
- Introduction
- Importance in Business
- Indian Contract Act
- Companies Act
- Consumer Protection Act
- Environmental Laws
- Labour Laws
- Competition Act
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Cyber Laws
- Corporate Governance
- Final Thoughts
Introduction
Legal Environment of Business Law are essential for the smooth functioning and regulation of business operations in any economy. These laws provide a framework that governs the conduct of business, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability. In India, business laws cover a wide range of areas, including contracts, consumer rights, corporate governance, intellectual property, and much more. These laws are designed to protect the interests of all stakeholders, including consumers, employees, companies, and the environment. The Indian legal system, with its complex set of statutes, regulations, and judicial pronouncements, ensures that business activities are conducted in a manner that aligns with the principles of justice and ethics. This makes business laws critical for the legal and operational aspects of organizations, both in the private and public sectors.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Importance in Business
Legal Environment of Business Law are crucial for establishing a level playing field, protecting rights, and fostering growth and competition. By adhering to these laws, businesses can prevent disputes, safeguard intellectual property, and ensure compliance with national and international standards. Here’s why business laws are vital:
- Legal Protection: Business laws help protect the interests of all stakeholders involved owners, consumers, employees, and investors. By ensuring legal frameworks for operations, businesses can prevent fraud, unethical practices, and disputes.
- Regulation and Accountability: They regulate the activities of businesses, ensuring that companies follow ethical standards and maintain transparency. These regulations ensure accountability, thus building trust with consumers and investors.
- Contract Enforcement: Business laws, especially those related to contracts, ensure that agreements between parties are legally enforceable. This reduces the likelihood of breaches and misunderstandings.
- Economic Growth: A stable legal environment fosters confidence in both local and international markets. When businesses follow laws and regulations, it leads to healthy competition, innovation, and economic development.
- Employee Rights: Labour laws protect employees, ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and the ability to voice concerns without fear of retaliation.

Indian Contract Act
The Indian Contract Act, 1872 is one of the most fundamental statutes governing contracts in India. It defines the legal framework for the formation, execution, and enforcement of contracts. It covers various aspects, such as offer, acceptance, consideration, and the consequences of breach.
Key Features:
- Offer and Acceptance: It defines how a contract is formed, with clear stipulations for offer and acceptance.
- Legality of Object: Contracts must have a lawful object and purpose.
- Breach and Remedies: It outlines the legal recourse available in the event of a breach of contract.
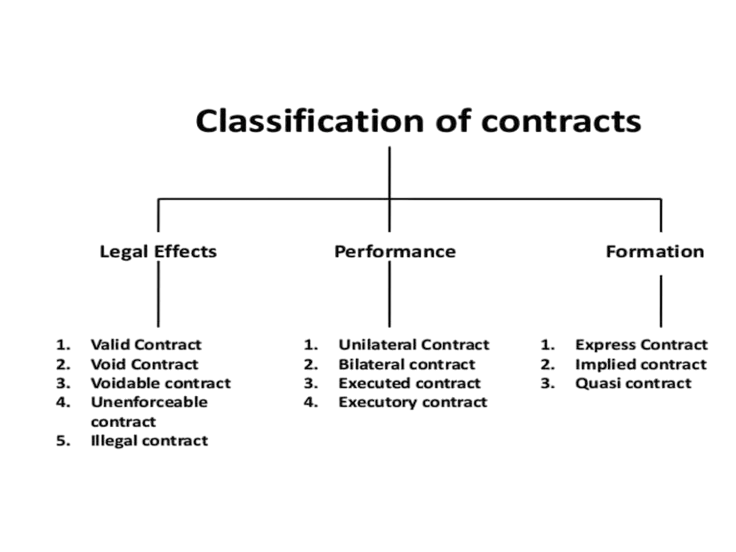
In business, the Indian Contract Act ensures that agreements are legally binding, and that parties who fail to uphold their obligations face penalties or compensatory action.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Companies Act
The Companies Act, 2013 governs the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies in India. It provides a comprehensive framework for the registration, regulation, and management of both private and public companies.
Key Features:
- Corporate Governance: The Act establishes rules regarding the board of directors, corporate disclosures, and shareholder rights.
- Company Registration: It lays down the procedures for registering a company, issuing shares, and transferring ownership.
