
- What is a Business Model
- Importance in Business Planning
- Key Components
- Types of Business Models
- Business Model Canvas
- Revenue Models
- Subscription & Freemium Models
- E-commerce Business Models
- Startup vs Enterprise Models
- Case Studies
- Innovation in Business Models
- Conclusion
What is a Business Model
A business model refers to the fundamental framework that defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It outlines the strategies and plans a business uses to generate revenue, create customer value, and achieve profitability. A business model is essential for any organization as it guides operational decisions, helps attract investors, and ensures long-term sustainability. A well-defined business model aligns the company’s vision with its operational processes, revenue streams, and target market position. A business model can be compared to a blueprint for a company—it outlines the key aspects of how the business will operate, generate income, and succeed in its chosen market. Without a clear model, businesses may struggle to survive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Importance in Business Planning
Importance in business planning, a well-defined business model serves as the foundation upon which the company builds its operations, target market strategies, customer acquisition plans, and financial projections. The business model plays a critical role in shaping the company’s decisions about product development, pricing, partnerships, and market expansion. A strong business model helps in:
- Guiding Decision-Making: By providing a clear structure, the business model assists leadership in making informed choices about resource allocation, operations, and strategic direction.
- Attracting Investment: Investors want to know how the business will generate revenue and grow. A compelling business model makes the company more appealing to potential investors.
- Differentiation: In competitive markets, the business model can help a company differentiate itself by offering unique value propositions and customer experiences.
- Risk Management: Understanding the business model allows a company to anticipate market trends and adapt to potential risks, improving its resilience.
Without a strong business model, businesses may face operational inefficiencies, financial instability, and difficulty in attracting customers and investors.
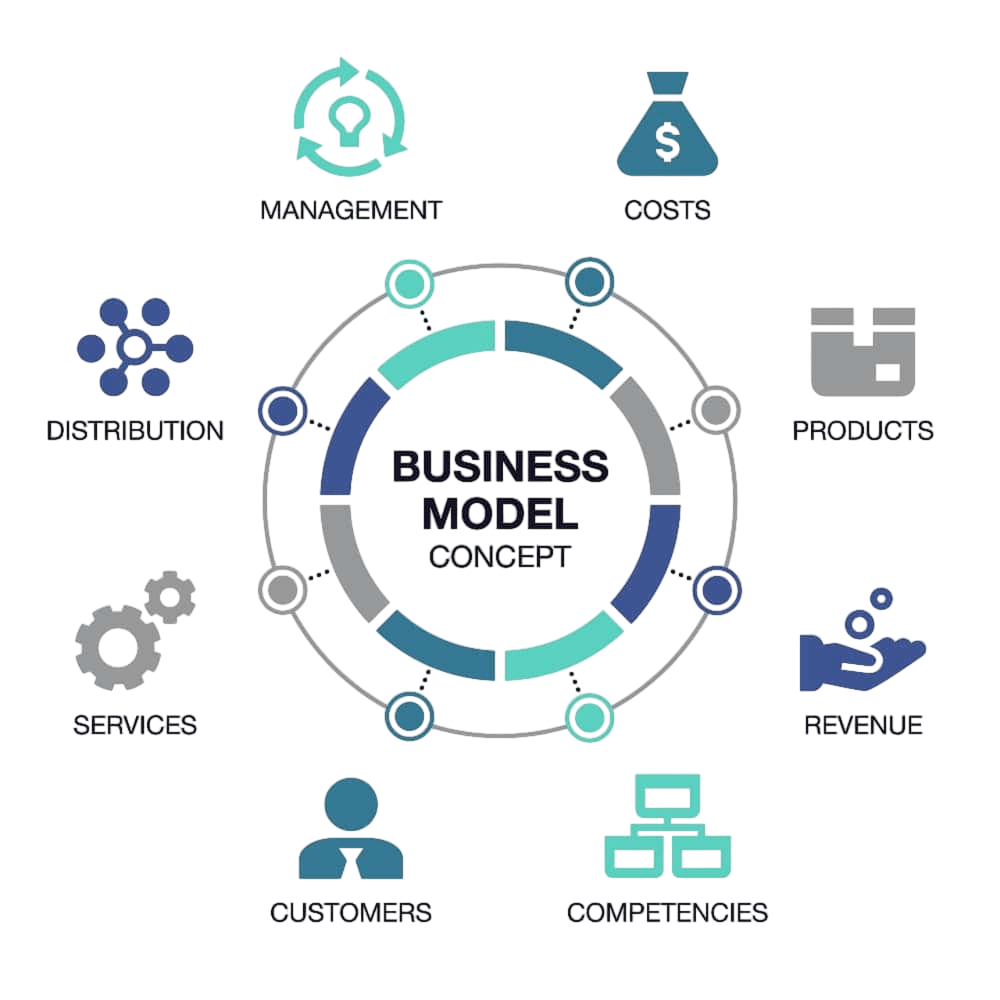
Key Components
A business model consists of several key components that collectively define how a company operates and generates profit. The most commonly discussed components include: Value Proposition: This is the unique value that the company offers to its customers. It answers the question, “Why would customers choose this company over competitors?”
