17. Explain the role of the ArcSight Risk Manager.
Ans:
ArcSight Risk Manager is a component that provides risk-based prioritisation of security events. It assesses the impact and likelihood of security incidents, helping organisations prioritise and respond to the most critical threats.
18. How does ArcSight handle log data encryption?
Ans:
ArcSight provides options for encrypting log data during transmission between components, such as between SmartConnectors and Logger. Encryption ensures the confidentiality and integrity of log data in transit.
19. What are Watchlists in ArcSight, and how are they used?
Ans:
Watchlists in ArcSight are user-defined lists of entities, such as IP addresses or usernames, that security teams want to monitor closely. Watchlists can be used in correlation rules and filters to trigger alerts based on specific entities.
20. Explain the concept of ArcSight Active Channels.
Ans:
ArcSight Active Channels are real-time, customizable dashboards within the ArcSight Console. They allow users to create and configure dashboards to monitor specific security events, trends, and key performance indicators.
21. How does ArcSight handle multi-tenancy?
Ans:
ArcSight allows multi-tenancy through the use of ArcSight Command Center and the management of multiple ArcSight environments from a centralised interface. Each tenant or environment can have its own policies, configurations, and data.
22. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Identity View module?
Ans:
ArcSight IdentityView is a module that provides identity-centric visibility into security events. It helps organisations monitor and analyse user activities, detect anomalies, and enhance security by focusing on user behaviour.
23. How does ArcSight support the integration of threat intelligence feeds?
Ans:
ArcSight can integrate threat intelligence feeds using the ArcSight Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP) or by customising connectors. Threat intelligence feeds enhance the ability to correlate events with known threats and indicators of compromise.
24. Explain the role of the ArcSight ArcMC (ArcSight Management Center).
Ans:
The ArcSight Management Center is used to manage ArcSight environments centrally. It provides a unified interface for configuration, policy management, and monitoring of multiple ArcSight components.
25. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Integration Package for ServiceNow?
Ans:
- The ArcSight Integration Package for ServiceNow allows organisations to integrate ArcSight with the ServiceNow platform for incident response and ticketing.
- It facilitates the automatic creation and updating of incidents in ServiceNow based on ArcSight alerts.
26. How does ArcSight handle log data parsing and categorization?
Ans:
ArcSight SmartConnectors are responsible for parsing and categorising log data. They use predefined parsing rules to extract relevant information from logs and normalise it into a common format for further analysis.
27. What is the significance of ArcSight Correlation Searches?
Ans:
ArcSight Correlation Searches are pre-defined correlation rules that help organisations identify specific threat patterns or attack scenarios. They provide a starting point for building customised correlation rules based on known threats.
28. How can ArcSight be used in a threat hunting scenario?
Ans:
ArcSight can be used in threat hunting by allowing security analysts to explore and analyse security data for anomalies, patterns, or indicators of compromise that may not be covered by pre-defined correlation rules.
29. What is ArcSight Investigate, and how does it enhance security analysis?
Ans:
ArcSight Investigate is a module that provides advanced search and investigation capabilities. It allows security analysts to conduct in-depth analysis, explore relationships between events, and perform forensic investigations.
30. Explain the role of ArcSight Recon in threat detection.
Ans:
- ArcSight Recon is a module that focuses on real-time threat detection and prioritisation.
- It helps organisations identify and respond to high-risk threats by leveraging analytics and machine learning.
31. How does ArcSight handle data retention and archiving?
Ans:
ArcSight Logger provides long-term storage and archiving of log data. Administrators can configure retention policies to define how long data should be retained before archiving or purging.
32. What is the purpose of the ArcSight Compliance Insight Package?
Ans:
The ArcSight Compliance Insight Package provides pre-built content and reports tailored to specific regulatory compliance standards. It simplifies the process of demonstrating compliance by offering predefined compliance-focused reports.
33. How can ArcSight assist in incident response?
Ans:
- ArcSight aids in incident response by providing real-time alerts, correlation of events, and detailed analysis of security incidents.
- It helps security teams identify, investigate, and respond to incidents promptly.
34. What is the role of ArcSight RiskIQ in security operations?
Ans:
ArcSight RiskIQ is a module that provides risk-based prioritisation of security events. It assesses the risk associated with security incidents, allowing organisations to focus resources on the most critical threats.
35. Explain the concept of ArcSight Use Case Management.
Ans:
ArcSight Use Case Management is a feature that allows organisations to define, manage, and deploy security use cases within the ArcSight ecosystem. It helps in organising and implementing specific security scenarios and detection logic.
36. How does ArcSight support the analysis of user behaviour?
Ans:
ArcSight IdentityView is specifically designed to provide visibility into user behaviour. It allows organisations to monitor and analyse user activities, detect anomalies, and enhance security by focusing on user-centric insights.
