
- Definition of Autocratic Leadership
- Characteristics and Traits
- Historical Background
- Advantages of Autocratic Leadership
- Disadvantages
- Autocratic vs Democratic Leadership
- Situations Where It Works
- Famous Examples
- Impact on Team Morale
- Modern Perspective
- Alternatives and Comparisons
- Conclusion
Definition of Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leadership also known as authoritarian leadership is a management style in which a single individual makes decisions unilaterally and maintains tight control over team operations and outcomes. In this model, the leader dictates policies, procedures, and tasks similar to the structured approach emphasized in PMP Training leaving little room for subordinate input. While this style ensures clear expectations and swift decision-making, it also restricts the autonomy and creative contributions of team members. Autocratic leadership is defined by direct oversight, strict control, and unilateral decision enforcement, making it especially effective in situations requiring precision, speed, or limited resources.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Historical Background
Autocratic leadership has historical roots in monarchical and militaristic systems, where order and obedience were prerequisites for survival. In the industrial revolution of the 19th century, factory owners applied rigid control systems to maximize output from assembly line production to Henry Ford’s manufacturing processes. Switching Careers , military leadership exemplified by generals and captains also leaned heavily on autocracy to coordinate complex, time-sensitive actions. Early management theories taught by figures like Frederick Taylor and Henri Fayol also favored hierarchical influence and centralized authority. Only later, in the mid-20th century, did theorists like Douglas McGregor and Mary Parker Follett begin promoting participatory leadership models, questioning the effectiveness of command-and-control styles.
Characteristics and Traits
Autocratic leaders possess several distinct traits guiding their approach:
- Decisiveness: They make swift decisions independently, relying on expertise and instinct.
- Control Orientation:They prefer top down communication and maintain oversight through strict guidelines and procedures, similar to the structured approach taught in some of the Most difficult courses in management and leadership training.
- Centralization of Power: Decision rights rest solely with the leader.
- Minimal Delegation: Team members are assigned tasks with directed execution, with little latitude for modification.
- Structured Environment: Rules, deadlines, and procedures are clearly defined and enforced.
These traits yield clarity and efficiency but may risk suppressing employee engagement and stifling creativity.
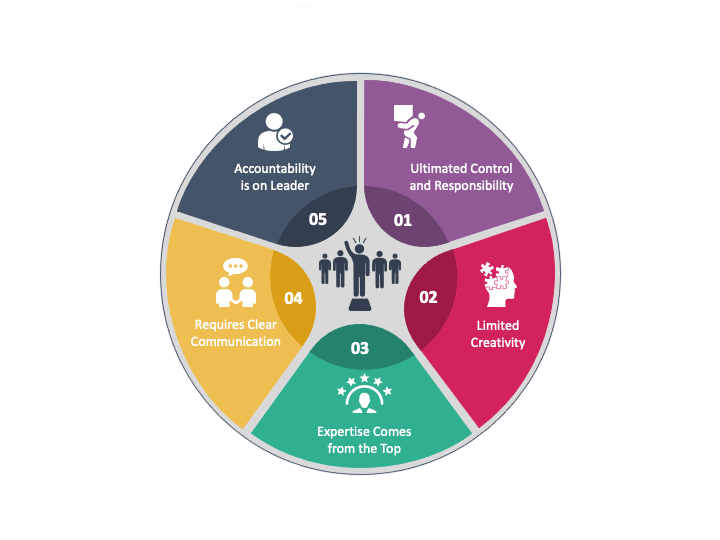
Advantages of Autocratic Leadership
Despite modern criticism, autocratic leadership remains valuable in specific contexts:
- Efficiency and Speed: Leaders authorize action swiftly, crucial in emergencies, tight deadlines, or fast-moving environments.
- Clear Direction: Employees receive unambiguous instructions and responsibilities, reducing uncertainty and ambiguity.
- Accountability: The Important resume skills , are reflected in the chain of command where measurable objectives and direct supervision ensure compliance.
- Unified Vision: Leaders can execute coherent plans without internal conflict or bureaucratic delays.
- Ideal for Inexperienced Teams: Where skill levels are low or training gaps exist, strict guidance prevents errors and maintains standards.
In short, autocratic leadership can deliver consistency, order, and results especially under demanding conditions where flexibility is less critical.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
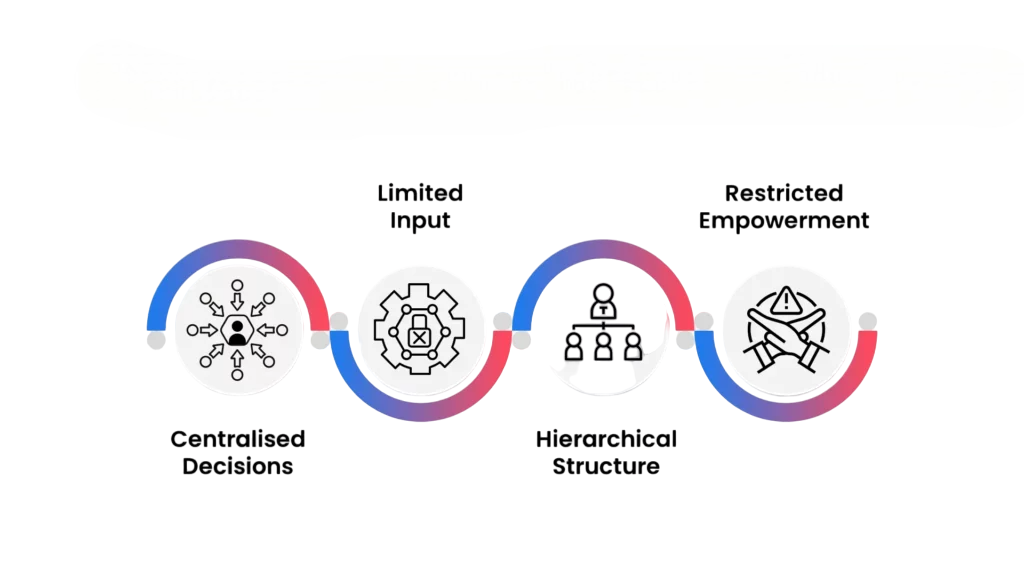
Disadvantages
However, numerous drawbacks are associated with autocratic leadership:
- Low Motivation: Without decision-making opportunities, employees may feel disengaged and undervalued.
