
- Introduction to Organizational Behavior
- Importance in Business
- Key Elements of Organizational Behavior
- Organizational Culture
- Motivation and Leadership
- Team Building and Group Dynamics
- Communication in Organizations
- Conflict Management
- Decision-making Processes
- Change Management
- Future Trends
- Conclusion
Introduction to Organizational Behavior
Organizational Behavior (OB) is the study of human behavior in organizational settings. It examines how individuals, groups, and structures influence and are influenced by behavior within an organization. This multidisciplinary field integrates principles from psychology, sociology, management, and anthropology to understand and improve organizational effectiveness. In any business or organization, individuals and groups exhibit behavior that can have a significant impact on productivity, Job satisfaction, employee satisfaction, external environment and overall performance. Understanding organizational behavior allows managers and leaders to guide employees, facilitate change, and design systems that promote a positive work environment. By analyzing patterns in behavior, OB provides insights into the various dynamics of the workplace, helping organizations optimize their processes and resources.
Importance in Business
Organizational Behavior plays a critical role in the success of any business. By understanding OB, businesses can address various challenges, improve communication, reduce turnover, enhance team collaboration, and ultimately increase profitability. Its importance can be broken down into the following areas:
- Improved Management Practices: OB helps leaders understand the motivations, needs, and behaviors of their employees, leading to better management practices that enhance productivity and morale.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: By fostering a supportive work culture and providing employees with the necessary tools and support, OB helps boost employee engagement, leading to higher retention rates.
- Conflict Resolution: OB also plays a role in resolving conflicts and tensions that may arise within an organization, fostering a harmonious work environment.
- Effective Decision Making: By understanding the behaviors that drive decision-making, OB allows managers to make informed, strategic decisions that are in line with the organization’s goals.
- Organizational Change: With a deep understanding of how individuals and groups react to change, OB helps businesses implement and manage transitions smoothly, reducing resistance and ensuring positive outcomes.
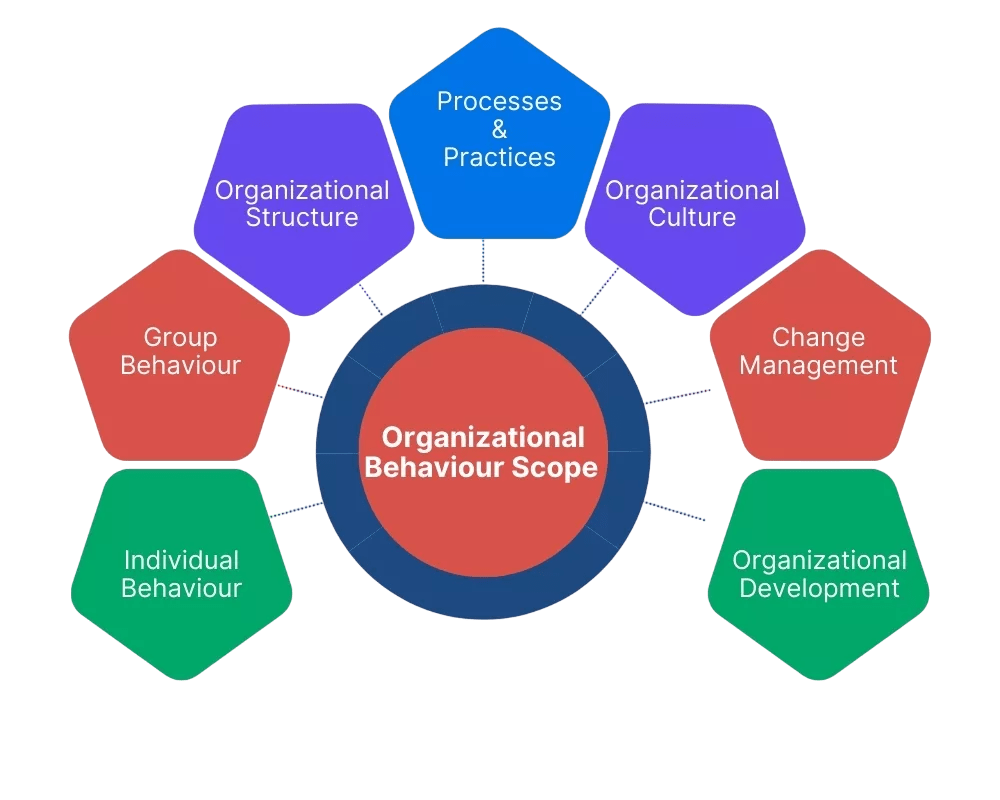
Key Elements of Organizational Behavior
Organizational Behavior consists of several key elements that impact both individual and group dynamics. These elements are foundational for understanding how behavior shapes an organization’s culture, Team building, effectiveness, and performance.
- Individual Behavior: This refers to the actions, attitudes, perceptions, and values of an individual within the organization. Factors such as personality, motivation, and perception influence individual behavior.
- Group Behavior: Groups play a crucial role in organizational success. OB studies group dynamics, including team formation, group norms, communication patterns, and decision-making processes.
- Organizational Systems: Organizational behavior also looks at the systems within an organization—structures, processes, and policies—that guide the human behavior of individuals and groups. The design of these systems can significantly impact productivity and morale.
- External Environment: Factors outside the organization, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and cultural influences, also affect organizational behavior.
