
- Introduction to Product Management
- Educational Requirements and Degrees
- Essential Skills and Competencies
- Gaining Relevant Experience
- Certifications and Courses
- Building a Strong Portfolio
- Networking and Industry Connections
- Applying for Entry-Level Roles
- Acing the Interview Process
- Advancing Skills and Continuous Learning
- Exploring Niche Specializations
- Tips for Long-Term Career Success
Introduction to Product Management
Product management is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that plays a crucial role in delivering customer-centric products and driving business growth. It encompasses managing the entire product lifecycle from ideation and development to launch and beyond. Professionals looking to strengthen their leadership and project management skills often benefit from PMP Training as product managers (PMs) must effectively bridge engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams to ensure the product aligns with both customer needs and business objectives. The growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making, customer experience, and technology adoption has significantly increased the demand for skilled product managers. Companies across industries, from technology and healthcare to finance and e-commerce, rely on PMs to guide product strategies and ensure market competitiveness. As a result, building a career in product management offers diverse growth opportunities, competitive salaries, and long-term stability.
Educational Requirements and Degrees
While there is no strict educational path for becoming a product manager, having a relevant degree or academic background can significantly boost your chances of entering the field. Most product managers hold degrees in business, engineering, computer science, marketing, or economics, as these disciplines provide the necessary technical and business acumen. A bachelor’s degree in computer science or engineering is advantageous for technical product management roles, offering a solid foundation in software development, APIs, and technology trends. For business-focused roles, a degree in business administration or marketing provides expertise in market research, business strategy, and product positioning. Supplementing your education with resources like PMP & Tutorial can further enhance your understanding of structured project management and practical product management skills. Pursuing an MBA in product management or business strategy can also provide a competitive edge. Many top companies prefer hiring PMs with MBA degrees due to their strategic mindset and leadership skills. However, even without a formal degree, you can enter the field by gaining relevant experience, building a portfolio, and earning certifications.
Become a Project Management expert by enrolling in this PMP Training Online Course today.
Essential Skills and Competencies
To succeed in product management, you need a diverse skill set that combines technical expertise, business acumen, and interpersonal abilities.
- Technical Skills: While you don’t need to be a developer, understanding basic coding, APIs, and technical architecture is essential. Familiarity with agile methodologies, JIRA, and product roadmapping tools will make you more effective in collaborating with engineering teams.
- Analytical and Data Skills: Product managers must be proficient in data analysis and interpretation. Skills in using tools like Google Analytics, SQL, and Excel help them make data-driven decisions, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and identify areas for improvement. Understanding how to align these insights with a well-defined Statement of Work ensures that project goals and deliverables stay on track.
- Business Acumen: A firm grasp of business models, pricing strategies, and market dynamics is critical. PMs must assess products’ financial viability and align them with organizational goals.
- Communication and Collaboration: Clear communication is essential for PMs who work with cross-functional teams. You must effectively convey product visions, requirements, and updates to technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: You should identify customer pain points, solve problems, and make quick decisions based on market trends and data insights.
Advance your Project Management career by joining this PMP Training Online Course now.
Gaining Relevant Experience
Gaining practical experience is key to launching a product management career. Fortunately, there are multiple ways to build relevant experience, even if you’re not in a PM role.
- Internships and Entry-Level Roles: A great way to enter the field is to start with internships or associate product manager (APM) roles. These roles offer hands-on experience with feature prioritization, customer research, and product testing.
- Transitioning from Related Roles: If you work in software development, marketing, business analysis, or UX design, you can transition into product management by highlighting your transferable skills. To gain experience, get involved in cross-functional projects, and collaborate with product teams.with product teams, and explore opportunities in Succession Planning.
- Freelance and Side Projects: Work on freelance product management projects or create your product to demonstrate your abilities. Building a portfolio with tangible projects strengthens your resume.
- Volunteering for Product Tasks: In your current job, volunteer for product-related responsibilities, such as conducting customer interviews, contributing to roadmaps, or participating in product launches.
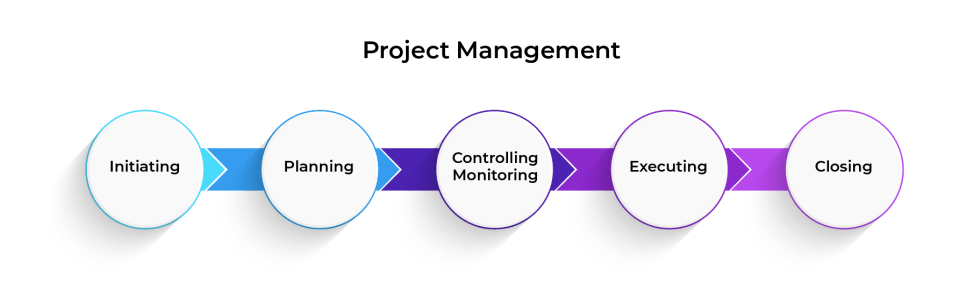
Certifications and Courses
Certifications enhance your credibility and demonstrate specialized knowledge in product management. Earning industry-recognized certifications also helps you stand out in the job market.
