
The powerful data integration tool SAP BODS, or SAP Business Objects Data Services, is made to make the process of extracting, converting, and loading (ETL) data across many systems as simple as possible. Efficient data transfer and transformation are facilitated by its extensive feature set for metadata management, data profiling, and data quality control. With its intuitive interface and robust features, SAP BODS enables businesses to guarantee data accessibility, correctness, and consistency, facilitating well-informed decision-making and propelling achievement.
1. What is SAP BODS and its primary use?
Ans:
SAP BODS (BusinessObjects Data Services) is a data integration tool for extracting, transforming, and loading data quality, data profiling, and data processing. It assists with data extraction from several sources, data transformation in accordance with business needs, and data loading into target systems. SAP BODS provides robust features for data cleansing and enrichment, ensuring that the data is accurate and ready for analysis or reporting.
2. Explain the architecture of SAP BODS.
Ans:
The architecture of SAP BODS consists of the Data Services Designer for designing ETL processes, the Job Server for executing jobs, Repositories (Local and Central) for storing metadata, the Data Integrator for handling data extraction, transformation, and loading, and the Management Console for monitoring and scheduling jobs. This comprehensive architecture enables seamless collaboration between development, execution, and management components, enhancing overall efficiency in data integration projects.
3. What are the key components of SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Designer: An interface for creating, managing, and executing data integration and transformation jobs.
- Job Server: Executes the jobs designed by the Designer.
- Repository: Stores metadata, job definitions, and configuration details.
- Management Console: Web-based tool for monitoring, scheduling, and managing data services operations.
- Data Integrator: Enables data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes.
4. What is a Data Flow in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Data Flow in SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) is a visual representation of the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process. It shows how data moves from source to destination through various transformations, enabling the efficient design, execution, and monitoring of data integration tasks.
5. What is the difference between Batch Processing and Real-time Processing in SAP BODS?
Ans:
| Feature | Batch Processing | Real-time Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Timing | Scheduled intervals or batches | Immediate or near-immediate upon data availability |
| Data Handling | Processes data in bulk, accumulated over a period | Processes data as it becomes available |
| Response Time | Response time may vary depending on batch schedule | Immediate response to changes in data |
| Suitability | Suited for handling large volumes of data efficiently | Ideal for scenarios requiring instant data availability |
| Decision-Making | Suitable for scenarios where delayed data processing is acceptable | Ideal for scenarios requiring instant data availability |
6. What are Workflows in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Workflows in SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) are a set of interconnected tasks designed to manage and control the data flow within a data integration project. They define the execution order and dependencies of dataflows, allowing for efficient data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes. Workflows enable error handling, conditional execution, and parallel processing.
7. What is a Data Store in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS), a Data Store is a connection that facilitates access to data in various sources like databases, applications, or flat files. It defines the location, type, and access credentials for these data sources.
8. Explain the concept of a Repository in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- In SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services), a repository is a type of central database used to hold metadata for ETL operations.
- There are three types: central, Local, and Profiler. The central Repository facilitates version control and collaboration among developers.
- The Local Repository contains project-specific objects for development.
- The Profiler Repository holds profiling data for data quality analysis.
9. What types of repositories exist in SAP BODS?
Ans:
The three types of repositories:
- Local Repository (stores metadata specific to individual developers).
- Central Repository (supports version control and collaboration among multiple developers).
- Profiler Repository (stores profiling data).
10. What is a Project in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, a Project is a container for organizing and managing development objects, such as data flows and workflows. It helps streamline development efforts by grouping related components and facilitating collaboration among team members. Projects in SAP BODS support version control and documentation, ensuring that development processes are well-documented and maintainable over time.
11. What is a Local Repository in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP Business Objects Data Services (BODS), a Local Repository is a storage location where metadata, such as data flows, jobs, and projects, are stored. It is specific to an individual developer or a particular development environment, allowing for version control and management of objects independently. Local Repositories are used for development and testing before moving objects to the central or production Repository.
