- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- The Evolution of AI: From Concept to Reality
- Pros of Artificial Intelligence
- Cons of Artificial Intelligence
- AI in Various Industries
- Ethical Considerations and Challenges
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence
- Conclusion
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on creating machines and systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from data, recognizing patterns, understanding natural language, making decisions, and solving complex problems. The goal of AI is to develop intelligent agents that can perceive their environment, reason about it, and take actions to achieve specific objectives. AI encompasses a variety of techniques, including machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. Machine learning, a core subset of AI, enables systems to improve their performance automatically by learning from data without explicit programming through Data Science Training. Deep learning, a more advanced form of machine learning, uses neural networks to model complex patterns in large datasets. The applications of AI are vast and growing rapidly, impacting industries such as healthcare, finance, automotive, and customer service. AI powers technologies like virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, recommendation systems, and fraud detection. While AI promises increased efficiency, innovation, and new capabilities, it also raises important ethical and societal questions regarding privacy, job displacement, and decision transparency. Overall, Artificial Intelligence represents a transformative technological force shaping the future of how humans interact with machines and data, offering both exciting opportunities and challenges.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
The Evolution of AI: From Concept to Reality
The evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a remarkable journey from a theoretical concept to a transformative reality impacting numerous aspects of modern life. The idea of creating machines that mimic human intelligence dates back to ancient times, but AI as a formal field began in the mid-20th century. In 1956, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined at the Dartmouth Conference, marking the birth of AI research and laying the foundation for techniques like Top Python Libraries For Data Science. Early efforts focused on symbolic reasoning and rule-based systems, attempting to program machines with explicit instructions to solve problems. Progress was initially slow due to limited computing power and a lack of large datasets. The field experienced periods of high optimism, known as AI summers, and setbacks called AI winters, when funding and interest declined.
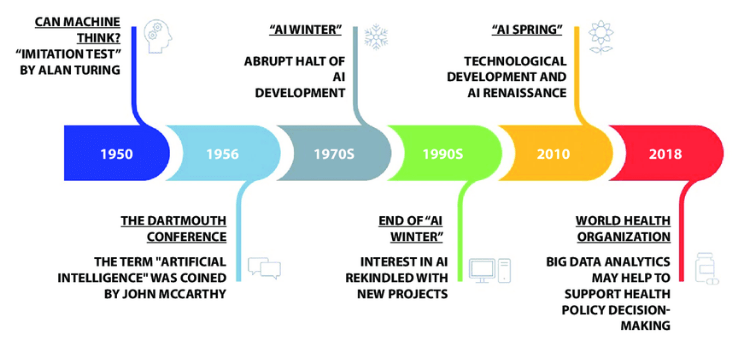
A breakthrough came with the rise of machine learning in the 1980s and 1990s, shifting the focus from hard-coded rules to systems that learn from data. The explosion of big data and advances in computing power in the 21st century propelled AI into practical applications. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, enabled significant progress in image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. Today, AI powers technologies like virtual assistants, self-driving cars, and personalized recommendations, illustrating how far the field has evolved from concept to impactful reality.
Pros of Artificial Intelligence
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI can automate mundane and repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative activities, thus improving productivity.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI systems analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, helping businesses and organizations make better, data-driven decisions.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike humans, AI-powered systems can operate continuously without fatigue, providing constant service and support, such as in customer service chatbots or monitoring systems.
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: AI algorithms can perform tasks with high precision, reducing errors in fields like medical diagnosis, manufacturing, and financial forecasting, which is explained by What is Logistic Regression.
- Personalization: AI enables personalized experiences by analyzing user behavior and preferences, which enhances marketing, recommendations, and user engagement.
- Handling Complex Data: AI excels at processing and interpreting large, complex datasets that are difficult for humans to analyze efficiently.
- Innovation and New Opportunities: AI drives innovation across various industries, leading to new products, services, and business models, fostering economic growth and technological advancement.
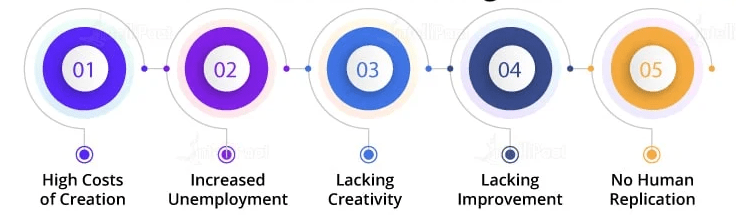
- Job Displacement: AI automation can replace human workers in many industries, leading to unemployment and social challenges, especially for low-skilled jobs.
- High Implementation Costs: Developing and deploying AI systems often require significant investment in hardware, software, and expertise, making it inaccessible for smaller organizations.
- Lack of Transparency: Many AI models, especially deep learning systems, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes and raising trust issues in Data Science Training.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can inherit biases present in training data, resulting in unfair treatment or discrimination in areas like hiring, lending, or law enforcement.
