
- Definition of AI
- History of AI
- Key Concepts in AI
- Branches of AI (ML, NLP, Robotics, etc.)
- How AI Works: Algorithms and Data
- Popular AI Tools and Platforms
- Applications in Daily Life
- Benefits and Risks of AI
- Role in Automation and Innovation
- Myths About AI
- Government and Regulation of AI
- The Road Ahead for AI
- Conclusion
Definition of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using it), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. In essence, AI aims to create systems that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the imitation of human cognition in robots programmed to think and act like humans. Learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making are some of these capabilities. From simple tasks such as data entry to complex ones such as autonomous cars, artificial intelligence is an enormous domain with numerous uses. Overall, artificial intelligence is a powerful technology that can significantly modify several aspects of our existence. We can optimally leverage its benefits and minimize any potential risks if we know about its potential as well as ethical implications.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
History of AI
The concept of AI dates back to ancient history with myths and stories about mechanical men. However, the modern history of AI began in the 1950s. Alan Turing, often called the father of AI, proposed the idea of a machine that could simulate any human intelligence task. In 1956, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined at the Dartmouth Conference. Over the decades, AI has gone through several cycles of hype and disappointment, known as AI winters. It wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s, with advances in machine learning and data availability, that AI began to realize its potential.Artificial intelligence (AI) has experienced both eras of great progress and “AI winters,” or periods when funding and interest were low. While early conceptions of thinking machines exist in myths and legends from ancient times, the creation of electronic computers during the mid-20th century was the start of current AI research.
Lastly, language translators like compilers, interpreters, and assemblers are system software that convert high-level programming code into machine language that the computer can understand and execute. Each type of system software plays a specific role in maintaining the functionality, stability, and performance of a computer system. Together, they form the foundation upon which all application software and user activities rely.
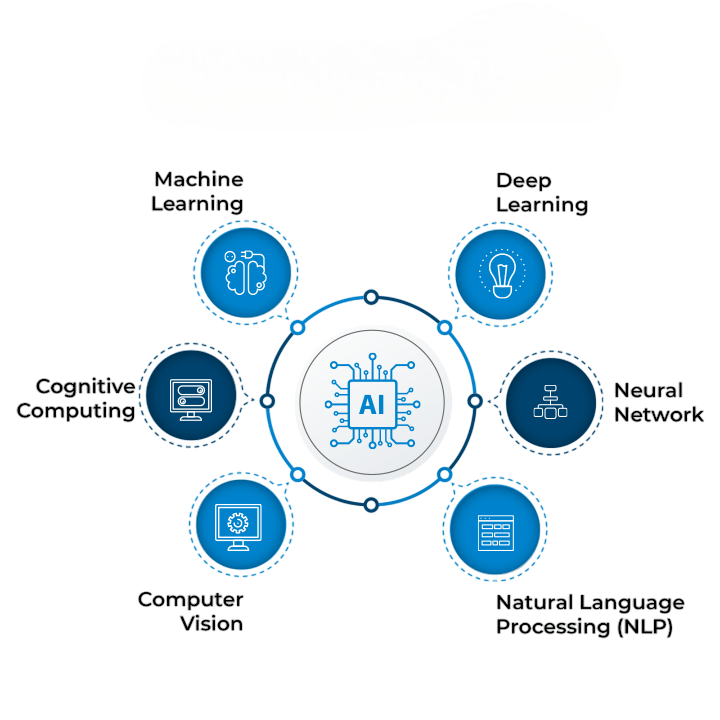
Key Concepts in AI
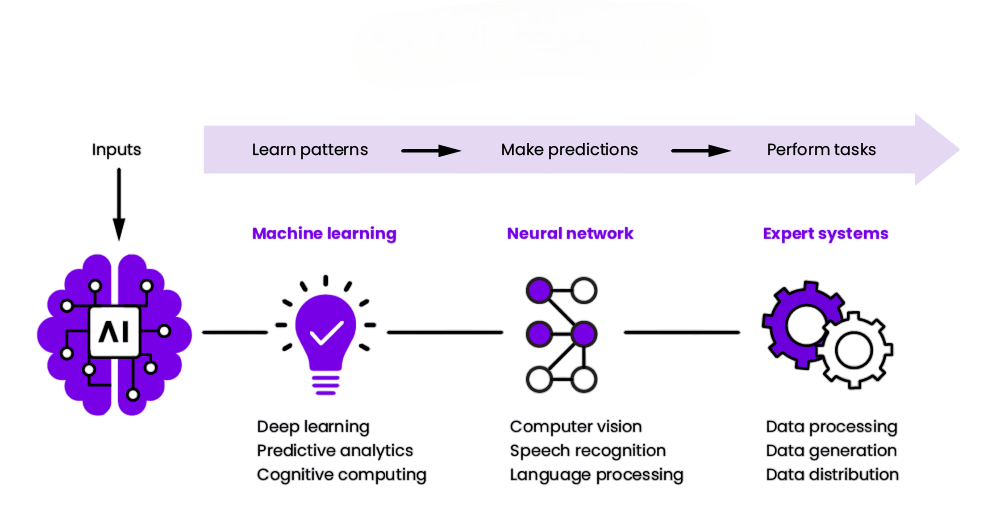
- Machine Learning (ML):Algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data.The underlying domain of machine learning (ML) allows the system to learn from experience without being programmed explicitly. It applies algorithms that can study data, identify patterns, and predict or make decisions.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML involving neural networks with many layers.A subset of machine learning known as “deep learning” utilizes multi-layered artificial neural networks to analyze data and detect subtle patterns. Based on the organization and function of the human brain, it performs well on speech recognition, image recognition, and natural language processing tasks.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):The ability of a machine to understand and respond in human language. The objective of NLP is to enable computers to understand, process, and generate human language. This enables the application of chatbots, text summarization, and machine translation.
