
SAP BW on HANA is the integration of SAP Business Warehouse with the SAP HANA in-memory database. This synergy allows for accelerated data processing and analytics by leveraging HANA’s in-memory computing capabilities. The combination eliminates the need for traditional aggregates, enabling real-time data access and faster reporting. It optimizes performance by storing and processing data in RAM, enhancing overall system efficiency.
1. What is SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA is an integration of SAP’s Business Warehouse (BW) software with the HANA in-memory database. It varies from traditional SAP BW by leveraging HANA’s high-speed processing capabilities, enabling faster data retrieval and analysis. This integration enhances the overall performance, accelerates data processing, and supports real-time analytics.
2. Explain the advantages of using SAP BW on HANA.
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA provides several advantages, including improved data processing speed, reduced data latency, and enhanced scalability.
- The in-memory computing capabilities of HANA allow for real-time analytics and quicker access to large datasets.
3. How does SAP BW on HANA handle data modeling and storage?
Ans:
In SAP BW on HANA, data modeling is optimized through the use of in-memory computing, eliminating the requirement for traditional aggregates and indexes. The HANA database allows for columnar storage and utilizes advanced compression techniques, resulting in much more efficient data storage and retrieval. This approach simplifies data models, accelerates query performance, and deduces the overall data footprint.
4. In SAP BW on HANA, what does CompositeProvider mean?
Ans:
Users of SAP BW on HANA can aggregate data from many sources, InfoProviders or Advanced DataStore Objects (aDSOs), using the CompositeProvider modeling object. By offering a uniform view of the data for reporting needs, it facilitates the development of composite providers to satisfy specific reporting requirements.
5. How does SAP BW support real-time analytics on HANA?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA uses the HANA database’s in-memory processing power to enable real-time analytics.
- Real-time data can be copied and processed straight into SAP BW on HANA with technologies like ODP and SDI.
6. What are InfoCubes in SAP BW on HANA designed for SAP HANA?
Ans:
InfoCubes in SAP BW on HANA that are optimized for SAP HANA are made to take advantage of HANA’s in-memory processing power. These provide better query performance and need less data storage because they are stored in columnar format and make use of features like partitioning, compression, and parallel processing, in contrast to regular InfoCubes.
7. Explain Smart Data Access (SDA) in SAP BW on HANA.
Ans:
Smart Data Access enables seamless integration of data residing in external sources, such as Hadoop or other databases, into SAP BW on HANA. By allowing virtual access to external data without physical replication, SDA supports a federated approach to data management, enabling organizations to combine and analyze data from diverse sources within their BW on HANA environment.
8. What is Data Tiering Optimization in SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
- Data Tiering Optimization is a feature in SAP BW on HANA that allows organizations to manage the storage of data based on its usage patterns.
- Frequently accessed and critical data is kept in memory, while less frequently used data is stored on lower-cost, persistent storage.
- DTO helps optimize system performance and reduce overall infrastructure costs.
9. What is SAP HANA Cockpit in SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
The SAP HANA Cockpit is a web-based administration tool used to monitor and manage SAP HANA systems. In the context of SAP BW on HANA, the cockpit provides insights into the health and performance of the HANA database, allowing administrators to optimize resource utilization, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the overall stability of the SAP BW on HANA landscape.
10. How does SAP BW on HANA support real-time data integration?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA enables real-time data integration through ODP, which facilitates the extraction and provisioning of operational data directly into SAP BW. ODP allows for real-time replication from SAP source systems and non-SAP source systems, ensuring that changes in source data are quickly reflected in the BW system for immediate analysis and reporting.
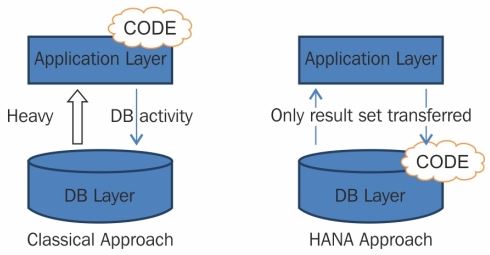
11. What are SAP HANA-Optimized DataStore Objects.
Ans:
- Advanced DataStore Objects (ADSO) is a key component in SAP BW on HANA, providing a unified modeling object for different data storage scenarios.
- HANA-Optimized ADSOs are specifically designed to harness the performance benefits of HANA, offering improved load and query performance.
