
- Introduction to Financial Management
- Objectives of Financial Management
- Importance in Business Organizations
- Functions of Financial Management
- Financial Planning
- Captial Structure Decisions
- Working Capital Management
- Investment Decisions
- Risk and Return Analysis
- Financial Reporting and Analysis
- Challenges in Financial Management
- Conclusion
Introduction to Financial Management
Financial management is a crucial aspect of running any business or organization. It involves planning, organizing, controlling, borrowing and monitoring financial resources with the aim of achieving the organization’s financial objectives. Financial management ensures that businesses are able to meet their financial goals, maintain financial stability, and effectively manage risks. The importance of financial management in today’s dynamic and competitive environment cannot be overstated, as it plays a key role in ensuring the survival, growth, and profitability of an organization. At its core, financial management is concerned with the decision-making processes that affect the financial health of an organization. These decisions include how to allocate resources, raise capital, investment management in assets, manage cash flow, and control expenses. In a nutshell, risk analysis, financial management is about making sound financial decision making that maximize value for stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, investing and customers.
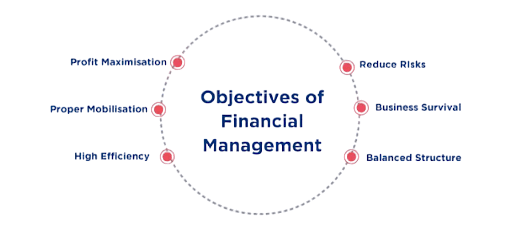
Objectives of Financial Management
The primary objectives of financial management can be categorized into several key areas:
- Profit Maximization: One of the key objectives of financial management is to ensure that the organization generates sufficient profit. Profit maximization aims to increase the organization’s earnings while minimizing costs and risks. However, it is important to note that profit maximization should not be pursued at the expense of long-term sustainability or ethical practices.
- Wealth Maximization: This objective focuses on increasing the overall wealth of the organization’s shareholders. Wealth maximization involves decisions that enhance the value of the organization’s stock and, by extension, increase the wealth of shareholders. It includes decisions on investing, risk analysis, capital structure, budgeting and dividend policies.
- Liquidity Management: Ensuring the organization has enough liquidity to meet its short-term obligations is another key objective. Financial management involves balancing the need for liquidity with the need for profitability. A company needs to manage cash flows efficiently to avoid liquidity crises.
- Risk Management: Financial management helps businesses understand and manage the various borrowing, financial risks they face, including market risks, credit risks, and operational risks. Managing these risks helps ensure the financial health and sustainability of the organization.
- Resource Allocation: Financial management ensures that the organization’s resources are allocated efficiently and effectively to maximize returns on investments.
- Optimal Capital Structure: A well-balanced capital structure (combination of debt and equity) is critical to reducing financial risks and maintaining financial stability.
- Strategic Planning: Financial management provides the necessary tools and data to help business leaders make informed strategic decisions.
- Profitability and Growth: By maintaining a focus on profitability and growth, financial management helps organizations expand their market presence, increase revenue, and achieve long-term goals.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Effective financial management builds trust and confidence among investors, decision making, creditors, and other stakeholders, which is essential for securing capital and business partnerships.
- Financial Control: Financial management helps businesses monitor their financial performance, control costs, and ensure that they stay within their budget.
- Financial Planning: This involves preparing financial projections, setting financial goals, and creating a budget to guide financial decisions. Financial planning helps ensure that the organization has sufficient funds for its operations and strategic initiatives.
- Investment Decisions: Investment decisions involve determining where to allocate funds in order to achieve the highest possible return while managing risk. This includes evaluating potential investments in assets, stocks, or other opportunities.
- Financing Decisions: Financing decisions revolve around how to raise capital for the organization, whether through debt, equity, or a combination of both. This decision also involves determining the optimal capital structure that minimizes costs while maximizing returns.
- Dividend Decisions: Financial management also involves deciding how much of the profit should be paid out to shareholders as dividends, and how much should be retained in the business for reinvestment.
- Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and managing the financial risks faced by the organization, including interest rate risk, currency risk, and credit risk.
- Uncertainty in Financial Markets: Fluctuations in interest rates, currency values, and commodity prices can create significant risks.