- Customer Segments: A business model identifies who the company’s target customers are. This could include specific industries, demographics, or geographical regions.
- Revenue Streams: This defines how the company makes money. It could include direct sales, subscription fees, licensing, or advertising revenue.
- Channels: These are the pathways through which the company delivers its product or service to the customer, such as physical stores, online platforms, or partnerships with distributors.
- Customer Relationships: This outlines how the business interacts with its customers. It could involve personalized service, automated tools, or a self-service approach.
- Key Activities: These are the most important tasks that the company must perform to deliver its value proposition. This includes product development, marketing, sales, and customer support.
- Key Resources: These are the assets required to operate the business, such as intellectual property, physical assets, or skilled labor.
- Key Partnerships: Businesses often rely on partnerships with suppliers, distributors, or other companies to deliver their products or services.
- Cost Structure: This defines the main costs involved in operating the business, such as manufacturing, marketing, and distribution expenses.
- Service-Based Business Model: Companies offering services, such as consulting, legal advice, or financial planning, follow a service-based model. These businesses rely on expertise and human resources to generate revenue.
- Subscription-Based Business Model: Subscription businesses charge customers a recurring fee for access to products or services. Examples include Netflix, Spotify, and SaaS (Software as a Service) companies.
- Freemium Business Model: This model offers basic services for free while charging customers for premium features. Examples include LinkedIn, Dropbox, and Zoom.
- E-commerce Business Model: businesses sell products or services online, either directly to consumers (B2C) or to other businesses (B2B). This model has grown rapidly due to the rise of digital platforms and online shopping.
- Marketplace Business Model: In this model, a company connects buyers and sellers, typically through an online platform. Examples include Amazon, eBay, and Airbnb.
- Franchise Business Model: In a franchise, a company allows others to operate businesses under its brand name and provides a proven business model, training, and support. Examples include McDonald’s, Subway, and 7-Eleven.
- Sharing Economy Model: Companies in the sharing economy facilitate the sharing of goods or services, often through digital platforms. Examples include Uber, Lyft, and TaskRabbit.
- Customer Segments: Who are the target customers?
- Value Propositions: What unique value does the business offer?
- Channels: How does the business deliver its value?
- Customer Relationships: How does the business interact with customers?
- Revenue Streams: How does the business generate revenue?
- Key Resources: What resources are needed to create value?
- Key Activities: What critical tasks are necessary to run the business?
- Key Partnerships: Who are the business partners and suppliers?
- Cost Structure: What are the major costs of the business?
- Direct Sales: This involves selling products or services directly to customers in exchange for a one-time payment.
- Subscription: Companies charge customers a recurring fee, often monthly or annually, for continued access to products or services.
- Freemium: Customers can use basic services for free, with the option to upgrade to premium features or services for a fee.
- Advertising: Companies earn revenue by displaying advertisements to users. Examples include Google and Facebook.
- Licensing: Companies license their intellectual property, such as software or patents, to others in exchange for a fee.
- Commission-Based: Companies earn revenue by taking a commission on transactions between buyers and sellers. Examples include eBay and Airbnb.
- Subscription Model: Companies like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon Prime use subscription models, where customers pay for access to services or products over a specified period. This model helps businesses ensure predictable revenue and foster customer loyalty.
- Freemium Model: In the freemium model, companies offer basic services for free while charging for premium features. This is commonly used in software, apps, and online services. Popular examples include Dropbox, LinkedIn, and Zoom.
- B2C (Business to Consumer): Companies sell products or services directly to consumers through their online store. Examples include Amazon, Alibaba, and Walmart.
- B2B (Business to Business): Companies sell products or services to other businesses. Examples include wholesale distributors and manufacturers.
- C2C (Consumer to Consumer): This model involves individuals selling products or services to other individuals. Examples include eBay, Craigslist, and Etsy.
- C2B (Consumer to Business): In this model, individuals offer products or services to businesses. Examples include crowdsourcing platforms like Fiverr and 99designs.
- Startups: Startups typically have more flexible and experimental business models Challenges. They often focus on innovation, scalability, and disrupting existing markets. Their models may be more adaptable and pivot based on market feedback.
- Enterprises: Large enterprises have more established and structured business models. They focus on efficiency, market dominance, and long-term stability. Their models are often more complex and require significant resources.