12. Explain the benefits of using CompositeProviders.
Ans:
CompositeProviders in SAP BW on HANA allow for the combination of data from different sources, InfoProviders or Advanced DataStore Objects, offering a flexible approach to data modeling. By creating CompositeProviders, organizations can create logical unions or join data, streamlining reporting efforts and providing a unified view for more comprehensive analytics.
13. How does SAP BW on HANA handle the migration of existing data?
Ans:
- The migration to SAP BW on HANA involves a systematic approach to transferring existing data from traditional BW systems.
- SAP provides tools such as the “Migration Cockpit” and “Data Transfer Process (DTP)” to facilitate the conversion.
- These tools help organizations move data and objects efficiently, ensuring a smooth transition to the HANA-based infrastructure.
14. How does SAP BW/4HANA differ from SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
| Feature | SAP BW on HANA | SAP BW/4HANA | |
| Architecture |
Traditional BW with HANA database |
Modern, optimized for HANA | |
| Data Modeling | Traditional InfoCubes and DSOs | Advanced HANA-optimized modeling | |
| Simplification |
Evolutionary changes |
Clean slate, streamlined solution | |
| Integration with HANA | HANA as a database with some traditional components | Full leverage of HANA capabilities |
15. How does SAP BW on HANA leverage in-memory computing?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA exploits the in-memory computing capabilities of the HANA database by storing data in RAM rather than traditional disk storage.
- In-memory computing also enables real-time analytics, as data is readily available for analysis without the need for extensive data-loading processes.
- The columnar storage structure of HANA further enhances compression and accelerates data retrieval, contributing to overall performance optimization.
16. Explain the integration of SAP BW on HANA with SAP HANA Live.
Ans:
AP HANA Live is a suite of pre-built, real-time operational analytics content. SAP BW on HANA seamlessly integrates with SAP HANA Live, enabling organizations to leverage predefined HANA views for rapid reporting and analytics. This integration eliminates the need for extensive data modeling efforts, allowing users to access real-time operational data directly from SAP HANA Live views.
17. What are the considerations for optimizing data loading performance?
Ans:
Optimizing data loading performance in SAP BW on HANA involves factors such as data modeling, use of advanced DataStore Objects (adios), and parallel processing. Employing delta mechanisms, partitioning tables, and leveraging Hana-optimized objects contribute to efficient data loading.
18. How does SAP BW on HANA handle data security and encryption?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA ensures data security through role-based access control, integrating with SAP HANA’s security features.
- User access is controlled based on roles, and encryption techniques are employed to secure sensitive data during transmission and storage.
- Organizations can implement SSL encryption for secure communication between components.
19. Explain HANA-optimized MultiProviders in SAP BW on HANA.
Ans:
HANA-Optimized MultiProviders in SAP BW on HANA allow for the combination of data from multiple InfoProviders, such as InfoCubes and Advanced DataStore Objects (aDSOs). These MultiProviders are designed to take advantage of the HANA in-memory computing capabilities, optimizing query performance and providing a unified view for analytical reporting.
20. How does SAP BW on HANA support the integration of unstructured data?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA supports the integration of unstructured data through Smart Data Integration (SDI) and Smart Data Access (SDA).
- These tools enable organizations to connect and integrate unstructured data sources, such as Hadoop or external databases, seamlessly into SAP BW on HANA.
- This capability ensures a holistic approach to data management, allowing organizations to analyze both structured and unstructured data.
21. What are the benefits of using SAP BW on HANA for data consolidation?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA facilitates data consolidation and harmonization by providing a unified platform for integrating data from diverse sources. The in-memory processing capabilities accelerate data consolidation and features like CompositeProviders enable the harmonization of data structures for consistent reporting.
22. How does SAP BW on HANA handle data aging and partitioning?
Ans:
- Data aging and partitioning in SAP BW on HANA are employed to manage historical data efficiently.
- Data aging involves moving older data to slower storage, while partitioning allows for the logical separation of data based on specific criteria.
23. What role does the SAP HANA Analysis Process play?
Ans:
The SAP HANA Analysis Process enhances performance by pushing down complex calculations and aggregations, and filters directly into the HANA database. This feature minimizes data movement between the application server and the database, reducing processing times for analytical queries. By leveraging HANA’s in-memory processing for calculations, SAP BW on HANA ensures that resource-intensive tasks are executed efficiently.
