
Introduction:
Kanban versus scrum is a conversation around two unique techniques for carrying out a light-footed turn of events or undertaking the board framework. Kanban philosophies are consistent and more liquid, while scrum depends on short, organized work runs.
Many Scrum teams also use Kanban as a visual process and project management tool. While some teams prefer to use only Scrum because of its prescriptive nature (there is less ambiguity), many Scrum teams have adopted select principles of Kanban that are useful in adding an extra layer of visibility to their projects.
Overview of the Difference between Scrum vs Kanban:
It’s not difficult to call attention to the contrasts between scrum rehearses and kanban rehearses, however that is exactly at the surface level. While the practices vary, the standards are to a great extent the equivalent. The two structures will assist you with building better items (and administrations) with less cerebral pains.
Spry is an organized and iterative way to deal with project the executives and item improvement. It perceives the instability of item improvement, and gives a philosophy to self-arranging groups to react to change without running wild. Today, nimble is not really an upper hand. Nobody has the privilege to foster an item for quite a long time or even a long time in a black box. This implies it’s a higher priority than at any other time to hit the nail on the head.
Kanban is tied in with picturing your work, restricting work underway, and expanding productivity (or stream). Kanban groups center around lessening the time an undertaking takes (or client story) beginning to end. They do this by utilizing a kanban board and persistently further developing their stream of work.
Scrum groups focus on transportation working programming through set spans called runs. They will likely make learning circles to rapidly assemble and coordinate client input. Scrum groups take on explicit jobs, make exceptional curios, and hold customary functions to keep things pushing ahead. Scrum is best characterized in The Scrum Guide.
Scrum: An organized lithe methodology
With scrum, your group vows to deliver some significant addition of work before the finish of each run. Scrum is based on experimentation, zeroing in on little additions of work that will assist you with gaining from your clients and better illuminate what you do straightaway. This is the way it separates:
Scrum rhythm
Scrum moves quick, with runs of two to at most a month with clear beginning and finish dates. The brief period of time powers complex undertakings to be parted into more modest stories and assist your group with learning.
Runs are interspersed by run arranging, run survey, and review gatherings and sprinkled with every day scrum (standup) gatherings. These scrum functions are lightweight and run consistently.
Discharge approach
These days, it’s normal to have specially appointed deliveries in scrum, yet it’s for quite some time been a best practice to deliver toward the finish of each run. Groups set a goal for each run, the run objective, and either supports it for discharge in the run survey meeting, or don’t.
Scrum Career
- The item proprietor advocates for the client, deals with the item build-up, and focuses on the work done by the improvement group.
- The scrum ace aides the group stay grounded in the scrum standards.
- The advancement group picks the work to be done, conveys augments, and shows aggregate responsibility.
- Who deals with the scrum group? All things considered, no one. Scrum groups are self-coordinating and everybody is equivalent, in spite of having various obligations.
- The group is joined by the objective of transportation worth to clients.
Scrum plays three obviously characterized parts.
Key measurements
Speed —The quantity of story focuses finished in a run is the focal measurement for scrum groups. It guides future run responsibilities, or how much work the scrum group takes on in ongoing runs. Assuming the group finishes a normal of 35 story focuses per run (Velocity = 35), it will not consent to a run accumulation that contains 45 focuses.
Change theoryGroups endeavor to not make scope changes during a run. Scrum groups once in a while get criticism and discover that what they’re dealing with isn’t as important to the client as they suspected. In such cases, the extent of the run should change to mirror the significance of delivery worth to the client most importantly. During the run review, scrum groups ought to talk about how to restrict change in future, as changes put the possibly shippable augmentation in danger.
Kanban: Continuous improvement, adaptable cycles
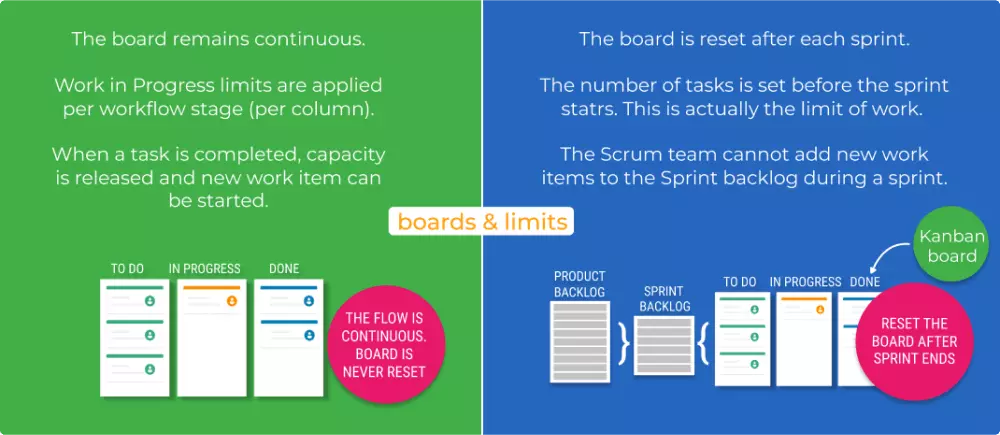
Kanban imagines your work, limit work underway (WIP) and as soon as possible move work from “Doing” to “Done.”