12. What is a Central Repository in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- In SAP BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS), a Central Repository is a shared storage location that facilitates collaborative development by allowing multiple users to manage, version, and share objects like projects, jobs, dataflows, and workflows.
- It ensures consistent development standards and supports team-based development by providing check-in/check-out functionality.
- The Repository enhances version control and enables reusability and governance of data integration assets.
13. How to create a new repository in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- To create a new repository in SAP BODS, Open Data Services Designer, navigate to `Local Object Library,` right-click on `Repositories,` select `New Repository,` fill in details, and click `Finish.`
- A new repository can be created using the Repository Manager tool in SAP BODS.
- To specify the database details and make the repository schema.
14. What is a Batch Job in SAP BODS?
Ans:
A Batch Job in SAP BODS is a scheduled or triggered process that automates data integration tasks and runs without user interaction. It executes predefined workflows to load, convert, and retrieve data from various sources into target systems. This automation not only improves efficiency but also ensures consistent and timely data processing, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs.
15. What is a Real-time Job in SAP BODS?
Ans:
A Real-time Job in SAP BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS) processes data instantly as it arrives, enabling immediate action based on the incoming data. It typically involves integrating data from various sources and transforming it in real time for reporting or operational use. This job type is crucial for applications requiring up-to-the-minute data accuracy and responsiveness. Real-time jobs utilize real-time services to trigger data processing whenever new data events occur.
16. How do users schedule a job in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Launch the Management Console, then choose the “Administrator” section.
- Select “Batch Job Configuration” and choose the job want to schedule.
- Click on “Schedule” and specify the desired schedule parameters (e.g., start time, frequency).
- Save the schedule.
- Monitor the job execution in the “Job Monitor” section.
17. Explain the concept of Transforms in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- In SAP BODS (BusinessObjects Data Services), Transforms are built-in functions that manipulate data within a data flow.
- They perform tasks such as filtering, cleansing, aggregating, and merging data.
- Transforms can be categorized into different types, including data integration, data quality, and platform transforms.
- They are essential for customizing and optimizing data processing to meet specific business needs.
18. What are the different types of transformations available in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS (BusinessObjects Data Services), various types of transformations are available, including Query, Case, Merge, Pivot, and Table Comparison. These transformations enable users to manipulate, cleanse, and integrate data from different sources efficiently. They facilitate tasks such as data filtering, aggregation, joining, and comparison, ensuring data quality and consistency in the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process.
19. What is a Query Transform?
Ans:
A Query Transform is a process of altering the structure or content of a search query to improve its effectiveness in retrieving relevant information. It involves modifying keywords, applying filters, or adjusting parameters to refine search results. Query Transforms are commonly used in information retrieval systems, search engines, and data analysis tools to enhance user experience and accuracy of results.
20. What is the Map Operation Transform used for?
Ans:
- The Operational Transformation (OT) is a technique used to synchronize concurrent edits made to a shared document or data structure.
- It ensures consistency and resolves conflicts in real-time collaborative editing systems such as Google Docs.
- OT enables users to edit the same document simultaneously while preserving the order of their edits and maintaining coherence across all versions.
- It’s beneficial for applications requiring real-time collaboration and synchronization among multiple users.
21. How to connect to different data sources in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, connect to different data sources using Datastore configurations. These configurations include relational databases, flat files, XML files, and more. To define connections via JDBC, ODBC, or native drivers depending on the data source type. This flexibility allows for seamless integration across diverse environments, enabling organizations to consolidate and manipulate data from multiple sources effectively.
22. Explain how SAP BODS handles data extraction.
Ans:
SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) extracts data utilizing a range of techniques, including direct database access, web services, and file ingestion. It employs a graphical interface for designing extraction jobs, allowing users to specify source connections and extraction logic. BODS utilizes parallel processing to optimize extraction performance and supports incremental extraction for efficient data updates.
23. Define what a Job in SAP BODS is.
Ans:
- In SAP Business Objects Data Services (BODS), a Job is a planned series of actions intended to perform data integration, transformation, and loading operations.
