
- Introduction to Production Management
- Importance of Production in Business
- Planning and Scheduling Production
- Managing Resources and Materials
- Quality Control and Assurance
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- Production Efficiency and Optimization
- Technology and Automation in Production
- Cost Management and Budgeting
- Compliance with Industry Standards
- Conclusion
Introduction to Production Management
Production management refers to the planning, organization, direction, and control of an enterprise’s manufacturing or production functions. PMP Training efficiently converts raw materials into finished goods while maintaining quality standards and maximizing resources. Proper production management guarantees timely delivery, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Manufacturing and service sectors must improve operations, eliminate waste, and maximize productivity. Production management is one of the most critical drivers of business success in the current competitive market, helping companies achieve consumer needs while staying profitable.
Importance of Production in Business
Production is the backbone of any business, directly impacting profitability, customer satisfaction, and market reputation. Its significance lies in:
- Revenue Generation: Production creates goods and services that generate revenue and fuel business growth.
- Customer Satisfaction: Efficient production ensures that products meet quality standards and are delivered on Product Manager Salary in India , enhancing customer trust.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizing production processes reduces waste, lowers production costs, and increases profit margins.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with streamlined production systems can offer better products at competitive prices.
- Resource Utilization: Effective production management ensures optimal use of materials, labor, and machinery.
- Scalability: Production efficiency supports business expansion and scalability.
- Outcome: A well-managed production system strengthens the business by boosting efficiency, ensuring customer satisfaction, and driving profitability.
Learn the fundamentals of PMP with this PMP Certification Training .
Planning and Scheduling Production
Production planning and scheduling are critical for ensuring the smooth execution of manufacturing processes. It involves determining what, when, and how much to produce.
Production Planning:
- Demand Forecasting: Estimating customer demand to determine production volumes.
- Resource Allocation: Assigning materials, machines, and labor effectively.
- Capacity Planning: Ensuring production capabilities align with demand.
- Timeline Creation: Defining production timelines with clear milestones.
- Task Assignment: Allocating tasks to teams and individuals.
- Prioritization: Sequencing tasks based on Product Manager Role and dependencies.
- Outcome: Proper planning and scheduling optimize resource utilization, minimize delays, and enhance productivity.
Production Scheduling:
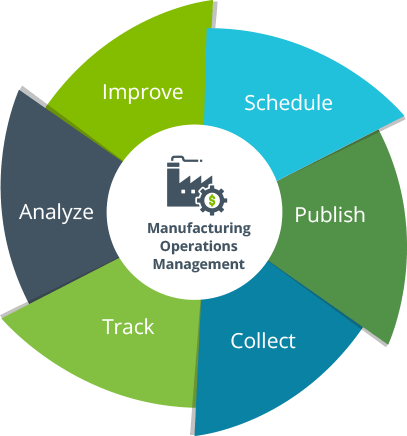
Managing Resources and Materials
Resource and material management ensures that production activities run smoothly without delays or shortages. It involves the efficient use of raw materials, machinery, and labor. Material Management, Procurement Sourcing quality raw materials at competitive prices. Inventory Control Monitoring stock levels to avoid overstocking or shortages. Waste Reduction Minimizing material waste through efficient processes. Resource Management Workforce Allocation Assigning skilled labor to Functions of Product Management tasks. Machine Utilization Ensuring optimal use of machinery and equipment. Capacity Optimization Preventing underutilization or overloading of resources. Outcome Efficient resource and material management reduces waste, controls costs, and enhances production efficiency.
Advance your PMP career by joining this PMP Certification Training now.
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) are essential for maintaining product standards and customer satisfaction. QC focuses on detecting defects, while QA emphasizes preventing defects.
Quality Control (QC):
- Inspection and Testing: Evaluating products at various production stages.
- Defect Identification: Detecting and addressing defective items.
- Corrective Actions: Implementing measures to fix quality issues.
- Process Standardization: Establishing standardized procedures.
- Preventive Measures: Identifying potential quality risks in Scrum Master Pay Trends by City and Industry India .
- Continuous Improvement: Refining processes to prevent future defects.
- Outcome: Strong QC and QA practices ensure consistent product quality, reduce rework, and build customer trust.
Quality Assurance (QA):
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Adequate inventory and supply chain management ensures a smooth flow of raw materials and finished goods throughout production.
Inventory Management:
- Stock Monitoring: Tracking raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products.
- Reorder Points: Setting minimum stock levels to PMP Training reordering.
- Inventory Turnover: Measuring the rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
- Supplier Coordination: Collaborating with reliable suppliers to ensure timely deliveries.
- Logistics and Distribution: Managing transportation and storage of materials.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing supply chain risks.
- Outcome: Efficient inventory and supply chain management prevent production disruptions, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Supply Chain Management (SCM):
Take charge of your PMP career by enrolling in ACTE’s PMP Master Program Training Course today!
Production Efficiency and Optimization
Improving production efficiency involves streamlining processes, reducing waste, and maximizing output with minimal resource utilization. Process Optimization Lean Manufacturing Eliminating waste to improve efficiency. Six Sigma Reducing defects and enhancing quality. Kaizen Continuous improvement through small, incremental changes. Technology Integration Automation Using robotics and AI to increase speed and accuracy. Process Monitoring Using software to track production performance. Outcome Production efficiency boosts output, Sprint Planning , and enhances profitability.
Technology and Automation in Production
Integrating technology and automation in production management has transformed manufacturing processes, enhancing speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Automation Technologies, Robotics Automating repetitive tasks to increase precision and reduce labor costs. AI and Machine Learning Using predictive analytics to optimize processes. IoT (Internet of Things) Connecting devices for real-time data monitoring. Software Solutions: ERP Systems Streamlining production, inventory, and resource management. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Tracking production processes. Outcome Automation reduces human error, enhances productivity, and improves product quality.
Are you getting ready for your PMP interview? Check out our blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers!
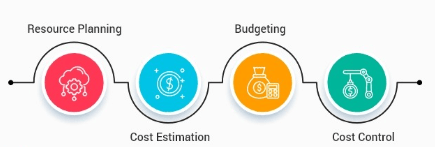
Cost Management and Budgeting
Cost management is essential for maintaining profitability and controlling production expenses. It involves monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing production costs.
Cost Components:
- Direct Costs: Raw materials, labor, and machinery expenses.
- Indirect Costs: Overhead costs like utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses.
- Fixed and Variable Costs: Identifying and managing fixed and variable production expenses.
- Cost Estimation: Forecasting production costs based on market trends.
- Expense Control: Monitoring expenses to prevent budget Retrospection Needed .
- Cost Reduction Techniques: Implementing waste reduction and process improvements.
- Outcome: Effective cost management ensures profitability and financial stability.
Budgeting Strategies:
Compliance with Industry Standards
Compliance with industry regulations and standards ensures that products meet legal requirements and maintain quality consistency.
Regulatory Compliance:
- ISO Standards: Adhering to international quality, safety, and efficiency standards.
- Environmental Regulations: Ensuring eco-friendly production practices.
- Health and Safety Compliance: Maintaining workplace safety standards.
- ISO 9001: Quality management system certification.
- Six Sigma: Certification for process improvement and defect reduction.
- Outcome: Compliance with standards ensures legal conformity, customer trust, and product reliability.
Quality Certifications:
Conclusion
Production management is critical in facilitating practical, affordable, and quality manufacturing. By integrating planning, resource utilization, quality assurance, and technology infusion, companies can optimize operations, minimize waste, and maximize customer satisfaction. Being ahead of industry trends and solving production problems is the key to sustaining a competitive advantage in PMP Training dynamic business environment.