- Security Risks: AI can be vulnerable to hacking, adversarial attacks, or misuse, which may lead to data breaches or malicious behavior.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of AI raises questions about privacy, surveillance, and consent, as well as broader moral issues about machines making critical decisions.
- Dependence on Data Quality: AI’s effectiveness heavily depends on the quality and quantity of data. Poor or insufficient data can lead to inaccurate or harmful outcomes.
- Data Privacy: Protecting personal and sensitive information from unauthorized access is critical. Misuse or leakage of data can harm individuals’ privacy and trust.
- Security Risks: AI and data-driven systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, manipulation, or adversarial inputs that compromise their reliability and safety.
- Job Displacement: Automation and AI may replace certain jobs, creating ethical concerns about workforce displacement, unemployment, socioeconomic inequality, and the use of Python Generators.
- Informed Consent: Users should be aware of how their data is collected, used, and shared. Obtaining genuine informed consent is often challenging but essential.
- Regulation and Accountability: Establishing clear laws and guidelines is necessary to govern the ethical use of AI and data science, ensuring developers and organizations are held accountable for misuse or harm.
- Bias and Fairness: Algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data, leading to unfair treatment or discrimination in areas like hiring, lending, or law enforcement.
- Transparency and Explainability: Many AI models, especially deep learning systems, act as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how decisions are made, which raises accountability issues.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Cons of Artificial Intelligence
AI in Various Industries
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming a wide range of industries by enhancing efficiency, improving decision-making, and enabling new innovations. In healthcare, AI is used for medical imaging analysis, disease diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and drug discovery, helping doctors provide better patient care. In the finance sector, AI powers fraud detection, algorithmic trading, risk management, and customer service through chatbots, improving security and operational efficiency. The automotive industry is leveraging AI to develop autonomous vehicles, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and predictive maintenance, promising safer and more efficient transportation through Python vs R vs SAS. In retail, AI helps optimize supply chains, personalize marketing, and improve customer experience through recommendation systems and demand forecasting. Manufacturing benefits from AI-driven automation, quality control, and predictive maintenance, increasing productivity and reducing downtime. The energy sector uses AI for smart grid management, energy consumption forecasting, and optimizing renewable energy sources. In entertainment and media, AI assists in content creation, recommendation engines, and audience analytics. These examples highlight how AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data and automate complex tasks is revolutionizing industries. As AI technology continues to advance, its applications will expand further, driving innovation and transforming the way businesses operate across the globe.
Looking to Master Data Science? Discover the Data Science Masters Course Available at ACTE Now!
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds immense promise, with the potential to revolutionize every aspect of society and industry. Advances in AI technology are expected to lead to smarter, more autonomous systems capable of performing increasingly complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Continued improvements in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision will enable AI to better understand and interact with the world, making technologies like autonomous vehicles, personalized medicine, and intelligent virtual assistants more widespread and effective. AI is also likely to drive innovation in emerging fields such as robotics, augmented reality, and quantum computing, opening new horizons for scientific discovery and practical applications in Why Data Science Matters & How It Powers Business Value. Moreover, AI will play a crucial role in addressing global challenges, including climate change, healthcare accessibility, and resource management, by enabling data-driven decision-making and automation. However, the future of AI also brings important ethical and societal considerations. Issues such as data privacy, bias, job displacement, and the need for transparent and accountable AI systems will require careful attention from policymakers, researchers, and industry leaders. Ensuring that AI development is responsible and inclusive will be key to maximizing its benefits while minimizing risks. Overall, AI’s future is one of tremendous opportunity and challenge, with the potential to fundamentally reshape how humans live, work, and interact with technology.
Preparing for a Data Science Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
In conclusion, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as one of the most transformative technologies of our time, reshaping industries, enhancing productivity, and driving innovation across various fields. From its early conceptual beginnings to today’s advanced applications, AI has evolved into a powerful tool capable of automating complex tasks, analyzing vast datasets, and enabling intelligent decision-making. Its impact spans healthcare, finance, automotive, retail, manufacturing, and beyond, offering solutions that improve efficiency, accuracy, and personalization. As AI continues to advance, it promises to unlock even greater potential through emerging technologies like robotics, natural language processing, quantum computing, and Data Science Training. However, the journey forward also brings significant challenges, including ethical considerations around privacy, fairness, transparency, and the socioeconomic effects of automation. Addressing these challenges responsibly will be critical to ensuring that AI benefits society as a whole. For professionals, researchers, and businesses alike, understanding AI’s capabilities and limitations is essential to harnessing its power effectively. By fostering collaboration between technology experts, policymakers, and society, we can guide AI development toward creating equitable, innovative, and sustainable solutions. Ultimately, AI’s future holds exciting possibilities that, when managed thoughtfully, can lead to profound improvements in how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.