- Computer Vision:Enabling machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data.It is the technology that enables machines to identify and understand scenes, objects, and individuals in images. The field processes visual inputs and identifies associated information using machine learning and deep learning techniques.
- Expert Systems:Programs that mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert.a computer program that replicates the decision-making and problem-solving abilities of a human expert in a given domain employing artificial intelligence (AI). It utilizes a knowledge base of data and rules to provide users with suggestions, direction, or responses.
- Robotics:The design and creation of robots capable of performing tasks in the physical world. This entails giving robots the capacity to sense their surroundings, absorb information, make judgments, and carry out activities with little assistance from humans.
- Machine Learning: Focuses on developing algorithms that can learn from and make predictions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables computers to understand, interpret, and produce human language.
- Robotics:Combines AI with mechanical engineering to design robots.
- Computer Vision: Teaches machines to interpret and understand the visual world.
- Expert Systems:Uses databases and inference rules to simulate decision-making.
- Speech Recognition:Allows machines to understand spoken language.
- Planning and Scheduling:Helps systems decide the best course of action to achieve a goal.
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant and quality data.
- Data Preprocessing: Cleaning and organizing the data.
- Model Selection: Choosing the appropriate algorithm.
- Training: Feeding the data into the algorithm.
- Evaluation: Assessing the model’s performance.
- Deployment: Using the model in real-world applications.
- TensorFlow:Open-source library by Google for machine learning and deep learning.
- PyTorch:Open-source ML library developed by Facebook.
- Scikit-learn:Machine learning library for Python.
- Keras:High-level neural networks API.
- OpenAI GPT:A state-of-the-art NLP model.
- Microsoft Azure AI:Cloud platform offering AI services.
- Google AI Platform: Tools and services for developing AI applications.
- Smart Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Recommendation Engines: Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify suggestions.
- Navigation Apps: Google Maps using AI for route optimization.
- Social Media Feeds: Facebook and Instagram use AI for personalized content.
- Email Filtering: Spam detection in Gmail.
- Smart Home Devices: Thermostats, lights, and security systems using AI.
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, saving time and cost.
- Accuracy: Reduces human error.
- 24/7 Availability: AI systems don’t require breaks.
- Data Analysis: Capable of analyzing large datasets quickly.
- Innovation: Drives breakthroughs in fields like medicine and education. Risks:
- Job Displacement: Automation may lead to unemployment in some sectors.
- Bias: AI systems can inherit biases from training data.
- Privacy: Collection and misuse of personal data.
- Security: Potential for AI in cyberattacks or autonomous weaponry.
- Lack of Accountability: Who is responsible when AI fails?
- AI Thinks Like Humans: Current AI is narrow and task-specific.
- AI Will Take Over the World: Reduces human error.
- AI Learns Without Data: AI relies heavily on large volumes of quality data.
- All AI Is Dangerous: Like any technology, its impact depends on how it is used.
- Data Protection Laws: GDPR in Europe.
- AI Ethics Guidelines: Promoting transparency, fairness, and accountability.
- Funding Research: Supporting AI development through public funding.
- Creating Task Forces: To monitor and guide the impact of AI on society. Countries like the U.S., China, and members of the EU are investing heavily in AI to maintain global competitiveness while ensuring ethical deployment.
- General AI: Progress toward machines that can perform any cognitive task.
- AI and IoT Integration: Smarter homes, cities, and industries.
- AI in Healthcare: Personalized medicine and robotic surgeries.
- Ethical AI: Development of systems that are transparent and accountable.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Enhancing human abilities rather than replacing them.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Branches of AI
How AI Works: Algorithms and Data
At the heart of AI are algorithms and data. Algorithms are step-by-step procedures or formulas for solving problems. AI systems use these algorithms to process data and learn from it. Data is the fuel of AI, providing the necessary information to train and improve models. The process typically involves
Do You Want to Learn More About Web Developer? Get Info From Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Popular AI Tools and Platforms
Applications in Daily Life
AI is increasingly embedded in our daily lives:
Benefits and Risks of AI
Benefits:Role in Automation and Innovation
AI is revolutionizing automation by enabling machines to perform complex tasks without human intervention. In manufacturing, AI-driven robots can assemble products, detect defects, and manage supply chains. In software, AI automates customer service, data entry, and fraud detection. AI also fuels innovation, helping researchers discover new drugs, engineers design smarter systems, and educators provide personalized learning.
Myths About AIGovernment and Regulation of AI
Governments around the world are beginning to implement regulations to ensure AI is used ethically and responsibly. This includes:
The Road Ahead for AI
The future of AI is promising but uncertain. Advancements in AI are expected to continue at a rapid pace, impacting every sector. Some key trends include:
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is more than just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force reshaping how we live, work, and interact. While it offers enormous potential for innovation and efficiency, it also poses challenges that require careful management. As we move forward, a balanced approach to AI development and deployment guided by ethics, inclusivity, and accountability will be essential in unlocking its full benefits for humanity. With the possibilities of further advancements and greater utility in a range of fields, artificial intelligence also has a promising future. To make AI developed and utilized responsibly, it is important to look into the ethical and societal implications surrounding it. We can leverage AI’s potential to enhance everyone’s future if we adopt it responsibly and with foresight.





