
- Introduction to Product Management
- Defining Product Vision and Strategy
- Key Responsibilities of a Product Manager
- Market Research and Analysis
- Roadmap Development and Prioritization
- Managing Product Lifecycle
- Setting and Tracking KPIs
- Overseeing Product Launches
Introduction to Product Management
Product management is a strategic process that guides a product from conception to market success. It involves identifying customer needs, defining clear product goals, and collaborating with cross-functional teams to develop products that align with business objectives. The product manager (PM) plays a crucial role by acting as a bridge between business, technology, and user experience (UX), ensuring that the product delivers value to customers while meeting organizational goals. A key responsibility of the PM in PMP Training is conducting market analysis to understand trends, competitor actions, and customer demands. Based on this analysis, the PM sets the product vision, prioritizes features, and defines a roadmap. This requires strategic planning and effective communication with development, marketing, sales, and support teams to deliver a product that meets market demands and user expectations. Throughout the product life cycle, the PM is responsible for continuous improvement, using customer feedback and performance data to refine and optimize the product. Effective product management ensures that products stay competitive, relevant, and profitable, driving growth and innovation for the business.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Defining Product Vision and Strategy
The product vision defines the overarching goal and long-term aspirations for the product, offering clear direction for the team and serving as a guiding principle throughout development. A compelling vision articulates the problem the product solves, the target audience and their needs, and the product’s unique value proposition. This vision is essential for ensuring that the entire team aligns with the product’s purpose and direction in the Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management. To achieve this vision, the product strategy is developed. The strategy includes defining measurable objectives, such as market penetration, revenue targets, or customer acquisition, to track progress and success. Positioning and differentiation are key aspects of the strategy, identifying how the product stands out from competitors and meets customer needs uniquely.
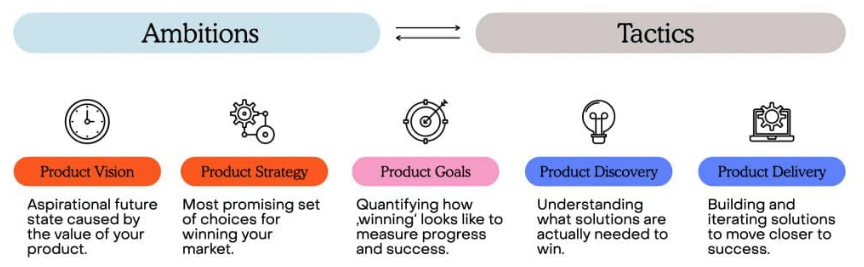
Prioritizing initiatives ensures that development efforts align with the most important business priorities. Finally, creating a roadmap outlines the features, enhancements, and timelines necessary to meet strategic objectives. This roadmap acts as a blueprint for execution, ensuring that all efforts are focused on fulfilling the product vision and achieving long-term success.
Key Responsibilities of a Product Manager
- Defining the Product Vision: Establishing a clear vision and strategic direction aligned with business goals.
- Market Research and Analysis: Identifying customer needs, market gaps, and competitive trends.
- Roadmap Development: Creating and managing a product roadmap that outlines features, timelines, and priorities.
- Collaboration with Teams: Working closely with engineering, marketing, sales, and customer support teams.
- Prioritizing Features: Managing the backlog by balancing customer needs, technical feasibility, and business objectives.
- Tracking Performance: Using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure product success and identify areas for improvement.
- Handling Customer Feedback: Collecting, analyzing, and integrating customer feedback into product iterations is an essential part of What is Project Cycle Management.
- Ensuring Timely Delivery: Overseeing the execution of product plans and coordinating with cross-functional cross functional teams.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about product progress, challenges, and plans.
- Customer Interviews: Conducting surveys, interviews, and focus groups is a powerful way to gather qualitative insights directly from customers. These interactions help uncover their pain points, needs, and preferences, providing valuable information to guide product development and improvements.
- Competitor Analysis: By studying competitors, product managers can identify their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning in How to Build a Career in Project Management. Understanding how competitors address customer needs and their unique selling points allows PMs to spot opportunities for differentiation and improve their own product offerings.
- Industry Trends: Staying updated on emerging technologies, consumer behavior shifts, and market dynamics is essential. By monitoring trends, PMs can anticipate changes in customer expectations, adopt new technologies early, and adjust the product strategy to maintain competitiveness in a fast-evolving market.
- SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis involves evaluating a product’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This framework helps PMs identify internal factors that need attention and external factors that could impact the product, enabling them to craft a strategy that leverages strengths, addresses weaknesses, and capitalizes on opportunities while mitigating potential threats.
- Decline: Over time, products may face market saturation or obsolescence. This phase involves deciding whether to continue investing, pivot, or phase out the product.
- End-of-Life (EOL): The product is retired, and proper communication is made with customers, offering alternatives or transitioning them to new solutions.
- Product Strategy: Define a clear vision and set strategic goals that align with the company’s objectives. A strong strategy ensures the product meets market demands and business goals.
- Development and Design: This stage focuses on turning the product concept into a tangible solution in Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep & PMBOK Guide.
- Market Launch: Successfully introducing the product to the market involves effective marketing, sales alignment, and clear communication with target audiences. A successful launch sets the foundation for product adoption.
- Growth and Optimization: After the launch, focus on expanding the customer base, optimizing features based on user feedback, and improving performance to increase adoption and retention.
- Maturity: The product reaches a point where growth slows down, and maintenance becomes a priority. At this stage, cost optimization, customer support, and occasional feature updates are essential.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
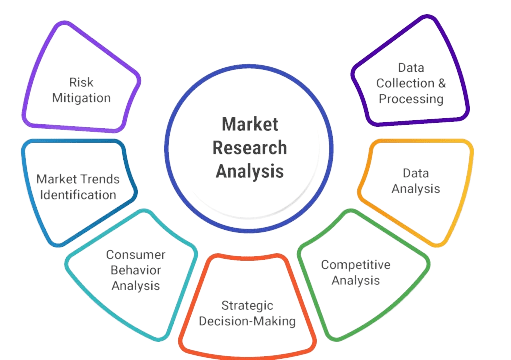
Market Research and Analysis
Roadmap Development and Prioritization
A product roadmap visually represents the product’s strategic direction, outlining key features, goals, and timelines. It provides clarity and alignment across teams and stakeholders, ensuring everyone is working toward a common vision. The development of a roadmap involves several key steps. First, defining clear, measurable objectives aligned with business strategies is essential for guiding the product’s development. Next, prioritizing features using frameworks like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) in PMP Training helps ensure the team focuses on high-impact features that address customer needs and business goals. Setting realistic timelines and milestones is also crucial for keeping development on track and ensuring timely delivery. Finally, communicating the roadmap with all teams and stakeholders is necessary for alignment and transparency. Regularly sharing the roadmap ensures that everyone understands the product’s direction and priorities. By following these steps, a product roadmap becomes an effective tool for prioritizing initiatives, focusing efforts on high-value features, and ensuring the product evolves strategically to meet business objectives.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Managing Product Lifecycle
Setting and Tracking KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial for product managers (PMs) to evaluate product performance and make data-driven decisions. Common KPIs help PMs track customer engagement, retention, and overall success. For instance, the Customer Acquisition Rate measures how effectively the product attracts new users, while the Retention Rate assesses the percentage of customers who continue using the product over time. Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) gauges customer satisfaction through feedback scores, offering insight into user experiences in What is Project & Process Metrics. For subscription-based products, Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) tracks revenue consistency, providing an important measure of financial health. Meanwhile, the Churn Rate measures the percentage of customers who stop using the product, offering a clear indication of potential issues with user satisfaction or product value. Regularly monitoring these KPIs enables PMs to identify trends, uncover potential problems, and optimize product performance. By using these metrics, PMs can make informed decisions, ensuring the product remains aligned with customer needs and business objectives while driving growth.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Overseeing Product Launches
Product launches require meticulous planning and seamless execution to ensure success. The process begins with Pre-launch preparation, which involves conducting thorough market research, testing the product, and segmenting customers to understand their needs and preferences. This step lays the foundation for a successful launch by ensuring that the product is aligned with market demands. The next step is developing a Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy in PMP Training, where pricing, positioning, and promotional activities are clearly defined to maximize product visibility and appeal to the target audience. Marketing and sales alignment is essential, as coordinating with both teams ensures a unified message and consistent communication to potential customers. Training and support are also crucial, as customer support teams must be equipped with product knowledge, troubleshooting guides, and FAQs to assist customers effectively. Once the product is launched, Post-launch monitoring comes into play, tracking user adoption, performance metrics, and gathering customer feedback for continuous improvement. A successful product launch involves careful coordination across these steps, ensuring maximum visibility, customer satisfaction, and long-term revenue growth.


