
- Introduction to UI Designer Skills
- Visual Design Principles
- Typography and Color Theory
- Layout and Grids
- Design Tools (Figma, XD, Sketch)
- Wireframing and Prototyping
- Interaction Design Basics
- Responsive Design
- Branding and Design Systems
- UI Designer Skills Updated
- Conclusion
Introduction to UI Designer Skills
User Interface (UI) Design refers to the process of designing interfaces in software or computerized devices with a focus on looks or style. The UI designer’s goal is to create interfaces that are easy to use and visually appealing an objective deeply rooted in UI/UX Training, where learners master layout principles, color theory, and usability heuristics to craft intuitive and engaging digital experiences. In UI design, designers focus on aesthetics, layout, and responsiveness, ensuring that users have a seamless experience when interacting with an app or a website. A well-designed user interface is intuitive, consistent, and user-friendly. It provides clear navigation, maintains visual balance, and leads users toward their goals with minimal friction. UI design is a critical component of the overall user experience and contributes significantly to user satisfaction and retention.
Ready to Get Certified in UI/UX Design? Explore the Program Now UI/UX Design Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Visual Design Principles
Visual design principles are essential for creating user-friendly and attractive interfaces. By carefully using key elements like hierarchy, balance, and contrast, designers guide users’ attention and improve interaction. Designers establish hierarchy by making important information stand out through thoughtful choices in size, color, and placement. They arrange visual elements to create a balanced layout. Designers also use contrast to differentiate various parts of the interface, which boosts readability and user focus. Through alignment and proximity, they enhance clarity by organizing elements logically and grouping related items. Keeping consistency across the interface lessens cognitive load, helping users navigate more easily. Visual Design Principles connected principles work together to create well-structured, visually appealing interfaces that not only appear professional but also significantly enhance user experience and engagement.
Typography and Color Theory
Typography and color are two of the most powerful tools in a UI designer’s toolkit:
Typography:
- Choose readable fonts.
- Maintain a clear typographic hierarchy using headings, subheadings, and body text.
- Ensure sufficient line spacing and contrast.
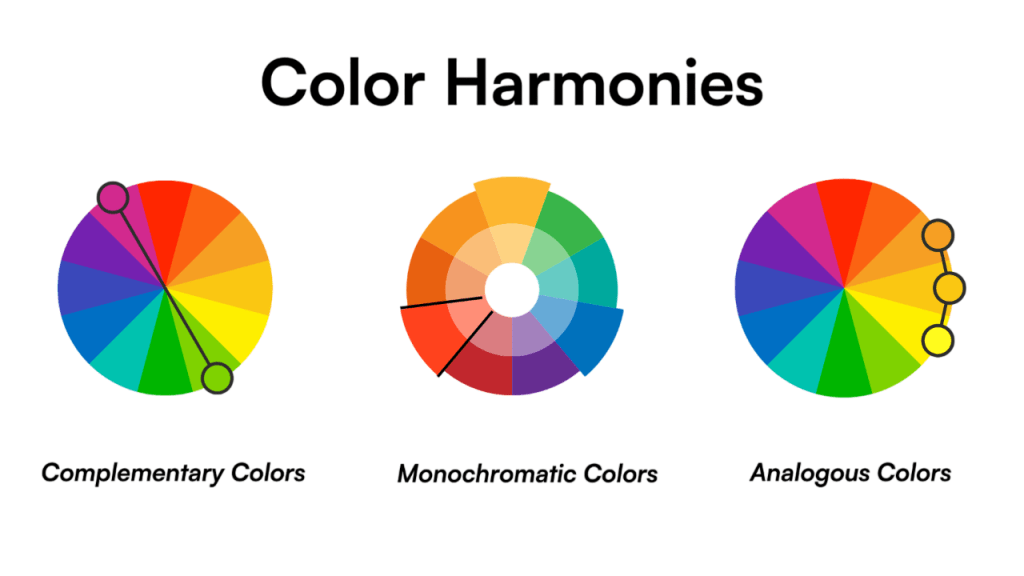
Color Theory:
- Use color to convey meaning, establish hierarchy, and trigger emotions.
- Understand color harmony, contrast, and accessibility (e.g., WCAG compliance).
- Limit the palette to maintain a cohesive look and feel.
Well-chosen typography and colors not only make content easier to read but also strengthen brand identity and improve user engagement.
To Explore UI/UX in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive UI/UX Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Layout and Grids
Layout and grid systems are essential for organizing content and creating a visually pleasing structure:
- Grids: Provide consistency across pages, help align content, and improve responsiveness.
- Columns and Gutters: Define the structure and spacing between elements.
- Modular Design: Breaks down the UI into reusable components for easier updates.
- Whitespace: Enhances clarity and focus by separating elements and reducing clutter.
A strong layout and grid system creates rhythm and flow, guiding users through the interface seamlessly.
Design Tools (Figma, XD, Sketch)
In the fast-changing world of UI design, professionals use strong design tools that improve their workflow and teamwork. Figma is a cloud-based platform that helps designers create smooth interfaces and prototypes. Adobe XD offers design, prototyping, and sharing features, and it works well with the Adobe ecosystem. Designers prefer Sketch, which is only for macOS, because of its advanced vector editing options. These tools have key strengths, like strong design systems, reusable components, and flexible plugin setups that greatly boost designer productivity. For today’s UI professionals, being skilled in at least one of these platforms is essential. This knowledge helps teams create innovative and visually appealing digital experiences efficiently and with great creativity.