24. Explain Smart Data Quality (SDQ) in SAP BW on HANA.
Ans:
Smart Data Quality (SDQ) in SAP BW on HANA focuses on ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data through data quality transformations. SDQ provides functionalities for data cleansing, validation, and enrichment, allowing organizations to maintain high data quality standards. By embedding data quality processes within the data warehouse, SAP BW on HANA ensures that the analytical insights derived from the system.
25. Explain SAP BW on HANA cockpit in system monitoring.
Ans:
- The SAP BW on the HANA cockpit serves as a central tool for monitoring and administering the SAP BW on the HANA landscape.
- It provides insights into system health, performance metrics, and resource utilization.
26. How does SAP BW on HANA handle the integration of Big Data sources?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA seamlessly integrates with Big Data sources through Smart Data Integration (SDI) and Smart Data Access (SDA). These tools enable organizations to connect to and process data from Hadoop, Apache Spark, and other Big Data platforms directly within SAP BW on HANA.
27. What is SAP HANA SQL Script in SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
- SAP HANA SQL Script is a scripting language used in SAP BW on HANA for advanced data processing and calculations.
- It allows developers to implement custom logic directly within the HANA database, optimizing the execution of difficult operations.
- SQLScript enhances data processing by enabling parallel execution, in-memory computations, and efficient handling of large datasets.
28. How does SAP BW from SAP source systems manage data replications?
Ans:
SAP BW uses Real-Time Data Acquisition (RDA) on HANA to replicate data in real-time from SAP source systems. RDA makes sure that modifications made in the source system are instantly mirrored in SAP BW, enabling real-time analytics. For cases like operational reporting and monitoring, which call for instant insights, this real-time replication is more advantageous.
29. What is the SAP BW on the HANA Virtualization Layer used for?
Ans:
Without requiring physical replication, data can be virtually integrated using SAP BW on HANA’s Virtualization Layer. It makes it possible to create virtual data models and views that make use of information kept in databases or other external systems like Hadoop. By doing away with the requirement for substantial data transportation and storage duplication, this method maximizes data retrieval.
30. How does SAP BW on HANA facilitate the integration of geospatial data?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA integrates geospatial data for location-based analytics through the use of spatial data types and functions within the HANA database. Organizations can store and analyze geospatial data directly within SAP BW on HANA models. This capability allows for the creation of location-aware reports, maps, and dashboards, providing valuable insights for business scenarios that involve geographic considerations.
31. Explain Advanced Data Transformation (ADT).
Ans:
- Advanced Data Transformation (ADT) in SAP BW on HANA represents an evolution of the traditional Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes.
- ADT focuses on pushing data transformations closer to the source and optimizing them within the HANA database.
- ADT leverages the HANA Calculation Engine for in-memory processing, enabling organizations to perform complex transformations efficiently.
32. How does SAP BW on HANA support multi-temperature data management?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA supports multi-temperature data management by allowing organizations to store data in different storage tiers based on its access frequency. Hot data, frequently accessed and critical for real-time analytics, is stored in memory. Warm data, less frequently accessed, is stored on high-performance disks, while cold data, rarely accessed, is stored on lower-cost, persistent storage.
33. What is SAP BW on the HANA Mixed Scenarios approach?
Ans:
- The Mixed Scenarios approach in SAP BW on HANA enables organizations to combine both traditional BW on any database and BW/4HANA in the same landscape.
- This approach supports phased migrations, allowing organizations to transition gradually based on their specific needs and priorities. It provides flexibility in leveraging the benefits of both solutions in a unified landscape.
34. What does the SAP Fiori interface play?
Ans:
The SAP Fiori interface enhances the user experience with SAP BW on HANA by providing a modern and intuitive user interface. Fiori applications are designed for various analytics scenarios, allowing users to access dashboards, visualizations, and reports in a responsive and user-friendly manner.
35. What Fiori applications are available?
Ans:
Fiori applications for SAP BW on HANA include Analytical Apps, Overview Pages, and fact sheets, offering role-based insights and actionable information. The Fiori interface promotes self-service analytics, making it easier for users to consume and interact with analytical content within the SAP BW on the HANA environment, ultimately improving the overall user experience.
36. How is parallel processing for data loading handled?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA optimizes performance by using parallel processing for query execution and data loading. In order to efficiently utilize resources, jobs are distributed over numerous processing units through the process of parallelization. The design of data models, the application of transformations that permit parallel processing, and the appropriate setup of system settings are all factors to take into account while optimizing parallelization.