- Creativity Suppression: Innovation suffers as ideas from the ground up are discouraged.
- High Turnover: Overly controlling environments can lead to stress, burnout, and high employee churn.
- Single-Point Dependence: A Certifications to get high paying jobs often highlight that organizations relying too heavily on a single leader risk collapse if he or she becomes unavailable or makes poor decisions.
- Poor Innovation Adaptability: Autocratic teams often struggle in dynamic or disruptive industries that demand agility.
- Morale Decline: Feeling powerless can make employees cynical, especially when praised less often than dictated to.
In many modern organizational cultures, these disadvantages outweigh traditional benefits, prompting a shift toward more collaborative styles.
Situations Where It Works
Autocratic leadership, as often discussed in PMP Training , can yield strong outcomes in specific scenarios:
- Emergency Response/Public Safety: Life-threatening situations demand quick top-down decisions.
- Military Operations: Field commanders coordinate complex, time-sensitive missions with absolute authority.
- Manufacturing Lines: Efficiency and quality control rely on standardization and supervision.
- Turbulent Markets: Certain firms use tight control to react swiftly to volatility.
- Turnaround Efforts: In struggling companies, strong leadership can reiterate focus and restructure priorities.
In these conditions, autocratic leadership mitigates risk, accelerates action, and maintains discipline beneficial during short-term critical phases.
Autocratic vs Democratic Leadership
| Feature | Autocratic Leadership | Democratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | Centralized, leader-driven | Decentralized, team-involved |
| Speed | Fast, efficient | Slower, due to consensus building |
| Innovation | Low (limited idea acceptance) | High (team contribution encouraged) |
| Employee Buy-in | Low | High |
| Operating Structure | Hierarchical, rigid | Flexible, collaborative |
| Best for | Crises, manufacturing, military | Creative, service-oriented, R&D |
Autocratic and democratic leadership each have clear use cases, with democratic approaches widely preferred in knowledge-driven or creative sectors.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Famous Examples
- Steve Jobs (Apple): Known for demanding perfection and maintaining strict control over product design and messaging.
- Henry Ford (Ford Motor): Centralized decision-making within tight process controls to scale automobile production.
- Martha Stewart (MSLO): Managerial Economics Concepts s were applied while emphasizing meticulous oversight of brand image, packaging, and quality.
- Margaret Thatcher (UK PM): Known as “The Iron Lady,” she imposed sweeping, top-down reforms across British institutions.
- Military Leaders: Exemplified by Winston Churchill or Dwight Eisenhower during wartime.
These leaders accomplished great feats, but were often polarized in perception respected by some, criticized by others.
Impact on Team Morale
Autocratic leadership can profoundly affect morale positively or negatively:
- Positive Impacts
- Clarity of purpose and well-defined roles help new employees gain footing quickly.
- Clear accountability makes performance metrics transparent.
- Team members appreciate structure in high-risk roles or uncertain environments. Negative Impacts
- Resentment and disengagement arise when contributions are ignored.
- Suppressed morale impairs long-term innovation and retention.
- Fear of appearing incompetent may suppress proactive behavior.
- Employee stress increases when autonomy is absent.
What is the training process that enables leaders to gain trust and competency, allowing rigid control to give way to more empowering approaches that boost morale sustainably? approaches to boost morale sustainably.
Modern Perspective
In today’s fluid workplace environments, rigid autocratic leadership is less common but not obsolete. In highly regulated sectors like healthcare or finance, strict protocols are still necessary. During periods of crisis, companies often revert to autocratic style to regain control and implement change. Overview Of Retail Management Models like ‘situational leadership’ blend authoritarian direction with democratic participation, depending on context. Additionally, leadership research suggests that blending empowering delegation with structured oversight sometimes called “benevolent dictatorship” or “directive coaching” can yield high performance while preserving autonomy.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Alternatives and Comparisons
Autocratic leadership exists along a continuum alongside other styles:
- Democratic/Participative Leadership: Encourages team input, promoting engagement and innovation.
- Laissez-Faire Leadership: Offers maximum autonomy, best for expert teams.
- Transactional Leadership: Rewards compliance while providing clear structure.
- Transformational Leadership: Inspires change through vision, empowerment, and cultural ownership.
- Servant Leadership: Focuses on developing people and supporting growth.
In modern organizations, hybrid models like adaptive leadership What is an MBA often explores switch between styles depending on the situation, moving from autocratic in crises to democratic during normal operations.
Conclusion
Autocratic leadership offers clarity, control, and fast responses essential in emergency, operational, or turnaround contexts. It flourishes in high-risk, high-stake situations where mistakes are costly. However, it risks demotivating employees, suppressing creativity, and causing burnout if applied over prolonged durations. For sustainable success, leaders should adapt styles according to context an approach often emphasized in PMP Training exercising strong direction during critical phases and shifting to collaborative leadership when stability returns. Mastering this balance allows leaders to harness the strengths of autocracy while mitigating its downsides fostering environments where speed, precision, creativity, and engagement coexist.
Final Thought:Like any leadership model, autocratic leadership is a tool useful, but best when applied strategically, situationally, and thoughtfully to maximize organizational and human outcomes.