- It includes workflows and data flows to extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from various sources to target systems.
- Jobs are created, scheduled, and monitored within the BODS environment to automate data processing tasks. They can handle complex data manipulation and are essentia
24. How do users perform data validation in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- In SAP BODS, data validation is performed using various techniques such as data profiling, data quality transforms, and custom validation scripts.
- This includes identifying and correcting inconsistencies, duplicates, and missing data.
- BODS offers built-in functionalities to validate data against predefined rules and constraints.
25. What does SAP BODS support the different data types?
Ans:
SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) supports date, time, binary, numeric, and alphanumeric data types. It also supports specialized kinds like XML, JSON, and spatial data (GIS). SAP BODS’s strong data integration capabilities enable it to manage a variety of data formats and structures, guaranteeing interoperability with a broad spectrum of systems and applications.
26. How do users handle data transformation in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Data transformation in SAP BODS involves mapping, cleansing, and enriching data. It’s done using transforms like Query, Case, and Map_Operation, ensuring data quality and compatibility. Integration with various data sources simplifies this process. These transformations not only enhance data accuracy but also enable the alignment of data with business requirements, facilitating more insightful analytics and reporting.
27. What is Data Cleansing in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- In SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services), data cleaning entails finding and fixing mistakes or inconsistencies in data sets.
- In order to guarantee data accuracy and dependability, it includes procedures like data validation, standardization, and de-duplication.
- SAP BODS offers features and methods for effectively cleaning data and enhancing data quality for more informed decision-making.
- Repetitive or erroneous data is found and corrected by automated workflows and rules, improving overall data integrity.
28. What are the common Data Quality Transforms in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- In SAP BODS, standardization, validation, enrichment, deduplication, and matching are examples of typical data quality transforms.
- Throughout the organization, these transformations guarantee data relevance, accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
- While validation compares data to predetermined rules, standardization harmonizes data types.
- Data enrichment adds new information to the data. Duplicate records are removed by deduplication, and related or similar data entries are found for analysis or consolidation through matching.
29. Explain the Address Cleanse Transform.
Ans:
The Address Cleanse Transform standardizes and corrects address data, ensuring consistency and accuracy. It rectifies formatting errors, validates addresses against databases, and enhances data quality for improved analytics and operations. By using this transform, organizations can reduce mailing errors and improve customer communication, ultimately leading to better service delivery and operational efficiency.
30. How to manage data loading in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, standardization, validation, enrichment, deduplication, and matching are examples of typical data quality transforms. Throughout the organization, these transformations guarantee data relevance, accuracy, consistency, and completeness. While validation compares data to predetermined rules, standardization harmonizes data types. Data enrichment adds new information to the data.
31. What are a Source Table and Target Table in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- The table or data source from which data is taken is referred to as a “Source Table” in SAP BODS.
- It could come from any source, including a flat file or database table.
- In contrast, the extracted data is loaded or placed in the Target Table following transformation.
- In SAP BODS, these tables are essential to the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data integration procedures.
32. How to use the Data Transfer Transform?
Ans:
- One effective tool for effectively converting data between formats is the Data Transfer Transform (DTT).
- It simplifies the process of moving data between apps or platforms.
- Users designate any required mapping or transformation rules in addition to the source and target formats.
- DTT guarantees consistent and seamless data movement while preserving integrity.
- For businesses juggling a variety of data formats and integration needs, it’s a valuable tool.
33. What is a Lookup Transform?
Ans:
In order to map values from one dataset to another based on a common key, data processing techniques such as lookup transforms are utilized. Database operations and data integration tasks are frequent uses for it. With the purpose of enhancing or augmenting the original dataset, the transform looks for matching keys in a reference dataset and obtains those values.