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture is the set of shared values, beliefs, and practices that shape the way employees behave within an organization. It is a powerful force that dictates how individuals and teams interact, how decisions are made, and how the organization responds to internal and external changes. An organization’s culture can be influenced by its founders, leadership, industry, and history. A positive culture promotes collaboration, innovation, and employee satisfaction, while a negative culture can lead to high turnover, low morale, and inefficiency. There are various types of organizational cultures, ranging from hierarchical (focused on structure and authority) to flexible (promoting creativity and innovation). The key is to align the culture with the company’s vision, mission, and goals.
Motivation and Leadership
- Motivation is a critical aspect Scope of organizational behavior. It refers to the forces that drive individuals to take action, achieve goals, and perform tasks.
- Motivation influences how employees’ external environment approach their work and how engaged they are in their roles.
- There are several motivational theories, such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, and McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y, each of which offers insights into what drives employee behavior and performance.
- Leadership is also a key element in OB, as effective leadership influences motivation and helps guide employees toward achieving organizational goals.
- Leaders inspire, influence, and provide direction. Leadership styles vary, from autocratic (centralized control) to democratic (shared decision-making).
- A leader’s ability to understand and motivate their team significantly impacts productivity and employee morale.
- Communication in Scope of Organizational Behavior is the lifeblood of any organization.
- It is essential for disseminating information, aligning team building with organizational goals, and fostering collaboration.
- Effective communication in Organizations helps reduce misunderstandings, clarify roles, and ensure that employees understand their responsibilities.
- In organizational behavior, communication is viewed as both a process and a tool.
- Communication processes involve encoding, transmitting, and decoding messages, while communication tools include face-to-face interactions, emails, memos, meetings, and digital platforms.
- Barriers to effective communication, such as language differences, cultural norms, and organizational hierarchy, must be overcome to ensure clear and accurate information exchange.
- Open, transparent, and timely communication promotes trust and cooperation, leading to improved organizational performance.
- In organizations, decision-making is a critical process that affects strategy, operations, and outcomes.
- Scope of Organizational Behavior examines how individuals and groups make decisions, both rationally and emotionally. It looks at the factors that influence decision-making, such as cognitive biases, groupthink, and risk tolerance.
- Decision-making processes can be centralized or decentralized, with varying levels of input from employees at different levels.
- The effectiveness of decision-making depends on the quality of the information, the diversity of perspectives, and the speed with which decisions are made.
- Leaders and managers play a key role in facilitating effective decision-making by providing the right information, ensuring diverse viewpoints, and encouraging collaboration.
- OB highlights how a structured decision-making process can lead to better outcomes and fewer mistakes.
Team Building and Group Dynamics
Effective team building is essential for organizational success. Teams are composed of individuals with complementary skills and diverse perspectives, and their ability to work together determines their overall success. Organizational Behavior provides insights into how teams develop, function, and overcome challenges. Team dynamics are the invisible forces that influence the interactions and performance of a group. These dynamics can either enhance or hinder group effectiveness. Factors like communication, trust, role clarity, and conflict management play a crucial role in the functioning of teams. OB emphasizes the importance of building trust and encouraging open communication to foster collaboration importance in Business. Group dynamics also relate to how power, authority, and leadership are distributed among team members. Understanding group behavior allows leaders to guide teams in a way that capitalizes on individual strengths and minimizes weaknesses.
Communication in Organizations
Conflict Management
Conflict is an inevitable part of any organization. It arises due to differences in opinions, goals, values, or expectations. While conflict can be disruptive, it can also serve as a catalyst for change and improvement if managed properly. Organizational behavior provides strategies for managing and resolving conflicts, ensuring they don’t escalate into larger problems. Conflict management styles range from avoidance to collaboration, depending on the situation. Effective conflict management involves understanding the underlying causes of disputes and finding solutions that satisfy all parties involved. It is essential for leaders to encourage healthy conflict resolution strategies, as unresolved conflicts can lead to reduced morale, increased stress, and poor team performance.
Decision-making Processes
Change Management
Change is constant in today’s business environment. Organizational behavior provides valuable insights into how organizations can manage and adapt to change effectively. Change management involves planning, implementing, Job satisfaction and monitoring changes within an organization to ensure they are successful. OB highlights the psychological and emotional impact of change on employees and provides strategies to reduce resistance to change. Key elements of successful change management include clear communication, employee involvement, training, and leadership support. By understanding the behaviors and reactions of employees during periods of change, organizations can ensure smoother transitions and more successful outcomes.
Future Trends
The future of Organizational Behavior is influenced by technological advancements, globalization, and evolving work environments. Trends such as the rise of remote work, the increased focus on employee well-being, and the use of AI in decision-making processes will shape how organizations approach OB in the future. Organizations will continue to prioritize diversity, equity, and inclusion, as these factors are critical for fostering innovation, creativity, and employee satisfaction. Additionally, the increased use of data analytics in OB will allow organizations to better understand employee behavior and make more informed decisions.
Conclusion
Organizational group Behavior is a vital field of study for understanding the complexities of human behavior within organizations. By applying OB principles, businesses can enhance management practices, improve employee engagement, and foster a positive work culture. As organizations evolve and face new challenges, understanding OB will remain essential for promoting collaboration, Job satisfaction, managing change, external Environment and achieving long-term success. Embracing OB insights not only leads to better decision-making and improved team dynamics but also prepares organizations for a rapidly importance in business landscape.





