
- Introduction to Strategic Management
- Definition and Key Concepts
- Role in Organizational Success
- Strategic Planning Process
- Enhancing Competitive Advantage
- Resource Allocation and Optimization
- Managing Business Growth
- Risk Management and Mitigation
- Improving Organizational Efficiency
- Long-term Vision and Goals
- Examples of Strategic Management in Companies
- Future Trends in Strategic Management
Introduction to Strategic Management
Importance Strategic Management is the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of all that is necessary for an organization to meet its goals and objectives. It involves defining a company’s direction and making decisions on allocating resources to pursue this direction. Strategic management provides a sense of purpose, aligning company activities with the overall vision and ensuring sustained competitive advantage. It is not just about setting goals but crafting detailed plans and deploying necessary measures to achieve and adapt to dynamic environments. Importance Strategic Management helps organizations stay proactive rather than reactive in the face of market challenges and opportunities.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Definition and Key Concepts
Strategic management can be defined as the art and science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating cross-functional decisions that enable an organization to achieve its objectives. It integrates both internal and external perspectives to drive performance. Key concepts within strategic management include strategy formulation, strategy implementation, competitive advantage, SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), and strategic control. Strategy formulation involves developing vision and mission statements, identifying external opportunities and threats, determining internal strengths and weaknesses, and establishing long-term objectives. Implementation focuses on mobilizing resources and motivating employees to execute the formulated strategies. Strategic control involves evaluating performance and making necessary adjustments.
For deeper insights, SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) is used to build multidimensional or tabular data models, enabling faster and more dynamic analysis. Finally, SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) provides robust reporting capabilities, allowing users to create detailed, paginated reports that can be delivered across various platforms. Together, these components of MSBI offer a comprehensive, integrated BI solution suitable for enterprise-level data management and decision-making.
Role in Organizational Success
Strategic management plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization. It ensures that a company is constantly analyzing its internal capabilities and external market conditions, making informed decisions, and adapting strategies to meet changes effectively. Companies that practice strategic management are more likely to outperform competitors as they are better prepared for uncertainties. Strategic management fosters innovation, increases operational efficiency, and ensures that all departments are working towards common organizational goals. It creates a clear roadmap for the future, ensuring that employees understand their role in achieving strategic objectives. Moreover, it promotes a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
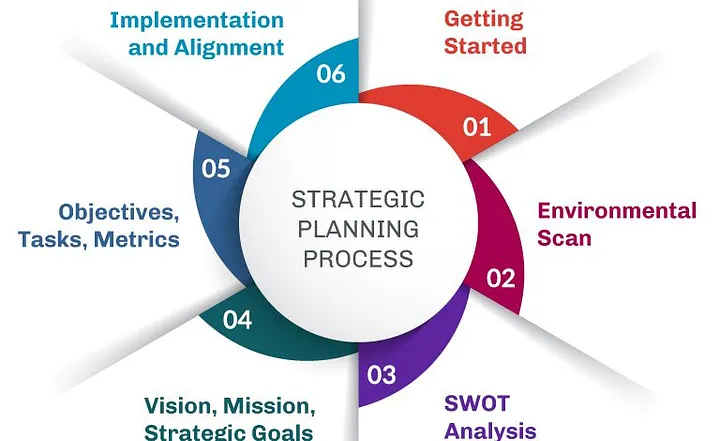
Strategic Planning Process
- The strategic planning process is structured and systematic. It usually begins with defining the organization’s mission and vision, which reflect the core purpose and aspirations.
- The next step involves conducting a thorough analysis of the internal environment (resources, capabilities) and the external environment (market trends, competition, regulations).
- Tools like SWOT analysis and PESTLE analysis are commonly used. Based on the analysis, strategic options are identified and evaluated for feasibility and potential impact.
- Organizations then set strategic goals, formulate action plans, allocate necessary resources, and assign responsibilities. The final steps involve implementation and ongoing evaluation, ensuring that the strategy remains relevant and effective in a changing environment.
- Every strategic initiative carries some level of risk, and managing this risk is an integral part of strategic management. Risks can stem from market volatility, technological disruptions, regulatory changes, or internal challenges.
- Through strategic planning, organizations can anticipate potential risks, assess their impact, and develop mitigation strategies. Risk management involves setting up controls, diversifying operations, building financial resilience, and creating contingency plans.