34. How to handle slowly changing dimensions (SCD) in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Slowly changing dimensions (SCD) in SAP BODS are managed using either the Type 1 or Type 2 method. Type 2 keeps historical records, but Type 1 replaces current data with fresh values. Tools such as the Type 2 History Preserving Transform and the Key Generation Transform for surrogate keys are offered by BODS. More complicated SCD cases can also be handled using custom scripting.
35. What is the Hierarchy Flattening Transform?
Ans:
The Hierarchy Flattening Transform simplifies complex nested structures by converting them into a flat representation, reducing hierarchy depth. It’s often used in data processing to make information more accessible and manageable. This transformation facilitates easier analysis and reporting, allowing users to quickly derive insights from previously intricate data structures without losing essential information.
36. Explain how to use the Merge Transform.
Ans:
- Merge Transform combines data from two or more sources based on a shared key.
- In data processing, it’s used to join datasets horizontally. Specify keys to match records, and choose join type.
- Customize output columns and handle unmatched records as needed.
37. What is the Table Comparison Transform?
Ans:
- In data analysis, the Table Comparison Transform is a tool used to compare two tables and find similarities or differences.
- It entails comparing records according to predetermined standards and emphasizing differences.
- Data integration and database management procedures frequently use this strategy.
- It guarantees data accuracy across many sources or versions and facilitates the simplification of data reconciliation processes.
38. How to implement data aggregation in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, to implement data aggregation using the Aggregate transform. Drag the Aggregate transform into the data flow, specify group-by fields, and select the aggregation functions for desired fields like SUM, AVG, COUNT, etc. Once configured, the Aggregate transform processes the incoming data stream, producing summarized results based on the specified criteria.
39. What is a Data Profiler in SAP BODS?
Ans:
One tool used in SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) for analyzing and rating the quality of data in an organization’s systems is a data profiler. It looks for patterns in the data, spots anomalies, and offers insights about the integrity and structure of the data. It facilitates the processes of data transformation and purification as well as analyzing the properties of the data.
40. How do users handle errors in data processing with SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Try-catch blocks and error tables are two standard error-handling strategies used in SAP BODS to handle data processing problems.
- Error messages are logged and can be examined for debugging and troubleshooting purposes.
- Implementing validations and quality checks on data can also help reduce processing errors.
- For SAP BODS error handling to be effective, regular maintenance and monitoring are necessary.
41. What is a Parameter in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- A parameter in SAP BODS (BusinessObjects Data Services) is a placeholder or variable that allows dynamic values to be passed into jobs or workflows.
- It enables flexibility and reusability by allowing users to input values at runtime or during job execution.
- This dynamic approach ensures that the same data flow can be utilized across different scenarios and datasets without requiring extensive modifications.
- By facilitating parameterization, users can adapt their workflows to varying business needs and environments with ease.
42. How does one use Variables in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, variables are utilized in scripts, expressions, and transformations. They’re defined at the job or workflow level and can hold dynamic values for reuse across the job. They’re set using script functions or through parameters in transformations. This capability enhances the flexibility of data flows, allowing for more tailored processing and enabling users to respond quickly to changing data requirements during execution.
43. Explain the use of Scripts in SAP BODS.
Ans:
SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) scripts are used for validations, transformations, and bespoke data processing. They enable developers to implement sophisticated logic that is not possible with conventional BODS transformations. Languages like SQL, Python, or Perl can be used to write scripts, which offer more flexibility in data manipulation.
44. What is a Conditional Split Transform?
Ans:
A Conditional Split Transform in SAP BODS is used to route data rows to different outputs based on specified conditions. It allows users to define multiple conditions that determine how data is divided, enabling the processing of different subsets of data within the same data flow. This transform is particularly useful for implementing complex business logic and improving the efficiency of data processing by ensuring that relevant data is handled appropriately.
45. Explain how to implement a Data Pivot in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- To implement a Data Pivot in SAP BODS, use the Pivot Transform. Define keys, attributes, and measures. Select pivot columns and aggregate functions.
- Configure output options like row order and data distribution. Finally, execute the job for the pivot transformation.