- Amazon: Amazon started as a bookstore but transformed into the world’s largest platform by adopting a customer-centric business model. It leveraged cloud computing (Amazon Web Services) and built a global logistics infrastructure.
- Airbnb: Airbnb disrupted the hospitality industry with its peer-to-peer marketplace model. By connecting hosts with guests through its platform, it created a new way for people to travel and stay in unique locations.
- Netflix: Netflix evolved from a DVD rental service to a global streaming platform by adopting a subscription-based business model. It focused on content production and delivering personalized experiences.
Each component must work in harmony to create a successful business model. Companies need to continually assess and adjust these components to stay competitive and profitable.
Types of Business Models
There are several types of business models that companies use, depending on their industry, target market, and goals. Some of the most common business models include: Product-Based Business Model: In this model, companies sell physical products directly to customers. It’s one of the most traditional business models and includes manufacturers, retailers, and wholesalers.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a visual tool that helps entrepreneurs and businesses design, analyze, and refine their business models. It provides a clear and concise way to map out the key components of the business and understand how they relate to one another. Created by Alexander Osterwalder, the canvas includes nine building blocks:
The Business Model Canvas is a useful tool for startups and established businesses alike, as it helps streamline strategy development and offers a high-level overview of business operations.
Revenue Models
Revenue models are an integral part of any business model, as they define how a company earns money from its customers. Common revenue models include:
Each revenue model has its strengths and challenges. The choice of a revenue model depends on the type of business, customer preferences, and market conditions.
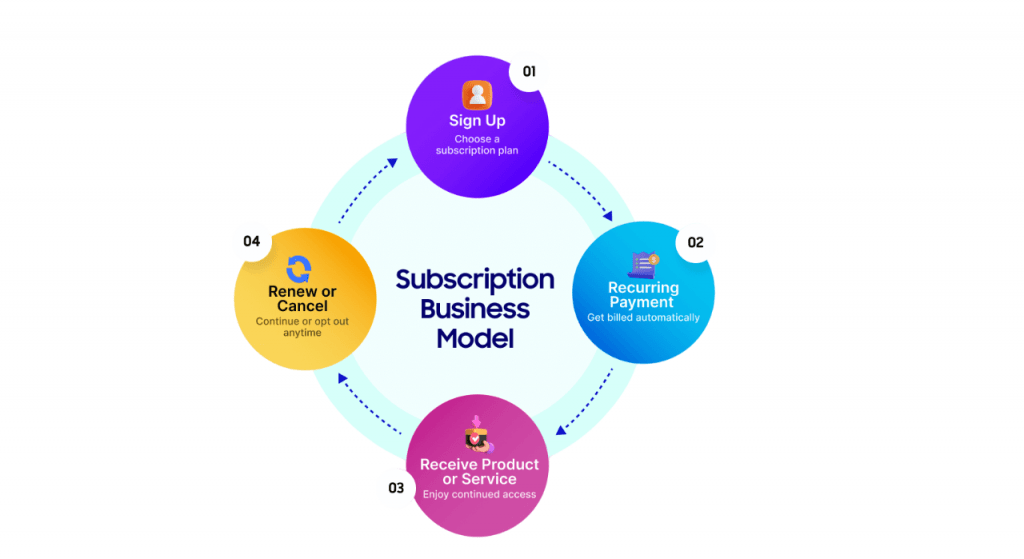
Subscription & Freemium Models
Subscription and freemium models have become increasingly popular in the digital design age. These models provide businesses with steady, recurring revenue streams while offering customers flexibility.
Both models have their advantages, such as customer retention and revenue predictability. However, they also require businesses to continually innovate and provide value to retain customers.
E-commerce Business Models
The has transformed how businesses operate, with several business models emerging to cater to online markets. These include:
The models have revolutionized the retail and service industries, offering flexibility and scalability to businesses while giving consumers more convenience.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Startup vs Enterprise Models
Startups and enterprises have different approaches to business modeling:
While startups tend to take risks in terms of business modeling, enterprises work within established frameworks to maximize profitability and manage operational complexity.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Case Studies
Innovation in Business Models
Innovation in business models is essential for companies to stay competitive. With the rise of technology, companies can continuously explore new revenue models, customer engagement strategies, and product offerings. Business model innovation can lead to disruptive companies that change industries and create new markets.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Conclusion
A business model is the core of any organization, determining how value is created, delivered, and captured. Understanding the components, types, target market and strategies for innovation in business models is essential for long-term success. Whether it’s through cloud computing, Customer Relationship, subscriptions, importance in business planning or disruptive models, Challenges, companies must continually evaluate and adapt their business models to thrive in a competitive world.