37. What are the advantages of HANA-Optimized InfoCube?
Ans:
- It stores data in a columnar format, allowing for efficient compression and faster data retrieval.
- HANA-Optimized InfoCubes are particularly beneficial for organizations requiring high-speed analytics.
38. How does SAP BW on HANA handle delta mechanisms?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA employs delta mechanisms to extract and load only the changed or new records from source systems, reducing processing time and system resources. Commonly used delta methods include Delta Queue (RSA7), Change Data Capture (CDC), and delta-enabled DataSources.
39. Explain SAP BW on HANA Planning Applications.
Ans:
The Planning Applications Kit (PAK) in SAP BW on HANA is a toolkit designed for developing custom planning applications, budgeting models, and forecasting scenarios. It leverages the in-memory processing capabilities of HANA for real-time planning and analysis. PAK allows organizations to create flexible planning solutions tailored to their specific business requirements, enabling efficient collaboration and decision-making.
40. How does SAP BW on HANA handle data compression?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA employs data compression techniques to optimize storage efficiency and reduce memory consumption.
- The columnar storage format in HANA contributes to compression by storing similar data types together, minimizing storage redundancy.
- Techniques such as dictionary encoding and run-length encoding are utilized to achieve high compression ratios.
41. What is SAP HANA Analysis for Office?
Ans:
HANA Analysis for Office is an Excel-based tool that enhances the reporting and analysis capabilities of end-users in SAP BW on HANA. It allows users to connect directly to HANA data models, create interactive reports, and perform ad-hoc analysis within the familiar Excel interface. Analysis for Office provides advanced features such as drag-and-drop functionality, dynamic formulas, and integration with SAP BW on HANA variables.
42. How does SAP BW on HANA handle the integration of external data sources?
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA seamlessly integrates external data sources through tools like SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI) and Smart Data Access (SDA).
- SDI enables real-time and batch data integration from various sources, including flat files and non-SAP databases, directly into SAP BW on HANA.
43. What is SAP BW on the HANA Data Archiving process?
Ans:
The SAP BW on the HANA Data Archiving process plays a crucial role in optimizing system performance and managing historical data. It involves the removal of infrequently accessed and historical data from the active storage layer, reducing the data footprint in memory. Archiving ensures that only relevant and actively used data remains readily available for analysis within SAP BW on HANA.
44. Explain the role of SAP BW on the HANA Workspace.
Ans:
- SAP BW on HANA Workspaces is a collaborative environment that enhances content management and collaboration within the system.
- Workspaces allow users to organize and manage analytical content, such as reports, queries, and dashboards, in a structured manner.
- Users can collaborate on projects, share insights, and collectively work on analytical tasks within designated Workspaces.
45. How does HANA support the implementation of Hierarchies?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA supports the implementation of Hierarchies for dimensional reporting through features like the HANA-Optimized InfoCube and Advanced DataStore Objects (also). Hierarchies provide a structured way to organize and analyze data hierarchically, such as organizational structures or product hierarchies.
46. Explain SAP BW on HANA RemoteCube.
Ans:
- The SAP BW on HANA RemoteCube enables the virtual integration of data from external SAP BW systems without physical replication.
- It allows users to access and query data from a remote SAP BW system as if it were a local InfoCube.
47. What is SAP BW on HANA Embedded Analytics?
Ans:
SAP BW on HANA Embedded Analytics integrates analytics directly into operational processes, allowing users to perform analytical tasks within the context of transactional applications. The SAP BW facilitates this capability on HANA Embedded Analytics features, such as Analytical Query Designer and Analytical Privileges. Users can create, customize, and execute analytical queries seamlessly within operational transactions, enhancing decision-making capabilities.
48. What language is used to develop SAP HANA?
Ans:
- SAP HANA is predominantly developed in the C++ programming language, with additional components implemented in Java and HTML5 for user interfaces.
- C++ provides the foundation for the in-memory database system, offering high-performance capabilities crucial for handling extensive data loads and real-time analytics.
49. What are the column- and row-based approaches?
Ans:
Column-based Approach: In the column-based approach, data is stored and processed by columns rather than rows. Each column contains a specific type of data, and all values for that attribute are stored together.
Row-based Approach: In contrast, the row-based approach stores and processes data by rows. Each row represents a record, and all attribute values for a particular record are stored together. This method is akin to traditional relational databases.