46. What is the History Preserving Transform?
Ans:
- A data transformation method called the History Preserving Transform (HPT) is used in machine learning to preserve temporal dependencies in sequential data.
- The input data is encoded into a format that is appropriate for training models while maintaining the sequential structure of the data.
- When preprocessing activities involving time-series data or sequences are involved, HPT is especially helpful in preserving the temporal pattern integrity.
47. How to implement change data capture (CDC) in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Configure the Change Data Capture (CDC) parameters in source system before implementing CDC in SAP BODS. Next, use CDC objects like CDC tables, CDC functions, and CDC views to create CDC jobs in BODS Designer. Determine the CDC extraction techniques, map the source and target tables, and carry out the task. Lastly, look for inconsistencies or mistakes in the CDC procedure.
48. What is the Role of a Data Services Management Console?
Ans:
The Data Services Management Console in SAP BODS is a web-based interface that plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing data integration jobs. It provides real-time visibility into job execution statuses, allowing users to track running, completed, or failed jobs. It facilitates job scheduling for automated execution, offers tools for error handling and troubleshooting, and enables user management for secure collaboration.
49. How do users monitor jobs in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Users monitor jobs in SAP BODS through the Data Services Management Console, where they can view real-time status updates on job executions. The console provides detailed information on running, completed, and failed jobs, along with logs that highlight any errors or warnings. Users can access historical job performance data, track execution times, and review success or failure messages to diagnose issues.
50. Explain the concept of Metadata in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- Metadata in SAP BODS acts as a repository for storing crucial information related to data integration processes.
- This includes details about source and target data structures, transformations, mappings, and data flow definitions.
- Metadata facilitates efficient job design, execution, and maintenance by providing a centralized reference for all data integration assets.
51. What is the Data Quality Dashboard in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- The Data Quality Dashboard is a feature of SAP BODS that offers insights into various data quality metrics.
- It enables users to monitor data completeness, accuracy, consistency, and other quality attributes.
- By visualizing these metrics, organizations can assess data quality levels and identify areas for improvement within their data integration processes.
52. How does one perform Data Lineage analysis in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Data Lineage Analysis in SAP BODS involves tracing the flow of data from its source to its destination within data integration jobs. It helps users understand how data is transformed and manipulated throughout the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process. Data lineage analysis is valuable for documenting data flows, identifying dependencies, and performing impact analysis.
53. What is a Data Flow Audit?
Ans:
A Data Flow Audit in SAP BODS is a mechanism for tracking data movement and transformations within ETL jobs. It captures information about data changes, errors, and transformations applied during job execution. Data flow auditing is essential for ensuring data integrity, compliance with regulatory requirements, and troubleshooting data-related issues.
54. Explain how to implement data masking in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Data masking is a technique used to anonymize sensitive data during ETL processes.
- In SAP BODS, data masking can be implemented using transforms such as Masking, Encryption, or Hashing.
- This helps organizations protect sensitive information while ensuring that data remains usable for analytics or reporting purposes.
55. What are SAP BOD’s best practices for performance tuning?
Ans:
- SAP BODS performance tuning involves optimizing various aspects of data integration processes to improve efficiency and throughput.
- Best practices include optimizing SQL queries, leveraging push-down optimization, partitioning large tables, using parallel processing, and monitoring resource usage to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance.
56. How to handle large data volumes in SAP BODS?
Ans:
To handle large data volumes in SAP BODS effectively, users can employ several strategies. Batch processing can be used to divide datasets into smaller increments, while incremental loads allow for transferring only new or modified records since the last load. Utilizing parallel processing enables multiple jobs to run concurrently, maximizing system resources.
57. What is the purpose of the Data Services Job Server?
Ans:
The Data Services Job Server is a component of SAP BODS responsible for executing data integration jobs. It manages job scheduling, execution, and resource allocation to ensure efficient processing of data integration tasks. The Job Server plays a crucial role in automating data integration processes and maintaining job performance. It offers logging and error handling, enabling users to monitor job status and troubleshoot issues effectively.