Looking to UI/UX Training? Discover the UI/UX Design Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Wireframing and Prototyping
In UI design, designers use wireframing and prototyping to create great digital experiences. Wireframes give low-fidelity views that outline basic structural elements like buttons, menus, and content blocks. They focus on functionality without the distractions of color or typography an essential early-stage technique taught in UI/UX Training, where learners use wireframes to validate layout, user flow, and interaction logic before advancing to high-fidelity design. As designers move forward, they create prototypes, which are high-fidelity interactive models that mimic user interactions. This lets them test usability and collect useful feedback before starting full-scale development. By using these tools, design teams can experiment with ideas, confirm new concepts, and make necessary changes early in the process. In the end, this method saves time and resources while ensuring a more polished and user-focused final product.
Interaction Design Basics
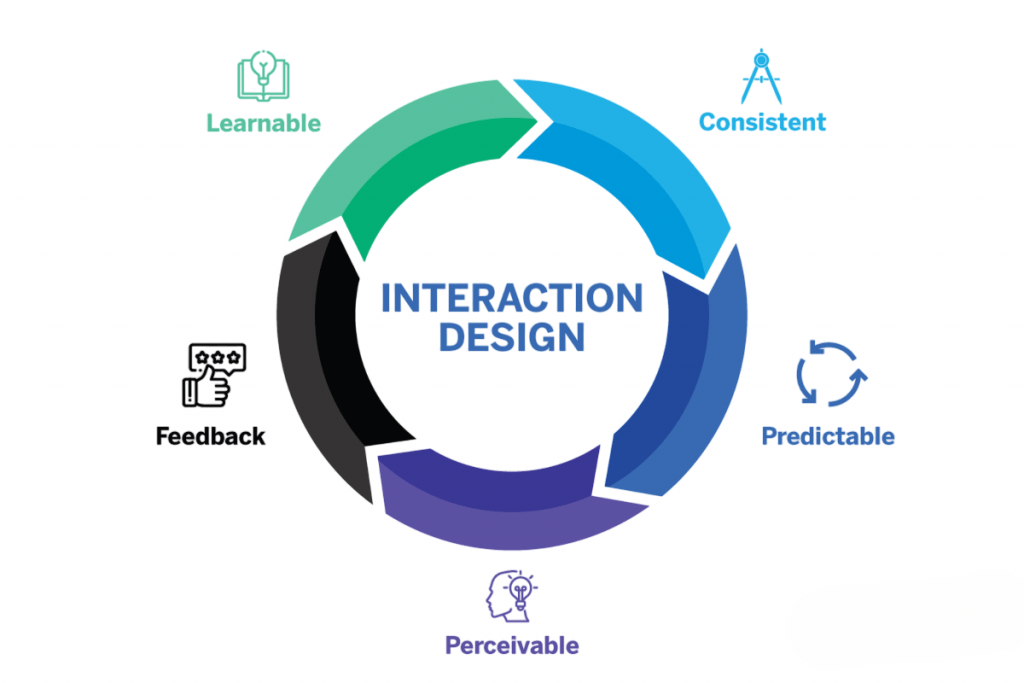
Interaction design (IxD) focuses on how users interact with a system. Key principles include:
- Feedback: Users should receive clear responses from the system for their actions.
- Affordance: Design elements should suggest their function (e.g., buttons look clickable).
- Consistency: Reusing familiar patterns ensures predictability.
- Visibility: Important features should be easily discoverable.
Designers must think about microinteractions (e.g., hover effects, loading animations) that enhance user experience and make interfaces feel alive and responsive.
Preparing for UI/UX Design Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on UI/UX Design Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that a UI works seamlessly across various screen sizes and devices:
- Fluid Grids: Adapt layout proportionally rather than using fixed widths.
- Flexible Images: Resize based on the screen.
- Media Queries: Apply different styles based on screen resolution.
Responsive design ensures accessibility and usability, improving user satisfaction across desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Branding and Design Systems
A cohesive user interface (UI) reflects brand identity by integrating essential branding elements like logos, unique typography, color palettes, and consistent voice. Organizations can use design systems, like Google’s Material Design or IBM’s Carbon Design System, to create collections of reusable components that follow established standards. These design systems improve team collaboration and maintain visual consistency across digital platforms. They also speed up development by cutting out unnecessary design work. Through careful UI design, companies can create a unified, recognizable brand experience that connects with users and shows professionalism and attention to detail.
UI Designer Skills Updated
The UI design field evolves rapidly. To stay competitive:
- Follow Trends: Stay informed via design blogs (e.g., Smashing Magazine, UX Collective).
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer updated content.
- Join Communities: Participate in design communities (e.g., Dribbble, Behance, Reddit).
- Attend Events: Webinars, conferences, and workshops provide insights and networking opportunities.
Consistent learning ensures that you stay ahead of the curve and continuously improve your craft.
Conclusion
UI designer skills is an evolving and multifaceted discipline that combines creativity, psychology, and technology. From understanding fundamental design principles to mastering tools and working collaboratively, a successful UI designer must balance form and function. With dedication, practice, and continuous learning, you can craft intuitive, engaging interfaces that delight users and solve real-world problems an outcome driven by UI/UX Training, where learners build practical skills, refine design workflows, and apply user-centered strategies to create impactful digital products. Whether you’re starting out or looking to refine your skills, keeping a strong foundation in these core areas will pave the way for a rewarding career in UI design.