50. How can one go about loading a non-cumulative cube?
Ans:
Loading a non-cumulative cube in SAP BW involves several key steps:
- First, activate the Data Transfer Process (DTP) for the relevant InfoProvider.
- Next, select the appropriate data source and establish mappings between source and target fields.
- Then, apply any necessary transformations to meet the cube’s requirements.
- After configuring the DTP settings, execute the data transfer process to load the non-cumulative cube with the desired data.
51. Is it possible to turn off the cache?
Ans:
Turning off the cache in SAP HANA is not recommended, as the cache significantly contributes to query performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory. However, if necessary, you can minimize its impact by adjusting cache configurations rather than turning it off entirely. This can be achieved through SAP HANA Studio or using SQL statements to modify cache settings.
52. In SAP BI, what is a multi-provider?
Ans:
- In SAP BI, a MultiProvider is a virtual InfoProvider that enables the integration of data from various InfoProviders, such as InfoCubes or DataStore Objects (DSOs).
- It acts as a logical container, allowing users to consolidate data from different sources without physically moving or duplicating it.
53. What characteristics do Multi-providers offer?
Ans:
MultiProviders offer characteristics such as the ability to create unions or intersections of data, providing a unified view for reporting. They enhance flexibility by supporting complex reporting scenarios, enabling users to analyze and present data seamlessly from multiple InfoProviders.
54. How can a bunch of information packages be transformed?
Ans:
Create a Process Chain: Access the Process Chain maintenance screen in SAP BW.
Define Process Steps: Add individual process steps within the process chain, representing each information package that needs to be executed.
Sequence the Steps: Arrange the process steps in the desired order to establish the flow of execution.
Set Dependencies: Specify dependencies between process steps to ensure that they execute in a logical sequence.
Configure Parameters: Adjust parameters for each step, including data selection criteria and transformation rules.
55. What is the DIM ID?
Ans:
- In SAP BW on HANA, DIM ID refers to the Dimension ID, a unique identifier assigned to each dimension table.
- DIM IDs are crucial for maintaining data consistency and integrity within the data warehouse, enabling retrieval of dimension attributes.
56. Which kinds of attributes are there?
Ans:
There are two main types of attributes in SAP BW on HANA: key attributes and navigational attributes. Key attributes are essential for uniquely identifying master data, while navigational attributes provide additional details that help in navigating and analyzing data within the system.
57. What is Ad Hoc Analysis?
Ans:
To provide fast results, traditional data warehouses like SAP BW use a lot of pre-aggregation. In other words, the administrator (IT department) chooses which data may be required for analysis and gets the output ready for end users. Although this produces quick performance, the end user needs more flexibility.
58. What is a source system?
Ans:
- In SAP BW on HANA, a source system is a system from which data is extracted and loaded into the data warehouse.
- Source systems can include various databases, ERP systems, or external systems that contribute data for analysis and reporting within the SAP BW on HANA environment.
59. Can users continue using SAP HANA Data Warehousing based on SQL?
Ans:
Yes, we will keep supporting the SQL approach. Customers now have an additional option to use SAP BW/4HANA. The customer’s priorities, level of expertise, and the model that determines their requirements all play a role in determining which solution is best. A hybrid approach is found by many customers to best suit their needs.
60. What is Transaction Manager and Session?
Ans:
The Transaction Manager plays a crucial role in managing and coordinating transactions within the system. It ensures the consistency and integrity of data by overseeing the execution of operations.
Sessions, on the other hand, represent individual work units within a transaction. They are responsible for grouping related operations and managing the flow of data during a transaction.
61. In a database, what is a functional dependency?
Ans:
Functional dependency in a database refers to the relationship between two sets of attributes in which the value of one set uniquely determines the value of another set. It ensures that for a given value of one attribute, there is a unique and corresponding value for another attribute. In other words, if two sets of attributes, A and B, have a functional dependency, knowing the value of A implies the unique value of B.
62. What is data redundancy exactly?
Ans:
- In SAP HANA BW, data redundancy refers to the presence of duplicated or repetitive information within the system.
- This redundancy can occur when similar data is stored in multiple tables or InfoProviders, leading to increased storage requirements.
- The goal of SAP HANA BW is to minimize data redundancy to optimize performance and reduce storage space.
63. How can a Sap Hana user connection be secured?
Ans:
Authentication: Enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as X.509 certificates, SAML, or Kerberos, to verify the identity of users attempting to connect to SAP HANA.