58. How to configure the Job Server in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Configuring the Job Server in SAP BODS involves setting parameters and options that govern its behavior.
- This includes configuring settings such as maximum concurrent jobs, resource allocation for job execution, scheduling options, and other parameters relevant to job management and execution.
- The configuration of the Job Server ensures optimal performance and resource utilization within the SAP BODS environment.
59. What are the common errors in SAP BODS, and how to troubleshoot them?
Ans:
- Connectivity problems, data mapping inconsistencies, transformation mistakes, job scheduling conflicts, and memory allocation concerns are common failures in SAP BODS.
- Troubleshooting involves verifying data sources, examining mapping logic, examining transformation configurations, modifying work schedules, and optimizing memory allocation settings.
- Debugging tools and system log monitoring can also be used to identify and effectively fix problems.
60. How does one handle delta loads in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Change Data Capture (CDC) techniques are used in SAP BODS to handle delta loads, allowing users to extract only the data that has changed since the last load. This includes creating triggers or log-based CDC, defining CDC tables, and processing the delta data using BODS transformations. By simply sending small changes, delta loads save processing costs and guarantee effective data synchronization.
61. How do users integrate SAP BODS with SAP BW?
Ans:
- Configure a DataStore object in SAP BW.
- Create a datastore connection in SAP BODS to connect to SAP BW.
- Develop data flows in SAP BODS to extract, transform, and load data into SAP BW.
- Utilize BODS transformations and mappings to align data formats with BW requirements.
- Schedule BODS jobs to automate data transfer between BODS and BW.
62. How do users connect SAP BODS to an SAP ERP system?
Ans:
Connecting SAP BODS to an SAP ERP system necessitates configuring Remote Function Call (RFC) connections within BODS. SAP application-specific adapters are utilized to extract data from ERP tables or via Business API. This integration architecture ensures seamless data exchange between SAP BODS and SAP ERP, enabling organizations to leverage real-time data insights for improved operational efficiency and decision-making.
63. Explain how to use Web Services in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- In Data Services Designer, define a Web Service data store.
- Drag the Web Service data store onto the canvas while creating a new data flow.
- Set up the Web Service connection’s URL, authentication, and other settings.
- Associate the Web Service’s input/output parameters with the appropriate Data Services objects.
- Carry out the data flow to communicate with the Web Service and handle the necessary data processing.
64. What is the role of the Adapter in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, the Adapter serves as a bridge between the data integration tool and various data sources or targets. Its primary role is to facilitate seamless data connectivity by enabling the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from diverse formats and systems, such as databases, flat files, and applications. Adapters manage communication protocols and data formats, ensuring smooth data flow between SAP BODS and external systems while supporting various data access methods.
65. How to configure Adapters in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Configuring Adapters in SAP BODS involves defining connection parameters, configuring data source/target objects, and specifying adapter-specific options within the BODS Designer environment. This entails establishing secure and reliable connections to diverse data sources, such as relational databases, enterprise applications, and file systems. This setup ensures efficient data integration and seamless interaction with various systems.
66. What are the different types of Adapters available in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- SAP BODS offers a diverse range of adapters, encompassing database adapters, application adapters, and file-based adapters.
- These adapters are meticulously designed and optimized to seamlessly connect SAP BODS with a multitude of data sources, including SAP ERP systems and relational databases such as Oracle, SQL Server, and MySQL.
67. How to use the SAP BODS Management Console for job scheduling?
Ans:
To use the SAP BODS Management Console for job scheduling, navigate to the Management Console, select the desired job, set scheduling parameters like frequency and time, and save the configuration. This automates job execution according to the defined schedule, streamlining data integration processes. This automation enhances operational efficiency by ensuring timely data processing without manual intervention.
