
- Introduction to Service Marketing
- Characteristics of Services
- Service Marketing vs Product Marketing
- 7 Ps of Service Marketing
- Consumer Behavior in Services
- Service Delivery Strategies
- Role of Customer Satisfaction
- Service Recovery Strategies
Introduction to Service Marketing
Service marketing refers to the strategies and tactics used to promote intangible offerings across sectors like healthcare, education, banking, hospitality, and professional consulting. Since services can’t be touched or stored, they come with quirks such as intangibility, inseparability, variability, and perishability, which make marketing them a whole different game. The core focus is understanding customer expectations, delivering consistent quality, and building strong, lasting relationships. Service marketing works through the traditional 4Ps product, price, place, and promotion expanded to include people, process, and physical evidence, creating a fuller strategy that shapes the customer experience. It also emphasizes managing service encounters, maintaining dependable service quality, and using customer feedback to continuously improve. With the rise of the global service sector and increasing demand for specialized professional development programs like PMP training effective service marketing has become essential. By aligning service offerings with customer needs, businesses can build trust, earn repeat usage, and secure long-term success in a competitive market.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Characteristics of Services
- Intangibility: Services cannot be seen, touched, or stored like physical goods. Customers often rely on brand reputation, reviews, or past experiences to judge service quality before purchase.
- Inseparability: Services are typically produced and consumed simultaneously. This means the provider and the consumer must often be present during the service delivery, making customer interaction a vital part of the process.
- Variability: The quality of services can vary greatly depending on who provides them, when, where, and how. Standardizing service delivery is a challenge due to human involvement.
Services are distinct from physical products due to several unique characteristics that influence how they are marketed, delivered, and consumed. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for effectively managing and promoting service offerings. Below are six key features that define services:
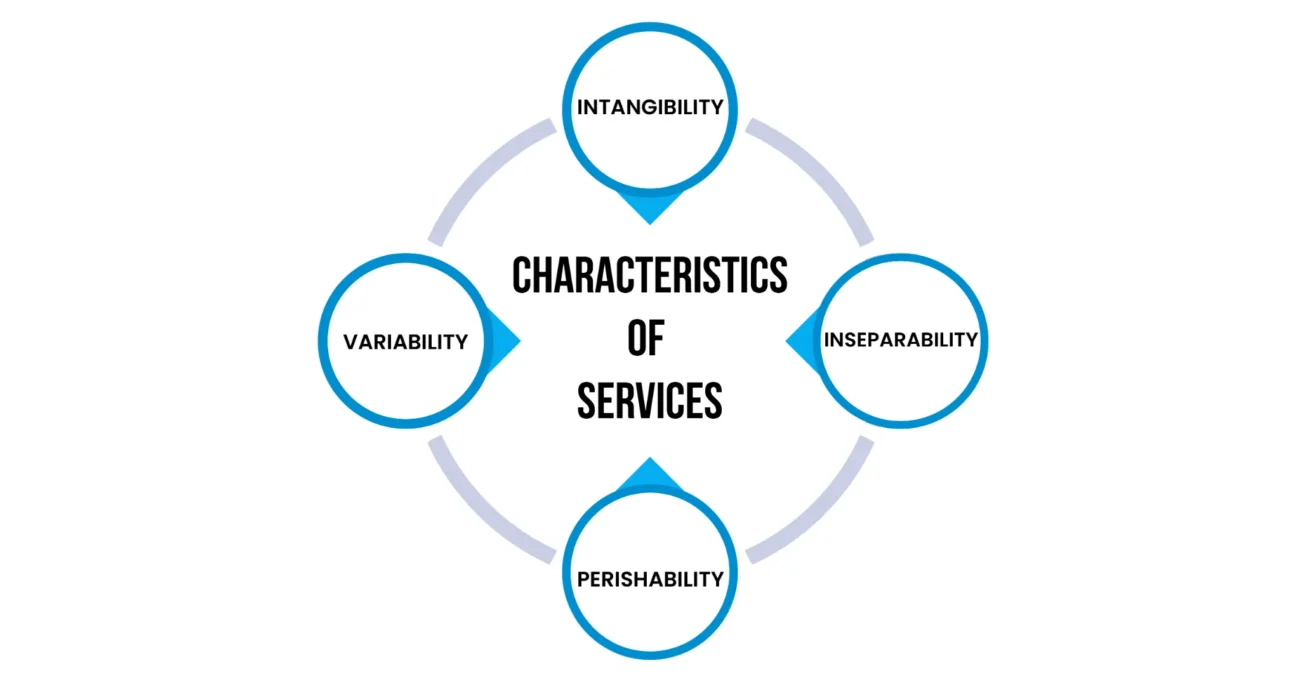
- Perishability: Services cannot be stored for future use; for example, an unsold hotel room or an empty airline seat represents lost revenue that can’t be recovered, and this idea closely connects with an Overview of Retail Management which focuses on efficiently managing products, customer demand, and sales cycles to minimize losses and maximize profitability.