- Auditing and Financial Reporting: It mandates the audit of company accounts and submission of annual financial statements to ensure transparency.
The Companies Act plays a crucial role in fostering a business-friendly environment, encouraging both domestic and foreign investment by ensuring that companies adhere to statutory requirements.
Consumer Protection Act
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 was created to safeguard the rights and interests of consumers in India. It aims to set up a clear framework for handling consumer complaints, preventing unfair trade practices, and ensuring that products and services are safe and reliable. A key part of the Act is the recognition of consumer rights, which includes the right to safety, information, choice, and the ability to seek compensation. To support this, the Act establishes Consumer Dispute Redressal Forums at the district, state, and national levels. These forums give consumers easy access to legal solutions for their issues. In addition, the Act applies to e-commerce, ensuring that online shoppers receive the same protections as those who shop in physical stores. This includes clear return policies, transparency about product information, and accountability for service issues. For companies, following the Consumer Protection Act is essential. It helps avoid legal problems and builds consumer trust, which is important for long-term success in a competitive market.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Environmental Laws
These rules ensure that industrial and commercial activities are done responsibly, causing minimal harm to natural resources. They cover important areas like pollution control, waste management, and environmental conservation. One of the main laws is the Environment Protection Act, 1986. This law serves as a framework for environmental regulation and gives broad powers to the central government for protecting the environment. The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 focuses on stopping water pollution by regulating the discharge of harmful substances into water bodies. Similarly, the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981 aims to improve air quality by controlling emissions from industries and vehicles. For businesses, following these environmental laws isn’t just a legal obligation; it’s crucial for their success. In a market that values sustainability, being compliant with environmental laws is essential for long-term growth and competitiveness.
Labour Laws
Labour laws in India aim to protect the rights of workers and ensure fair treatment in the workplace. These laws govern various aspects, such as wages, working conditions, hours of work, and industrial relations.
Key Features:
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948: Ensures that workers receive a fair wage for their work.
- Factories Act, 1948: Provides for the health, safety, and welfare of workers in factories.
- Industrial Disputes Act, 1947: Deals with the settlement of industrial disputes and strikes.
Adherence to labour laws ensures that businesses operate within legal boundaries while fostering positive relationships with employees and reducing the likelihood of disputes.
The Competition Act, 2002 regulates business practices in India to promote fair competition and prevent monopolies and anti-competitive practices. The Act empowers the Competition Commission of India (CCI) to take action against businesses involved in price-fixing, market manipulation, and other anti-competitive activities. Key Features: The Competition Act promotes innovation, protects consumers from monopolistic practices, and encourages fair business practices. These legal protections allow individuals and businesses to control how they use or share their innovations and creations. This helps promote growth and fair competition.
This prevents unauthorized use. The Copyright Act of 1957 ensures that writers, musicians, artists, and developers keep ownership of their creative work. The Trade Marks Act of 1999 protects brand symbols, names, and logos. This helps companies build and defend their brand identity in the market.
By securing ownership of intellectual creations, IPR encourages innovation and investment. Businesses benefit by maintaining a competitive edge, protecting their assets from imitation, and building long-term value through legal recognition of their unique contributions.
With the rise of digital business and e-commerce, cyber laws have become crucial for ensuring security and privacy in the online world. These laws govern digital transactions, online behavior, and cybercrimes. Key Acts: Cyber laws ensure that businesses can operate safely in the digital world, protecting consumer data, preventing cybercrimes, and enforcing rules around e-commerce. Corporate governance refers to the systems, principles, and processes by which companies are directed and controlled. Good governance ensures that companies are accountable, ethical, and transparent in their operations. Key Principles: Corporate governance plays a critical role in business operations by ensuring that companies adhere to ethical standards, reducing the risk of fraud, and promoting investor confidence. Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today! Competition Act
Intellectual Property Rights
Cyber Laws
Corporate Governance
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to Legal Environment of Business Law is critical for the smooth operation of any organization. From Indian Contract Act to Cyber Laws, each legal framework serves a distinct purpose in ensuring that businesses are ethical, transparent, and fair. As businesses grow and evolve, it is essential to stay updated with the latest regulations and legal reforms. By following the law, companies not only avoid legal pitfalls but also contribute to a healthier, more competitive business environment.