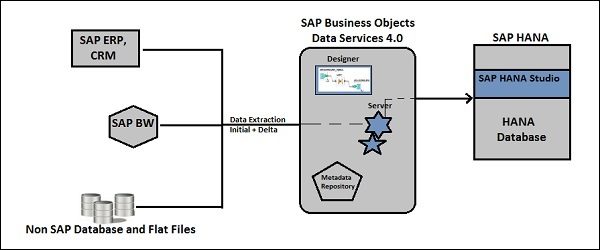
68. Explain the integration of SAP BODS with HANA.
Ans:
SAP BODS integrates seamlessly with HANA through native connectivity or ODBC/JDBC drivers. BODS extracts data from various sources, transforms it, and loads it into HANA, leveraging HANA’s capabilities for real-time analytics and reporting. The Data Services Management Console enables monitoring and administration of the integration process.
69. How to load data into SAP HANA using SAP BODS?
Ans:
To load data into SAP HANA using SAP BODS, begin by creating a new data flow in the Data Services Designer to define extraction and transformation processes. Establish source connections with the appropriate adapters and apply necessary transformations to align the data with the target schema. Configure a target connection to SAP HANA and incorporate the SAP HANA Load transform for data loading.
70. What is the process of upgrading SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Review system requirements and compatibility.
- Backup databases and repositories.
- Install the new version.
- Apply patches or service packs.
- Migrate existing projects and configurations.
- Conduct testing and validate functionality.
- Roll out to production environment.
71. How do users manage project dependencies in SAP BODS?
Ans:
In SAP BODS, manage project dependencies by creating reusable objects, organizing workflows logically, and utilizing shared resources like data stores and job templates. Leverage job chaining and metadata propagation to ensure seamless integration and efficient data flow within the project.
72. Explain the process of migrating jobs from development to production in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- Export jobs from the development environment.
- Import them into the production environment.
- Validate connections and dependencies.
- Execute tests to ensure functionality.
- Schedule jobs in a production environment as needed.
- Monitor for any issues post-migration.
73. What are the steps to deploy a job in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- Develop the job in BODS Designer.
- Validate the job for errors.
- Export the job to a repository.
- Create a batch job in the Management Console.
- Assign the job to a Data Services agent.
- Execute the job on the scheduled time or manually.
74. Explain version control jobs in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Version control in SAP BODS allows users to manage different versions of data integration jobs, facilitating better collaboration and change management. It enables tracking changes made to jobs, workflows, and other development objects over time. Users can create, modify, and revert to previous versions as needed, ensuring consistency and stability in data processing.
75. What is the Central Repository in SAP BODS used for?
Ans:
The Central Repository in SAP BODS is used to store and manage metadata, including data integration jobs, data flows, and transformation logic. It serves as a centralized location that enables collaboration among multiple developers by allowing them to access and share project components. This repository also supports version control, ensuring that changes to jobs and workflows are tracked and managed effectively.
76. How to use the Central Repository for collaboration?
Ans:
Utilize the Central Repository for collaboration by storing project files, version control, and enabling team members to access, contribute, and update project resources. It fosters coordination, ensures consistency, and facilitates seamless teamwork in software development endeavors. This centralized approach streamlines development and enhances accountability by keeping a clear history of changes and team contributions.
77. Explain the concept of object promotion in SAP BODS.
Ans:
- Object promotion in SAP BODS involves moving objects (like jobs and data flows) between development, testing, and production environments.
- It ensures consistent deployment, testing, and release of data integration solutions, maintaining integrity and minimizing errors across different stages of the development lifecycle.
78. What is the role of the Administrator in SAP BODS?
Ans:
The SAP BODS administrator oversees system configuration, user management, and performance monitoring. They ensure smooth operation, handle security settings, and troubleshoot technical issues, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of data integration processes. The administrator is responsible for managing system upgrades and implementing best practices to optimize data workflows and overall performance.
79. How do users backup and restore repositories in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Use the Management Console to export repository objects in SAP BODS to back up repositories. After selecting the repository, choose “Export” to produce a backup file. Import the backup file via the Management Console and choose the relevant repository to begin the restoration process. System dependability and data integrity are thus guaranteed.