Kanban is extraordinary for groups that have bunches of approaching solicitations that fluctuate in need and size. Though scrum processes require high command over what is in scope, kanban we should you take the path of least resistance. How about we investigate similar five contemplations to assist you with choosing.
Kanban rhythm
Kanban depends on a nonstop work process structure that keeps groups agile and prepared to adjust to evolving needs. Work things—addressed via cards—are coordinated on a kanban board where they stream from one phase of the workflow(column) to the following. Normal work process stages are To Do, In Progress, In Review, Blocked, and Done. However, that is exhausting.
The most amazing aspect of kanban is making custom sections for how your group functions. My group ships content, so our columns(simplified) go from Backlog, to Prioritized, to Outlines Ready, to Writing, Designing, Technical Review, and Shipped. Our board assisted us with discovering that we transport around one piece of content each week, and where our bottlenecks are (checking out the Technical Review!).
Discharge technique
- In kanban, refreshes are delivered at whatever point they are prepared, without an ordinary timetable or foreordained due dates.
- In principle, kanban doesn’t recommend a proper chance to convey an assignment. Assuming the undertaking gets finished before (or later), it tends to be delivered depending on the situation without hanging tight for a delivery achievement like run audit.
Kanban Career
The entire group possesses the kanban board. A few groups enroll a deft mentor be that as it may, in contrast to scrum, there is no single “kanban ace” who keeps everything moving along as expected. It’s the aggregate liability of the whole group to team up on and convey the assignments on the board.
Key measurements
Lead time and process duration are significant measurements for kanban groups. The arrangement with the normal measure of time that it takes for an assignment to move beginning to end. Further developing process durations demonstrates the accomplishment of kanban groups.
The Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD) is one more scientific apparatus utilized by kanban groups to comprehend the quantity of work things in each state. CFDs assist with distinguishing explicit bottlenecks that should be settled for better throughput.
One more method for managing bottlenecks is through Work In Progress (WIP) limits. A WIP limit covers the quantity of cards that can be in any one segment at one time. At the point when you arrive at your WIP limit, a device like Jira Software covers that section, and the group swarms on those things to push them ahead.
Change reasoning
A kanban work process can change whenever. New work things can get added to the overabundance and existing cards can get impeded or taken out all together dependent on prioritization. Likewise, in the event that the group limit changes, WIP breaking point can be recalibrated and work things changed as needs be. Everything unquestionably revolves around being adaptable in kanban.
Scrum apparatuses versus kanban instruments
The spry local area accepts this discussion shouldn’t be about the apparatuses. We frequently see the instrument of decision driving the structure of decision and the system driving the standards the group embraces. We accept the choice should stream the other bearing.
Whenever you’re adjusted on scrum standards and content with the scrum structure, then, at that point, it’s an ideal opportunity to observe a scrum apparatus that serves you well. The equivalent goes for kanban. We’re one-sided, yet as the number 1 programming improvement apparatus utilized by lithe groups, we think Jira Software takes care of you.
With Jira’s committed undertaking types for scrum and kanban, you can understand the standards of every structure. We’re additionally here to assist you with getting everything rolling with our aides on the best way to do scrum with Jira programming and how to kanban with Jira Software.
Kanban versus scrum: What in the event that you mightn’t?
- Scrum and kanban are light-footed by-the-books. They work in a reliable design that is truth be told hard to contend against. Acquiring from another popular expression, you may say that, Nobody gets terminated for picking scrum.
- Yet, your choice shouldn’t be so highly contrasting. Many groups are utilizing cross breed models affected by both scrum and kanban. We set off to assist groups with doing in Jira Software, which is the reason we made group oversaw projects.
- Group oversaw projects, as the name proposes, permit groups to single out the deft highlights that seem OK for them; regardless of whether that is scrum, kanban, or a blend of both. Rather than executing one structure on the very first moment, group oversaw projects permit you to continuously layer on an ever increasing number of strong highlights as you realize what works for your group (and what doesn’t).
- You can unquestionably pick group oversaw Scrum or group oversaw Kanban realizing that the two layouts can develop to suit the necessities of your group.
- Despite what you pick, stay with it for a brief period. Take some work from the accumulation the whole way to done and afterward ask your group what worked out positively and what went inadequately. By attempting scrum and kanban and posing these inquiries, you’re well en route to dexterous rapture.
Conclusion:
Kanban programming deftly adjusts to any group, while Scrum instruments depend on a structure. Kanban depends on persistent improvement, and Kanban programming assists with dissecting the work process ceaselessly. In its turn, Scrum depends on the story focuses arranging, and the Scrum instruments just assist you with estimating how fruitful you are at meeting the assessment. Kanban programming allows you to restrict WIP to keep the group’s efficiency by offsetting work with genuine limit. Scrum programming keeps the group from beginning or changing the work line once the run has started, assisting with focusing on current things yet making it difficult to adjust to any change outside of runs.





