
- Introduction to Compensation Management
- Components of Compensation
- Objectives of Compensation
- Factors Influencing Compensation
- Pay Structures
- Job Evaluation Methods
- Performance-Based Pay
- Incentives and Bonuses
- Legal Aspects
- Global Compensation Practices
- Compensation Trends
- Summary
Introduction to Compensation Management
Compensation management refers to the processes and strategies employed by an organization to determine the appropriate compensation for its employees.
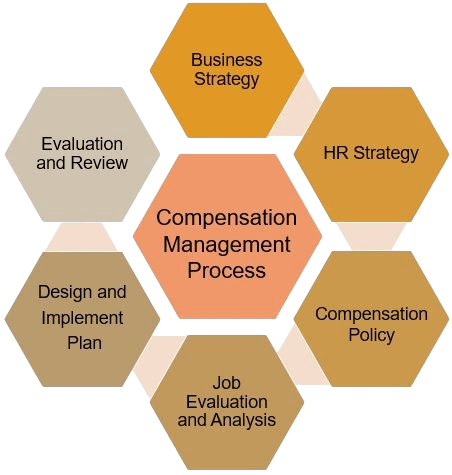
It involves designing, implementing, and administering policies that align with the company’s goals, culture, and legal requirements while ensuring fair and equitable pay for employees. Compensation management is essential for attracting, retaining, and motivating talent, and it plays a crucial role in shaping the employee experience. It can include various components, such as base salary, bonuses, benefits, and other perks. Effective compensation management contributes significantly to employee satisfaction, productivity, and organizational success.
Components of Compensation
Type of Components of Compensation Management consists of several key components that provide employees with both financial and non-financial rewards. These components can be broadly categorized into direct and indirect compensation.
Direct Compensation:- Base Salary: This is the fixed amount of money an employee receives regularly (weekly, monthly, or annually) as agreed upon in their employment contract.
- Wages: For hourly workers, compensation is based on the number of hours worked, often paid on a weekly or biweekly basis.
- Overtime Pay: Employees who work beyond their regular hours are entitled to overtime compensation, often calculated at a higher hourly rate. Indirect Compensation:
- Benefits: This includes health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other non-cash benefits.
- Perks: These are non-monetary incentives, such as flexible work hours, wellness programs, company events, or professional development opportunities.
Objectives of Compensation
The primary objectives of Compensation Management in HRM Meaning are to ensure that employees are rewarded fairly for their contributions while also aligning the organization’s compensation strategy with its business goals. The main objectives include:
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Factors Influencing Compensation
Several factors influencing compensation is structured within an organization. These factors can include:
- Industry Standards: The compensation provided by other organizations within the same industry plays a significant role in determining an organization’s compensation structure. Companies must stay competitive to attract top talent.
- Company’s Financial Position: The health of a company dictates how much it can afford to pay its employees. Organizations with stronger resources tend to offer higher compensation packages.
- Geographical Location: The cost of living in a particular location influences compensation. Employees in cities with higher living costs are often paid more to compensate for the increased expenses.
- Employee’s Experience and Skill Level: Compensation is often influenced by an individual’s experience, education, and skills. Highly experienced employees with specialized skills are typically compensated at a higher rate than entry-level workers.
- Market Demand and Supply: The demand for certain skill sets, along with the supply of qualified candidates, can affect compensation levels. For example, in fields like technology and healthcare, there may be a higher demand for workers, leading to higher wages.
Pay Structures
Pay structures refer to the way an organization organizes its compensation system to ensure consistency and fairness. A pay structure typically consists of salary ranges, job classifications, and pay grades. Key elements of pay structures include:
- Salary Ranges: These are defined salary bands that set the minimum and maximum pay for each role within the company. Employees are typically placed within these ranges based on their qualifications, experience, and job performance.
- Job Classifications and Pay Grades: Companies may use job classifications to group similar positions, which then fall within specific pay grades. This allows for consistency in pay decisions and ensures that employees with similar responsibilities and skill sets are compensated similarly.
- Market-Based Pay: Some organizations choose to structure their compensation around the market rate for specific roles. This involves researching industry salary surveys and adjusting compensation packages based on what competitors are offering.
- Senior vs. Junior Pay Levels: Pay structures are also defined by employee rank or seniority. More experienced employees typically earn higher salaries than less experienced ones within the same job classification.
Job Evaluation Methods
Job evaluation is the process of determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization. It helps in establishing a fair and equitable pay structure by assessing the complexity, skill level, and responsibility of different roles. Common job evaluation methods include:
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Performance-Based Pay
Performance-based pay is a compensation system where employees are rewarded based on their job performance. This type of compensation motivates employees to work harder and meet organizational goals. There are various types of performance-based pay, including: Bonuses: Bonuses are additional payments given to employees based on their performance. These can be awarded annually, quarterly, or for specific achievements or milestones.