37. What is the role of the ArcSight AssetView module?
Ans:
ArcSight AssetView provides visibility into the organisation’s assets and their associated security events. It helps security teams understand the context of events by providing information about assets involved in security incidents.
38. How can ArcSight help in the detection of insider threats?
Ans:
ArcSight can assist in detecting insider threats by monitoring user activities, identifying anomalies in behaviour, and correlating events that may indicate unauthorised or malicious activities conducted by insiders.
39. Explain the concept of ArcSight Playbooks.
Ans:
ArcSight Playbooks are predefined workflows or sequences of actions that guide security analysts through the process of responding to specific security incidents. They help standardise and automate incident response procedures.
40. How does ArcSight support the integration of threat feeds for threat intelligence?
Ans:
ArcSight supports the integration of threat intelligence feeds by allowing organisations to connect external threat feeds to the ArcSight ecosystem. This integration enhances the ability to correlate events with known threats and indicators.
41. What is the ArcSight User Behaviour Analytics (UBA) module?
Ans:
The ArcSight User Behavior Analytics module analyses user behaviour patterns to identify potential insider threats or compromised accounts. It leverages machine learning and statistical models to detect deviations from normal user behaviour.
42. How can organisations scale their ArcSight infrastructure for large deployments?
Ans:
- Organisations can scale their ArcSight infrastructure by deploying multiple ArcSight components, such as Logger and ESM, in a distributed manner.
- Load balancing and redundancy strategies can also be implemented for high availability.
43. Explain the role of ArcSight Command Center in managing distributed environments.
Ans:
ArcSight Command Center provides a centralised management interface for overseeing and managing multiple ArcSight environments.It facilitates the coordination of policies, configurations, and updates across distributed instances.
44. How does ArcSight support custom content creation for specific security use cases?
Ans:
ArcSight allows custom content creation through the use of rules, filters, dashboards, and reports. Organisations can tailor ArcSight to their specific security use cases by defining custom correlation rules and content.
45. What are the key considerations for ArcSight deployment in a cloud environment?
Ans:
When deploying ArcSight in a cloud environment, considerations include proper network connectivity, secure communication between components, data privacy and compliance, and scalability to accommodate dynamic workloads.
46. Explain the role of ArcSight Connectors in the integration of third-party security tools.
Ans:
ArcSight Connectors facilitate the integration of third-party security tools by providing standardised interfaces for data ingestion. They enable the seamless flow of security event data from diverse sources into the ArcSight ecosystem.
47. How does ArcSight address compliance challenges in regulated industries?
Ans:
- ArcSight provides predefined compliance packages, reports, and dashboards tailored to specific regulatory standards.
- It assists organisations in meeting compliance requirements by offering tools for monitoring, reporting, and auditing security events.
48. What is the ArcSight Common Event Format (CEF), and how is it used?
Ans:
ArcSight Common Event Format (CEF) is a standard format for log and event data. It simplifies the integration of events from various sources into the ArcSight ecosystem, ensuring consistent data representation.
49. How does ArcSight support threat intelligence sharing with external organisations?
Ans:
- ArcSight can support threat intelligence sharing by integrating with Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) and participating in information-sharing communities.
- It allows organisations to benefit from collective threat intelligence.
50. What are the key security challenges that ArcSight helps organisations address?
Ans:
ArcSight helps organisations address key security challenges such as:
Threat Detection: Identifying and responding to security threats.
Incident Response: Rapid response to security incidents.
Compliance: Meeting regulatory.
51. How can ArcSight integrate with external systems using APIs?
Ans:
Use of Web Services Connectors: ArcSight provides Web Services connectors for popular APIs
Automation through Scripts:Utilise scripts to automate data transfer between ArcSight and external systems.
Real-time or Batch Integration:Decide whether real-time or batch integration is appropriate based on the use case.
52. Explain the role of ArcSight FlexConnectors in handling custom log formats.
Ans:
Custom Log Format Handling:FlexConnectors are crucial for handling custom log formats not covered by pre-built connectors.
FlexConnector Architecture:FlexConnectors consist of a parser, normalizer, and mapping components.
Configuration and Customization:ArcSight FlexConnectors can be configured to handle specific log sources.
53. Demonstrate how you would use aggregation functions in AQL for trend analysis.
Ans:
Trend Analysis with AQL:Use the COUNT function to analyse the frequency of events over time.
Time-Based Aggregation:Utilise time-based aggregation to identify trends over hours, days, or weeks.
Combining Aggregation Functions:Combine multiple aggregation functions to gain comprehensive insights.