- Globalization: Managing financial operations across multiple countries and currencies presents complexities, especially in terms of tax laws, regulations, and currency exchange.
- Cash Flow Management: Ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet short-term obligations is an ongoing challenge, particularly for small businesses.
- Technology: Adopting new financial technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data, requires significant investment and understanding of the associated risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up with changing regulations and compliance requirements can be a significant burden for financial managers.
Importance in Business Organizations
Financial management is crucial to business organizations for several reasons:
Functions of Financial Management
The primary functions of financial management include:
Financial Planning
Financial planning is a critical function within financial management, involving the process of estimating the capital required and determining its competition. This aspect of financial management deals with forecasting both short-term and long-term financial needs, taking into account external factors, such as market conditions, and internal factors, budgeting such as cash flow and revenue projections. The process of financial planning starts with setting clear financial goals for the business, followed by identifying the resources required to achieve those goals. Planning involves careful analysis and forecasting, with the ultimate aim of ensuring the business has the necessary funds to continue operations, investing in growth, and weather economic uncertainties.
Capital Structure Decisions
Capital structure decisions are essential to financial management as they deal with how a company finances its overall operations and growth through different sources of funds, such as debt and equity. The decision regarding the optimal capital structure is one of the most important aspects of financial management because it directly impacts a company’s profitability and risk. A well-balanced capital structure reduces the cost of capital and maximizes the value of the business. Debt financing (e.g., loans, bonds) allows a company to leverage its operations and expand without diluting ownership, while equity financing (e.g., issuing stock) involves selling ownership in the business in exchange for capital. The decision-making process in this regard involves evaluating the risks and benefits of each type of financing.
Working Capital Management
Working capital management focuses on managing a company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure it has enough liquidity to carry out its day-to-day operations. Effective working capital management ensures that a company can meet its short-term obligations while maximizing its efficiency in using available resources. The key components of working capital include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable. Financial managers focus on optimizing the balance between these components to improve liquidity, profitability, and operational efficiency. A company needs to strike the right balance between having enough working capital to avoid liquidity issues and minimizing the costs of holding excessive inventories or overcapitalized receivables.
Investment Decisions
Investment decisions refer to the process of determining which projects or assets the company should invest in to achieve its financial budgeting.This includes evaluating potential investment management, determining their expected return, and assessing their risk. Investment decisions are often based on metrics such as the net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and payback period. A company needs to be strategic in its investment decisions to ensure that funds are allocated effectively. This process also involves selecting projects or investments that align with the company’s long-term goals, whether those goals involve expanding operations, developing new products, or entering new markets.
Risk and Return Analysis
In financial management, risk analysis and return analysis is a key aspect of decision-making. Every investment carries some level of risk, and the potential return is often correlated with the amount of risk taken. The goal of risk and return analysis is to evaluate the expected return on an investment in light of the associated risks. Financial managers assess various types of risks, including market risk, credit risk, and operational risk. They use tools such as the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and portfolio theory to assess the risk-return trade-off and make informed investment decisions.
Financial Reporting and Analysis
Financial reporting and analysis involve preparing financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, to reflect the company’s financial performance. These reports provide essential information to stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and management, about the company’s financial health. Financial analysis involves interpreting the data in these reports to assess profitability, liquidity, solvency, risk analysis and operational efficiency. Financial ratios, such as return on investment (ROI), debt-to-equity ratio, and current ratio, are commonly used to evaluate the company’s financial performance and make comparisons with industry benchmarks.
Challenges in Financial Management
Financial management faces several challenges, including:
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial management is a vital function for the survival and growth of any business. It involves a comprehensive approach to planning, managing risks, making investment decision making, borrowing and optimizing capital structure. By focusing on key aspects such as financial planning, risk analysis, working capital management, and investment strategies, financial managers can ensure the long-term success and profitability of the organization. While challenges such as economic volatility and regulatory compliance persist, the role of financial management remains central to maintaining stability and ensuring the organization’s continued financial health. Effective investment management financial management is, therefore, a cornerstone of business success, fostering sustainable growth and maximizing shareholder value.