User Role Management: Assign roles and privileges to users based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring that each user has only the necessary permissions for their specific tasks.
SSL/TLS Encryption: Implement Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption to protect data transmitted between the SAP HANA client and server, safeguarding against unauthorized interception.
64. What role does SAP HANA’s Persistence Layer actually play?
Ans:
It is a crucial part that comes later in SAP HANA and has a significant impact. Since HANA has a computational engine built right in, customers must use the data straight away without creating a backup. It is essential to maintain a backup of the same since it may cause problems in the event of a significant breakdown. This layer is a lifesaver since it ensures that no data is lost in a crisis like this.
65. How should sap Hana systems be operated and maintained?
Ans:
- A new database with intriguing SAP HANA features is called Sap Hana. Sap Hana is an in-memory database to start.
- While managing databases directly from the server is not the most comfortable option, it is still possible with hdbsql.
66. Explain Sap Hana Studio’s Data provisioning.
Ans:
SAP HANA Studio’s data provisioning is a set of tools and mechanisms that facilitate the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data into SAP HANA from various source systems. It enables users to efficiently bring in data from different sources and make it available for analysis in real-time.
67. Mention SAP HANA’s capabilities.
Ans:
Multi-Model Processing: SAP HANA is capable of storing and handling a wide range of data types and sets in many formats, such as tables, graphs, and documents.
Hybrid Processing: HANA is a database that can function as an analytical and transactional system. It can concurrently handle both kinds of queries on the same collection of data.Application Development Tools: SAP HANA comes with a number of tools for developing applications, including the Web IDE and Eclipse.
68. What is Data Definition Language exactly?
Ans:
- Data Definition Language (DDL) is a subset of SQL used to define and manage the structure of database objects.
- It includes statements for creating, altering, and deleting objects like tables, views, and indexes.
- DDL in SAP HANA BW allows data modelers to specify the characteristics, relationships, and constraints of data structures.
69. Does SAP HANA function exclusively within a SAP system?
Ans:
No, SAP HANA does not function exclusively within an SAP system. While commonly used as the underlying database for SAP applications, HANA can also be employed independently or integrated with non-SAP systems. Its versatility allows organizations to utilize it for custom development, analytics, and data processing beyond the scope of SAP applications, making it a standalone solution for various enterprise needs.
70. Which use cases are there for SAP HANA?
Ans:
SAP HANA supports numerous use cases for real-time analytics. Here are a few instances:
- Enhancing communications
- Optimization of the supply chain
- Optimization of retail sales
- Fraud detection
- Forecasting profitability
71. Differentiate between a variable and an input parameter in HANA.
Ans:
Variables are linked to columns and utilized for filtering through the use of WHERE clauses. To put it another way, they may take into account the values found in the columns to which they relate. Variables do not affect the performance of HANA. The execution is directed by the input parameters based on user input. It’s only sometimes desirable for a variable to do nothing more than limit the data in a view.
72. Explain what schema mapping is.
Ans:
- When the physical schema of the source system and the target system differ, schema mapping is used to bridge the gap.
- Considering that we are moving parts from the Development System (DEV) to the Production System (PROD).
- The Development System’s tables are located in the DEV_SCHEMA, while the Production System’s specific tables are found in the PROD_SCHEMA schema.
73. What is meant by SAP Collections Insight?
Ans:
SAP Collections Insight, which SAP HANA powers, gives you access to real-time mobile association and collections account information anywhere, at any time. It helps you to better manage your collection efforts, improve business relationships, get payment quickly, and fix collection-related issues.
74. What is the difference between activate and redeploy?
Ans:
Activation typically refers to the process of making a software component or feature operational. In the context of SAP BW on HANA, activation might involve enabling or configuring specific features or functionalities associated with the integration of BW with the HANA database.Redeployment generally means the process of deploying or installing a software component again. This could be necessary when changes are made to the system, configurations need to be updated, or new versions of the software are released.
75. What is LSA++ in the context of SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
- LSA++ is an evolved version of the Layered Scalable Architecture used in SAP BW. It emphasizes simplification and flexibility in data modeling by promoting a layered approach.
- LSA++ aims to reduce redundancy, enhance agility, and optimize the use of SAP HANA features, providing a more scalable and efficient architecture for data warehousing.
76. What is meant by SAP Collections Insight?
Ans:
SAP Collections Insight, which SAP HANA powers, gives you access to real-time mobile association and collections account information anywhere, at any time. It helps you to better manage your collection efforts, improve business relationships, get payment quickly, and fix collection-related issues.