- Lack of Ownership: When consumers buy a service, they gain access to or experience of it, not ownership. For instance, a person using a taxi service does not own the vehicle.
- Customer Participation: Customers often play an active role in the service process, influencing the outcome and experience, such as in education, healthcare, or fitness services.
Service Marketing vs Product Marketing
Service marketing vs product marketing highlights the core differences in how businesses promote and deliver their offerings, with product marketing centered on tangible goods that can be seen, touched, stored, and standardized, making their quality easier to control and communicate. In contrast, service marketing focuses on intangible experiences that vary depending on the provider, the moment, and the customer’s involvement, especially since services are produced and consumed at the same time. This creates a heavier dependence on customer participation and perception, requiring service providers to carefully manage expectations, consistency, and trust. In many organizations, especially those emphasizing Operations Manager Responsibilities service delivery becomes even more complex because these managers must ensure smooth processes, quality control, and customer satisfaction in a setting where outcomes can change daily. While both product and service marketing rely on pricing, promotion, and distribution, the real edge in service marketing comes from enhancing the overall experience, building strong relationships, and overcoming challenges like intangibility, variability, and the lack of physical evidence.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
7 Ps of Service Marketing
- Product: In service marketing, the “product” refers to the service itself. It encompasses the offerings that meet customer needs and includes the design, features, and variety of services provided.
- Price: Pricing in service marketing has to match the value customers feel they’re getting, while also balancing competition, demand, and overall perception, and since services are intangible, pricing often shifts depending on timing, customization, or customer involvement, which is why many organizations also study areas like What is Human Resource Management to better align people-driven service delivery with pricing strategies; and because services can’t be stored or resold later, prices sometimes need to stay flexible and dynamic to make sure each service moment actually earns its worth.
- Place: This refers to how and where the service is delivered to customers. In service marketing, distribution channels can include physical locations, online platforms, or mobile services, depending on the type of service.
- Promotion: Promotion in services focuses on communicating the value of the service, building awareness, and highlighting customer benefits. It involves advertising, public relations, and word-of-mouth marketing.
The 7 Ps of Service Marketing provides a framework that helps businesses effectively market and deliver services. Unlike product marketing, services are intangible and require additional elements to address their unique characteristics. The 7 Ps include the traditional 4 Ps of marketing product, price, place, and promotion along with three additional elements specific to services: people, process, and physical evidence. Each element plays a critical role in ensuring the service meets customer expectations and delivers a positive experience. Here are the 7 Ps explained:
- Promotion: Promotion in services focuses on communicating the value of the service, building awareness, and highlighting customer benefits. It involves advertising, public relations, and word-of-mouth marketing.
- People: Since services are often produced and consumed in person, the interaction between service providers and customers is crucial. Well-trained, friendly, and knowledgeable staff enhance the service experience and customer satisfaction.
- Process: The process encompasses the procedures, mechanisms, and flow of activities involved in delivering the service. Streamlining and standardizing processes ensures consistency, efficiency, and quality in service delivery.
- Physical Evidence: This refers to the tangible elements that help customers evaluate the intangible service, such as physical facilities, brochures, uniforms, or even online presence. Physical evidence creates a visual or sensory experience that supports the service’s credibility and quality.
- Standardization: Standardizing service delivery ensures consistency, making it easier for customers to expect and receive the same level of quality every time. This can be achieved through clear guidelines, training, and predefined procedures for staff.