54. How can you implement custom correlation using ArcSight ESM?
Ans:
Custom correlation in ArcSight ESM involves creating correlation rules tailored to an organisation’s specific security requirements. The Rule Editor allows defining conditions, filters, and actions for custom event correlation.
55. Explain the role of ArcSight User Roles and Permissions.
Ans:
ArcSight User Roles determine the level of access and permissions for users within the ArcSight environment. Admin, Analyst, and Operator roles can be configured to control actions such as rule modification, data querying, and system configuration.
56. What steps are involved in adding a new user in ArcSight ESM?
Ans:
New users can be added through the ArcSight Console by navigating to the user management section. The process includes specifying user details, assigning roles, and configuring access permissions based on job responsibilities.
57. Discuss the scalability considerations for ArcSight ESM architecture.
Ans:
Scalability in ArcSight ESM involves proper hardware sizing, load balancing, and distributed deployment of components such as SmartConnectors. Organisations should plan for growth and adjust resources accordingly to maintain optimal performance.
58. How does ArcSight handle failover and high availability in its architecture?
Ans:
ArcSight supports failover and high availability through redundant components such as SmartConnectors and managers. Clustering and load balancing configurations ensure continuous operation in the event of component failures.
59. What are the key elements to consider when designing an effective correlation rule?
Ans:
Effective correlation rules consider specific event conditions, time frames, and the relationships between events. Clear definitions of rule logic, actions, and exceptions contribute to the rule’s accuracy and relevance.
60. Explain the difference between a filter and a rule in ArcSight.
Ans:
A filter is a predefined condition used to narrow down the scope of events, while a rule in ArcSight involves specifying conditions and actions for event correlation. Filters are often used as components within correlation rules.
61. How can you use AQL to identify outliers or anomalies in log data?
Ans:
Threshold-based Anomaly Detection: Set thresholds based on historical data or expected behaviour.
Pattern Recognition:Use AQL queries to identify patterns that deviate from the norm.
Correlation and Contextual Analysis: Combine AQL queries with correlation rules to analyse contextual information.
62. Explain the process of creating a custom parser using ArcSight FlexConnector Toolkit.
Ans:
Steps for Creating a Custom Parser:Identify log format patterns and specify extraction rules in XML format.
Normalisation Process:Normalise extracted data to align with ArcSight’s data model.
Map to Common Event Format (CEF):Map normalised data to the Common Event Format for consistency.
63. How do you design and implement custom correlation rules?
Ans:
Identify Security Scenarios:Define specific security scenarios that require correlation analysis.
Gather Relevant Data:Identify the necessary data fields and sources required for correlation.
Design Correlation Logic:Develop correlation logic based on the identified security scenarios.
64. Explain the concept of Categorization and how it is applied in ArcSight ESM.
Ans:
Categorization Overview:Categorization in ArcSight ESM involves grouping events based on common characteristics.
Role of Categorization:Events are categorised based on predefined criteria such as severity, source, or type.
Custom Categorization:ArcSight allows the creation of custom categories to align with specific organisational needs.
65. How does ArcSight handle high-volume event scenarios?
Ans:
- Event Handling Mechanisms
- Scaling ArcSight Infrastructure
- Use of Load Balancers
- Retention and Archiving Policies
- Performance Tuning
66. Discuss the best practices for managing ArcSight content.
Ans:
- Naming Conventions
- Regular Content Review
- Collaboration and Training
- Optimization for Performance
67. How does ArcSight assist organisations in achieving regulatory compliance?
Ans:
ArcSight aids in compliance by providing robust log management, real-time monitoring, and reporting capabilities. Organisations can use ArcSight to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements through audit trails and compliance reports.
68. Discuss the role of ArcSight in GDPR compliance.
Ans:
ArcSight helps organisations comply with GDPR by facilitating the secure handling of personal data, monitoring data access, and providing tools for incident response in case of data breaches.
69. How can AQL be leveraged for threat intelligence integration in ArcSight?
Ans:
Threat intelligence feeds can be integrated into AQL queries to correlate events with known indicators of compromise (IOCs). Example: SELECT * FROM events, threat_intel WHERE event.srcIP = threat_intel.IP.
70 .Demonstrate the use of time-based AQL queries for trend analysis.
Ans:
SELECT AVG(value), MIN(value), MAX(value) FROM events WHERE deviceVendor = ‘Router’ GROUP BY time(1h); This query calculates the average, minimum, and maximum values of a specific field over a one-hour time window for router events.
71. How can ArcSight be utilised for threat hunting?
Ans:
- Threat Hunting in ArcSight
- Use of AQL Queries
- Behavioural Analysis
- Intelligence Integration
- Incident Simulation
72. Discuss strategies for optimising the performance of ArcSight ESM
Ans:
- Scalability Planning
- Resource Allocation
- Load Balancing
- Database Optimization
- Regular Maintenance
- Monitoring and Alerting
73. How does ArcSight assist organisations in achieving regulatory compliance?
Ans:
ArcSight aids in compliance by providing robust log management, real-time monitoring, and reporting capabilities. Organisations can use ArcSight to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements through audit trails and compliance reports.