77. How does SAP HANA Accelerator work?
Ans:
The SAP HANA Accelerator is a feature that allows certain BW queries to be pushed down to the HANA database for faster execution. This minimizes data transfer between the BW application server and the HANA database, leading to significant performance improvements in query execution and response times.
78. What is the purpose of a Hybrid Provider in SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
- A Hybrid Provider combines data from different sources, including DataStore Objects (DSOs) and InfoProviders, to provide a unified view for reporting.
- It addresses reporting challenges by allowing users to seamlessly analyze data from both real-time and historical perspectives.
79. Discuss the advantages of using SAP BW Query on HANA.
Ans:
SAP BW Query on HANA utilizes in-memory processing to accelerate query performance significantly. It eliminates the need for aggregates and allows users to leverage HANA-specific functions. Unlike traditional BW queries, SAP BW Query on HANA directly operates on HANA views, optimizing the execution of queries and enhancing overall reporting efficiency.
80. What data store item is in use?
Ans:
The DataStore object enables quick access to data for analysis and reporting and allows for instantaneous updates. It handled data in a different way than conventional DSOs. Since data is kept in the same format as when it was stored in the DataStore object, applications can alter it directly.
81. How is the SAP BW system’s Info area utilized?
Ans:
- Info Areas in SAP BI are used to bring together similar object kinds. Info Area is used to manage Info Cubes and also Info Objects.
- Every Info Object can specify a folder to keep relevant files together, and each Info Area contains an Info Object.
82. Explain a star schema.
Ans:
A star schema is one type of data warehouse schema used for data organization. In addition to a main fact table containing numerical data, it has multiple dimension tables providing context. Because it increases productivity and streamlines and simplifies queries, this approach is widely utilized in business intelligence for efficient reporting and analysis.
83. What is transformation, and how does BW mapping operate?
Ans:
Through the transformation process, data integration, cleansing, and consolidation are accomplished. Importing data from one BI entity to another results in data transformation. Transformation can be used to change a source field into a destination object format. Transformation rules are used to generate maps between source and target data.
84. How do Ods differ from Multiprovider and Infocube?
Ans:
ODS: It provides legible tables with rewriteable, fine-grained data, making it appropriate for both drill-down and RRI.
Cube: Only able to append data and follow the star schema. This model is appropriate for primary reporting.
MultiProvider: Does not have concrete data. It provides access to data from many InfoProviders, including Cube, ODS, and InfoObject. It’s also preferred for reporting.
85. What are the different BW system info object categories?
Ans:
For Info Objects, the following categories apply:
- Characteristics like a client, product, etc.
- Units like dollars, sales volume, etc.
- Vital information, including overall sales, profit, etc.
- Features that relate to time, like the year, quarter, etc.
86. What do the terms “Start,” and “Transfer,”?
Ans:
The start procedure for each DataPackage is triggered after data is written to the PSA but before the transfer rules are executed. It enables complex computations for an important variable or characteristic. Transfer and update procedures are outlined at the InfoObject level, much like a Start Routine.
87. What is the Open Hub Service?
Ans:
The Open Hub Service facilitates the distribution of data from an SAP BW system to external data marts, analytical apps, and other applications. It is able to deliver a controlled dispersion through a variety of techniques. The primary component for exporting data is called InfoSpoke, and it allows you to specify the source and destination objects for the data.
88. How are RMS applications operated?
Ans:
- Electronic record management is made possible by the SAP Records Management component of the SAP Web Application Server.
- Paper-based data can be incorporated into electronic records stored in the SAP RMS.
- The RMS allows certain user groups to access particular records as needed for business activities.
89. What is the SAP HANA Analysis Process in SAP BW on HANA?
Ans:
The SAP HANA Analysis Process is a feature in SAP BW on HANA that enhances reporting capabilities. It leverages the power of HANA by pushing down complex calculations and aggregations directly into the HANA database, reducing the load on the BW application server. This optimization results in faster query response times.
90. What is ODS in SAP BW/BI?
Ans:
An operational data store contains detailed data storage. The BW architectural element visible between infocubes and PSA (Permanent Staging Area) allows BEX reporting.
In contrast to info cubes, ODS objects do not aggregate data. The RECORDMODE value indicates whether new records should be added, updated, or removed before data is loaded into an IDS object.