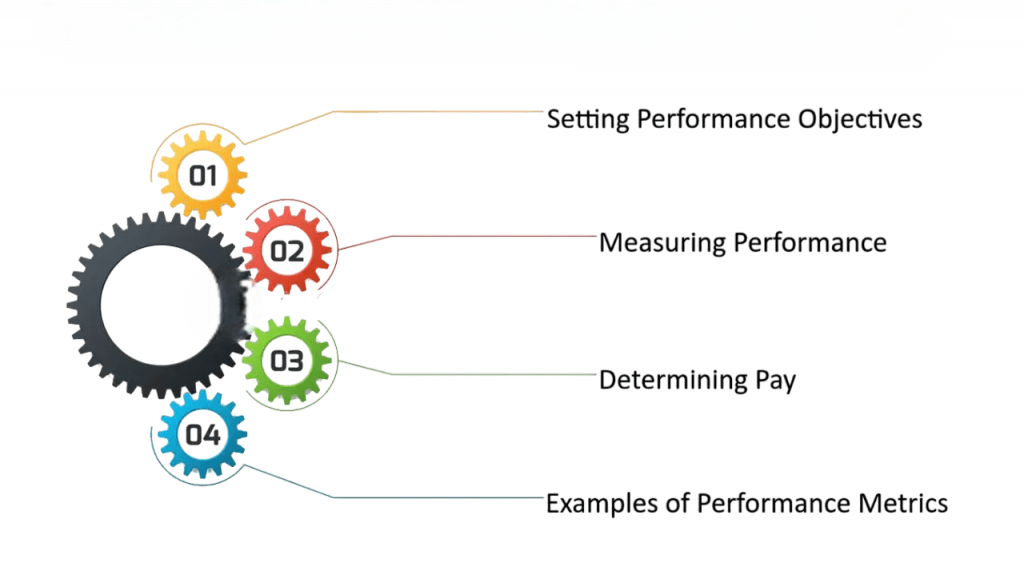
- Commission-Based Pay: Common in sales, commission-based pay ties an employee’s compensation directly to their performance, typically as a percentage of the sales they generate.
- Profit Sharing: Employees receive a share of the company’s profits, which incentivizes them to contribute to the company’s overall success.
- Merit Pay: Merit-based pay increases are awarded based on an employee’s performance during their annual review, rewarding those who meet or exceed performance expectations.
Incentives and Bonuses
Incentives and bonuses are additional forms of compensation designed to motivate employees to achieve specific goals or targets. These can vary based on job roles, industries, and organizational objectives. Examples include:
- Sales Incentives: Sales teams may receive a bonus or incentive based on the volume of sales they achieve.
- Team-Based Incentives: These rewards are given to entire teams for achieving collective performance goals, fostering collaboration and teamwork.
- Spot Bonuses: Given on the spot as a reward for exceptional work, often used for short-term achievements or extraordinary contributions.
- Retention Bonuses: Offered to employees to encourage them to stay with the company, particularly in competitive industries.
Legal Aspects
Compensation management in HRM must adhere to various legal regulations and standards to avoid legal issues and ensure fair practices. These include:
- Minimum Wage Laws: Governments set minimum wage rates that employers must pay their employees. Failing to comply can result in penalties.
- Overtime Regulations: According to labor laws, employees working beyond a certain number of hours must be compensated with overtime pay, typically at a higher rate.
- Equal Pay for Equal Work: Legal standards prevent gender, race, or other discriminatory pay practices. Companies must ensure that employees are paid fairly for equal work.
- Taxation: Employers must also comply with tax laws, withholding the appropriate amount of tax from employee wages and making contributions to social security or pension plans.
Global Compensation Practices
Compensation practices can vary significantly across countries due to differences in labor laws, economic conditions, and cultural norms. Organizations with a global presence must navigate these differences to establish fair and competitive compensation systems. Global compensation strategies often involve:
- Adapting to Local Laws and Regulations: Each country has unique rules about minimum wages, benefits, taxes, and work hours, and companies must comply with these laws.
- Currency and Exchange Rates: When compensating employees in different countries, currency fluctuations and exchange rates must be considered to ensure fair pay.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Compensation packages should be sensitive to local cultural preferences, such as benefits that align with local practices or holidays.
- Expats and Expatriate Packages: Companies often offer specialized compensation packages for employees working in foreign countries, including allowances for housing, travel, and cost of living adjustments.
Compensation Trends
Compensation trends are continuously evolving due to changes in the economy, technology, and workforce expectations. Some notable trends include:
- Flexible Pay Packages: Employees now prefer more personalized compensation packages, which may include options for remote work, health and wellness benefits, and flexible schedules.
- Employee Benefits Over Base Salary: Many companies are offering better employee benefits, such as mental health support, stock options, and paid family leave, to attract top talent.
- Transparency and Fair Pay Practices: With growing demands for fairness, many organizations are becoming more transparent about how compensation is determined, using structured and equitable pay systems.
- Pay for Skills: As the labor market evolves, some companies are shifting from traditional pay-for-role structures to pay-for-skills models, compensating employees for the specific competencies and expertise they bring to the organization.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Summary
Components of Compensation management is a vital component of human resources, designed to attract, retain, and motivate employees while maintaining equity and legal compliance. Effective compensation strategies balance base salary, bonuses, benefits, and performance-based pay to support organizational goals and employee satisfaction. Factors such as industry standards, financial resources, location, and employee experience all influence compensation decisions. By understanding the components, objectives, and global trends in compensation management, organizations can create fair and competitive pay systems that drive success.