- Customization: Offering personalized services based on individual customer preferences can enhance satisfaction and loyalty. Customization allows businesses to cater to unique needs, providing a more tailored experience that sets them apart from competitors.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology can streamline service delivery by automating processes, improving communication, and providing customers with self-service options. For example, using chatbots, mobile apps, or AI-based tools can speed up service delivery and enhance convenience.
- Employee Training: Well-trained employees are essential to effective service delivery. Providing continuous training helps staff improve their skills, understand customer needs, and deliver exceptional service, which ultimately enhances customer satisfaction.
- Service Recovery: In cases of service failure, having a strong service recovery strategy in place can turn a negative experience into a positive one. This involves responding quickly, offering solutions, and compensating customers where necessary.
- Outsourcing: For certain services, outsourcing can be an effective strategy to improve delivery. Partnering with third-party providers can help businesses focus on their core competencies while ensuring specialized services are offered efficiently and cost-effectively.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Consumer Behavior in Services
Consumer behavior in services is shaped by factors that differ significantly from those influencing decisions about tangible products, mainly because services are intangible and often require direct interaction with providers. Since customers heavily rely on emotional and experiential cues, the perception of service quality formed through previous experiences or word of mouth plays a major role in decision making. As services are produced and consumed at the same time, the customer’s involvement directly affects their satisfaction and loyalty, especially in high-involvement areas like healthcare or specialized professional programs such as PMP training Elements like convenience, availability, and price sensitivity further influence behavior, with consumers often judging services based on perceived value that blends price, quality, emotional satisfaction, and social benefits. Because service delivery can vary, customers develop expectations based on reputation or past interactions, making it crucial for service marketers to understand these dynamics and craft strategies that guide decisions and elevate satisfaction.
Service Delivery Strategies
Service delivery strategies are crucial for ensuring that services are provided efficiently and effectively, meeting or exceeding customer expectations, and keeping the entire experience smooth from start to finish. These strategies revolve around optimizing processes, aligning resources, and empowering people to deliver consistent quality across every customer touchpoint, no matter how chaotic things get. Midway through this approach, businesses also benefit from incorporating Understanding Scope of Management Accounting which helps them analyze costs, allocate resources wisely, and improve overall service performance. Effective service delivery depends on clear communication, well-designed workflows, trained staff, and a commitment to continuous improvement, ensuring that customers feel valued and stay loyal.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Role of Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction plays a pivotal role in the success and sustainability of a service-oriented business. It is a key indicator of how well a company’s offerings meet or exceed customer expectations, directly influencing customer loyalty, retention, and positive word-of-mouth. Businesses can also leverage insights from Tools and Techniques in Management Accounting to better understand customer behavior, allocate resources effectively, and optimize service delivery. Satisfied customers are more likely to return for future services, creating a strong base for long-term business growth. Beyond repeat business, high customer satisfaction drives customer advocacy, where customers recommend the service to others, expanding the brand’s reach. Furthermore, customer satisfaction serves as a valuable feedback mechanism, helping businesses identify areas for improvement and adapt to changing customer preferences. In competitive markets, delivering excellent service that results in high satisfaction is often what differentiates one company from another. Dissatisfied customers, on the other hand, can damage a business’s reputation, leading to customer churn and negative reviews that can impact the brand’s image. By focusing on customer satisfaction, companies can strengthen their brand reputation, reduce customer attrition, and foster stronger relationships with their target audience. Ultimately, it creates a win-win situation where both the customer and the business benefit from a positive, ongoing relationship built on trust, quality service, and consistent value.
Service Recovery Strategies
Service recovery strategies are essential for addressing service failures and ensuring customer satisfaction even when things go sideways. When customers encounter issues, a solid recovery approach can flip a bad moment into a loyalty-building win. The process starts with acknowledging the problem quickly and offering a genuine apology, showing customers that their experience matters. As industries evolve especially those involving professional development like PMP training businesses must also be prepared to offer fair compensation such as refunds, discounts, or complimentary services to rebuild trust. Empowering frontline employees to resolve complaints on the spot boosts customer confidence, while clear communication throughout the process keeps expectations in check. Companies that dig into the root causes of failures and make meaningful improvements not only prevent repeats but also strengthen their overall service quality. Following up after the resolution closes the loop and reassures customers that their concerns led to real action, ultimately helping brands turn setbacks into long-term loyalty.