74. Discuss the importance of ArcSight in the incident response process.
Ans:
ArcSight plays a crucial role in incident response by providing real-time alerts, contextual information, and historical data analysis. Security analysts use ArcSight to investigate and mitigate security incidents promptly.
75. How does ArcSight facilitate collaboration among security teams?
Ans:
ArcSight allows multiple analysts to work on the same case simultaneously, share investigation notes, and collaborate through the centralised incident console.
76. Explain the process of developing a custom FlexConnector.
Ans:
Custom FlexConnectors are developed using the FlexConnector Toolkit. The process involves defining log format details, creating parsing rules, and testing the connector to ensure accurate log data normalisation.
77. How can Flex Connectors be optimised for performance?
Ans:
Optimization involves streamlining parsing rules, reducing unnecessary field extractions, and implementing parallel processing where applicable. Regular performance testing ensures that FlexConnectors meet the demands of high-volume log sources.
78. How can ArcSight reports be customised to meet specific business requirements?
Ans:
ArcSight reports are customised by selecting the appropriate data fields, defining report parameters, and formatting the output. Custom reports can be scheduled for automatic generation and distribution.
79. Explain the concept of Watchlists in ArcSight and their applications.
Ans:
- Watchlists are used to monitor specific entities, such as IP addresses or usernames, for relevant events.
- Security teams can create and manage Watchlists to focus on events associated with entities of interest.
80. How can Watchlists be integrated with correlation rules for enhanced threat detection?
Ans:
Watchlists can be incorporated into correlation rules to trigger specific actions or alerts when events involve entities listed in the Watchlist. This enhances the ability to detect and respond to threats targeting specific assets.
81. Discuss best practices for maintaining high availability in an ArcSight deployment.
Ans:
Best practices include deploying redundant components, implementing load balancing, and regularly testing failover scenarios. Properly configured clustering ensures that critical ArcSight components remain available during system disruptions.
82. How can organisations effectively scale their ArcSight deployment to meet growing demands?
Ans:
Effective scaling involves assessing current and future needs, planning for hardware upgrades, and optimising the deployment architecture. Distributed deployment, load balancing, and proactive monitoring contribute to a scalable ArcSight environment.
83. What are the key considerations for reviewing and updating ArcSight rules regularly?
Ans:
Regular reviews involve assessing rule effectiveness, adjusting correlation logic, and incorporating changes in the threat landscape. Collaboration with security analysts and stakeholders ensures that rules remain aligned with organisational security goals.
84. Discuss strategies for maintaining the relevance of ArcSight reports over time.
Ans:
Strategies include periodic reviews of report criteria, adjusting parameters based on evolving business needs, and incorporating feedback from report consumers. Continuous improvement ensures that reports provide meaningful insights for decision-making.
85. How can ArcSight be integrated with a Security Orchestration
Ans:
Integration involves utilising ArcSight connectors or APIs to exchange information with the SOAR platform. This enables automated incident response actions based on ArcSight alerts and correlates data from multiple sources.
86. Discuss the benefits of integrating ArcSight with a SORE platform for incident response.
Ans:
Integration enhances the efficiency of incident response by automating repetitive tasks, orchestrating workflows, and ensuring a coordinated response across security tools. This results in faster threat containment and reduced manual effort.
87. Explain how ArcSight can be configured to detect advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Ans:
Configuring ArcSight for APT detection involves creating correlation rules that analyse patterns indicative of sophisticated attacks. Incorporating threat intelligence feeds, behavioural analytics, and anomaly detection enhances the platform’s capability to identify APTs.
88. How does ArcSight contribute to threat hunting activities within an organisation?
Ans:
ArcSight supports threat hunting by providing powerful query capabilities, correlation rules, and access to historical data. Threat hunters can use the platform to proactively search for indicators of compromise and uncover hidden threats.
89 .Discuss the considerations for integrating ArcSight with cloud-based log sources.
Ans:
Cloud integration involves deploying SmartConnectors in the cloud environment or utilising APIs to collect log data from cloud services. Organisations should ensure secure communication, proper authentication, and compliance with cloud provider guidelines.
90 .How can ArcSight be adapted for monitoring and securing hybrid cloud environments?
Ans:
Hybrid cloud monitoring involves configuring SmartConnectors to collect logs from both on-premises and cloud-based sources. Integration with cloud-native security services and adherence to cloud security best practices contribute to effective hybrid cloud security.