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO): This certification covers agile product ownership, sprint planning, and feature prioritization essential skills for PMs in agile environments.
- Pragmatic Institute Certification: This program focuses on market-driven product management and equips you with skills in market research, customer personas, and product strategy.
- Google Product Management Certificate: This certification provides insights into product lifecycle management, design thinking, and data analysis.
- Product School Certification: A popular program that offers practical training in road mapping, prioritization, and stakeholder management.
- General Assembly’s Product Management Course covers end-to-end product management concepts, including product-market fit and agile methodologies.
Building a Strong Portfolio
A well-crafted portfolio showcases your skills, projects, and achievements, helping you stand out to potential employers. Even if you’re new to the field, you can create a portfolio by working on side projects or case studies.
- Include Real-World Projects: Showcase product-related work, such as feature prioritization, customer research, or market analysis. Include metrics and tangible results to demonstrate your impact.
- Highlight Problem-Solving Abilities: Showcase case studies with clear descriptions of problems identified, solutions proposed, and outcomes achieved. Incorporating frameworks learned through PMP Training can strengthen your approach, and using data to validate your results adds further credibility.
- Use a Clean and Professional Format: Organize your portfolio with clear sections, visuals, and concise descriptions. Include links to prototypes, presentations, or reports you’ve created.
Networking and Industry Connections
Networking is a powerful tool for career growth in product management. Building connections with industry professionals, recruiters, and fellow PMs can lead to job opportunities and mentorship. Engaging with a Virtual Team can also help expand your network and provide diverse perspectives on managing remote collaboration.
- Join Product Management Communities: Participate in platforms like LinkedIn, ProductHunt, and Mind the Product. Engage in discussions, share insights, and stay active.
- Attend Industry Events and Meetups: Join conferences, webinars, and workshops to network with professionals. These events provide insights into industry trends and best practices.
- Connect with Current Product Managers: Contact product managers on LinkedIn for informational interviews. Ask for advice, career tips, and insights into the industry.
Are you getting ready for your PMP interview? Check out our blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers!
Applying for Entry-Level Roles
You can apply for entry-level product management roles once you’ve acquired the necessary skills and experience.
- Tailor Your Resume: Highlight your skills, certifications, and portfolio projects. Quantify your achievements with metrics and results.
- Optimize Your LinkedIn Profile: Update your LinkedIn profile to showcase your skills, certifications, and accomplishments. Use keywords related to product management to increase your visibility.
- Leverage Job Portals and Referrals: Apply on platforms like Naukri, LinkedIn, AngelList, and Indeed. Seek referrals from connections or industry alums.
Acing the Interview Process
Cracking a product management interview requires thorough preparation and problem-solving skills.
- Prepare for Product Sense Questions: Expect questions like, “How would you improve a popular product?” Demonstrate customer empathy, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
- Showcase Analytical Skills: Be prepared for data interpretation and metric-based questions. Demonstrate how you make data-driven decisions.
- Practice Behavioral Questions: Prepare answers to situational and behavioral questions using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result).
Advancing Skills and Continuous Learning
To thrive in product management, continuous learning is essential.
- Learn New Tools: Master tools like Figma, Amplitude, Mixpanel, and JIRA. Stay updated with emerging technologies.
- Follow Industry Trends: Stay current by subscribing to product management blogs, podcasts, and publications.
- Upskill with Advanced Courses: Upskill with Advanced Courses: Expand your expertise by taking courses in data science, UX design, agile methodologies, and PMP Training to enhance your project management capabilities.
Exploring Niche Specializations
As you progress, consider specializing in niche areas like:
- Technical Product Management: APIs and infrastructure.
- Growth Product Management: User acquisition and retention.
- AI Product Management: AI-powered solutions.
Tips for Long-Term Career Success
To excel as a product manager:
- Stay curious and adaptable.
- Build strong relationships with engineering and marketing teams.
- Seek mentorship and feedback regularly.
- Keep your skills and certifications updated.
- Maintain a growth mindset and embrace challenges.