80. What is the importance of documentation in SAP BODS projects?
Ans:
- In SAP BODS initiatives, documentation is essential for upholding openness, encouraging cooperation, and guaranteeing project continuity.
- It offers a thorough reference for operating procedures, transformation logic, data mappings, and system design.
- Projects with adequate documentation facilitate team knowledge transfer, expedite troubleshooting, and promote regulatory compliance.
81. What is the latest version of SAP BODS?
Ans:
As of my last update in January 2022, the latest version of SAP BODS (SAP BusinessObjects Data Services) I’m aware of is 4.2 SP14. However, for the most accurate information, recommend checking SAP’s official website or documentation. Staying updated through official channels ensures have access to the latest features, enhancements, and support resources for SAP BODS.
82. Explain the licensing model for SAP BODS.
Ans:
SAP BODS typically follows a per-user licensing model, where users are licensed based on their roles and usage levels. Additional costs may apply for add-ons or specific functionalities. Licensing terms can vary based on deployment options (on-premises or cloud) and subscription models. It’s essential for organizations to review their specific needs and consult with SAP representatives to determine the most suitable licensing structure for their requirements.
83. How do user manage user roles and permissions in SAP BODS?
Ans:
- In SAP BODS, manage user roles and permissions through the Central Management Console (CMC). .
- Define roles with specific privileges, assign users to roles, and control access to objects like jobs, data stores, and repositories.
- Regularly review and adjust permissions to ensure security and compliance.
84. What is the future roadmap for SAP BODS?
Ans:
- SAP BODS roadmap likely includes enhancements in data integration, cloud adoption, AI-driven automation, and improved connectivity.
- Expect advancements in real-time processing, scalability, and compatibility with emerging technologies, ensuring BODS remains a robust solution for enterprise data management.
85. How to ensure data security in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Ensure data security in SAP BODS by implementing role-based access control, encrypting sensitive data in transit and at rest, regularly updating system patches, and monitoring user activities for suspicious behavior. Restrict access to sensitive information and enforce robust authentication procedures to prevent unwanted access. These measures strengthen data integration security, protecting sensitive information from potential threats and breaches.
86. Explain how to implement GDPR compliance using SAP BODS.
Ans:
Implement GDPR compliance in SAP BODS by ensuring data anonymization, pseudonymization, and encryption. Use SAP BODS data masking transformations to protect sensitive information. Implement access controls and audit trails to monitor data usage and ensure compliance with GDPR. Regularly review and update data handling practices to align with evolving GDPR requirements and maintain ongoing compliance.
87. How to use SAP BODS for ETL processes?
Ans:
- SAP BODS (Business Objects Data Services) facilitates ETL processes by extracting data from several sources, processing information to meet business requirements, and loading it into target systems.
- Users define workflows, data mappings, and transformations within BODS Designer, leveraging its graphical interface.
- Integration with SAP and non-SAP systems ensures seamless data movement, supporting data warehousing, analytics, and other business needs.
88. What are the benefits of using SAP BODS over other ETL tools?
Ans:
- SAP BODS offers robust integration with SAP systems, extensive data transformation capabilities, real-time data integration, and compatibility with various data sources.
- Its unified platform reduces complexity and ensures seamless data movement, making it a preferred choice for organizations already invested in the SAP ecosystem.
89. How to stay updated with the latest features and updates in SAP BODS?
Ans:
Stay updated with SAP BODS features and updates by reading SAP’s official documentation, attending webinars, joining SAP communities or forums, subscribing to newsletters, and following relevant blogs or social media accounts. Engaging with these resources not only enhances knowledge but also helps leverage new functionalities effectively in data integration projects.
90. What are some common challenges faced while working with SAP BODS?
Ans:
Common challenges include performance bottlenecks, data quality issues, connectivity problems, and version control conflicts. These challenges can be addressed through performance tuning, data profiling, troubleshooting techniques, and effective communication and collaboration among team members. Proactively identifying and resolving these issues can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of data integration processes.