- Strategic management also encourages a proactive culture where risks are identified early, and employees are trained to respond effectively. By systematically addressing risks, strategic management minimizes the chances of major disruptions and ensures business continuity.
- Apple Inc., for instance, uses differentiation strategy by offering unique, high-quality products backed by a strong brand. Their strategic management ensures consistent innovation and customer loyalty.
- Amazon strategically focuses on cost leadership and customer service excellence, enabling it to dominate e-commerce and cloud computing markets.
- Tesla leverages a focused differentiation strategy, concentrating on cutting-edge electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions.
- These companies constantly analyze market trends, invest in research and development, and refine their strategies to maintain leadership positions. Their success stories highlight the critical role of strategic management in building and sustaining competitive advantage.
Enhancing Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage refers to the attributes that allow an organization to outperform its competitors. Strategic management enhances competitive advantage by helping firms recognize their unique strengths and market opportunities. Companies use strategies such as cost leadership, differentiation, and focus strategies to gain a competitive edge. Strategic management enables firms to invest in technology, talent, brand development, and customer relationships, creating value that is difficult for competitors to replicate. Continual innovation, understanding customer needs, and adapting to market shifts are essential components of sustaining competitive advantage, and strategic management ensures these activities are well-orchestrated and aligned with the organization’s broader goals.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Resource Allocation and Optimization
Efficient resource allocation is central to strategic management. It involves deciding where and how an organization’s resources time, money, talent, technology should be used to achieve maximum impact. Strategic management prioritizes initiatives that align with the organization’s goals, ensuring resources are not wasted on low-impact activities. It also optimizes resource utilization by identifying synergies across departments and projects, reallocating underutilized resources, and eliminating redundancies. By balancing short-term demands with long-term goals, strategic management helps in making informed investment decisions. It supports budgeting, staffing, technology deployment, and capital investments, ensuring that every resource contributes towards the strategic direction of the organization.
Managing Business Growth
Business growth, whether organic or through mergers and acquisitions, requires strategic oversight. Strategic management helps businesses scale sustainably by planning for expansion, identifying new markets, and diversifying product lines. It evaluates potential growth opportunities, such as entering new geographic regions, launching new products, or adopting new business models. Growth strategies are assessed for their risks and returns, and careful planning ensures that expansion does not dilute the core brand or stretch resources thin. Strategic management also facilitates leadership development and organizational restructuring to support growing operations. It ensures that growth initiatives are aligned with the company’s mission and vision, maintaining focus even as the organization evolves.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Risk Management and Mitigation
Improving Organizational Efficiency
Strategic management directly contributes to improved organizational efficiency. It identifies bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in processes and systems. By aligning resources, streamlining operations, and setting clear priorities, strategic management enhances productivity and reduces waste. It fosters a culture of accountability where performance metrics are regularly monitored, and improvements are continuously sought. Strategic initiatives often involve the adoption of new technologies and process innovations that automate tasks and reduce manual errors. Moreover, effective communication of strategic goals ensures that every department and employee is focused on activities that contribute the most towards organizational success, thereby maximizing overall efficiency.
Long-term Vision and Goals
A clear long-term vision is fundamental to guiding an organization’s strategic decisions. Strategic management helps in articulating this vision and setting achievable, measurable long-term goals. These goals serve as benchmarks for success and provide motivation for all stakeholders. A long-term vision transcends short-term market fluctuations and helps maintain focus during periods of uncertainty. Strategic management ensures that every initiative, project, and investment is aligned with the overarching vision. It promotes sustained growth, innovation, and leadership positioning in the industry. Regularly revisiting and refining the vision and goals ensures they remain relevant as internal capabilities and external conditions evolve.
Examples of Strategic Management in Companies
Several successful companies are prime examples of effective strategic management.
Future Trends in Strategic Management
The future of Importance Strategic Management is being shaped by rapid technological advancement, globalization, and changing consumer expectations. One major trend is the increasing use of data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) in strategic decision-making. Organizations are leveraging big data to forecast trends, optimize operations, and personalize customer experiences. Sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) are also becoming central to strategic planning, as stakeholders demand more ethical and environmentally responsible business practices. Additionally, agility and resilience are becoming key strategic priorities, with businesses adopting flexible strategies to quickly respond to disruptions like pandemics or economic crises. Importance Strategic Management is also moving towards more collaborative and decentralized models, empowering frontline employees and fostering innovation at all levels. Embracing digital transformation, nurturing talent, and maintaining strategic flexibility will be critical for future success.


