
- Introduction Of a finanace manager
- Budget Preparation
- Financial Reporting
- Investment Decisions
- Cash Flow Management
- Tax Planning
- Risk Management
- Cost Reduction
- Auditing and Compliance
- Forecasting and Planning
- Coordination with Other Departments
- Conclusion
Introduction Of a finanace manager
Financial management is a cornerstone of organizational success, serving as the backbone that supports strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and long-term sustainability. Whether in a small startup or a multinational corporation, sound financial management enables leaders to allocate resources effectively, assess performance accurately, best practices finance manager and plan for the future with confidence. This comprehensive guide explores critical areas of financial management including budget preparation, financial reporting, Finance manager, investment decisions, market risk and more, highlighting best practices and the role of finance in achieving organizational goals.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Budget Preparation
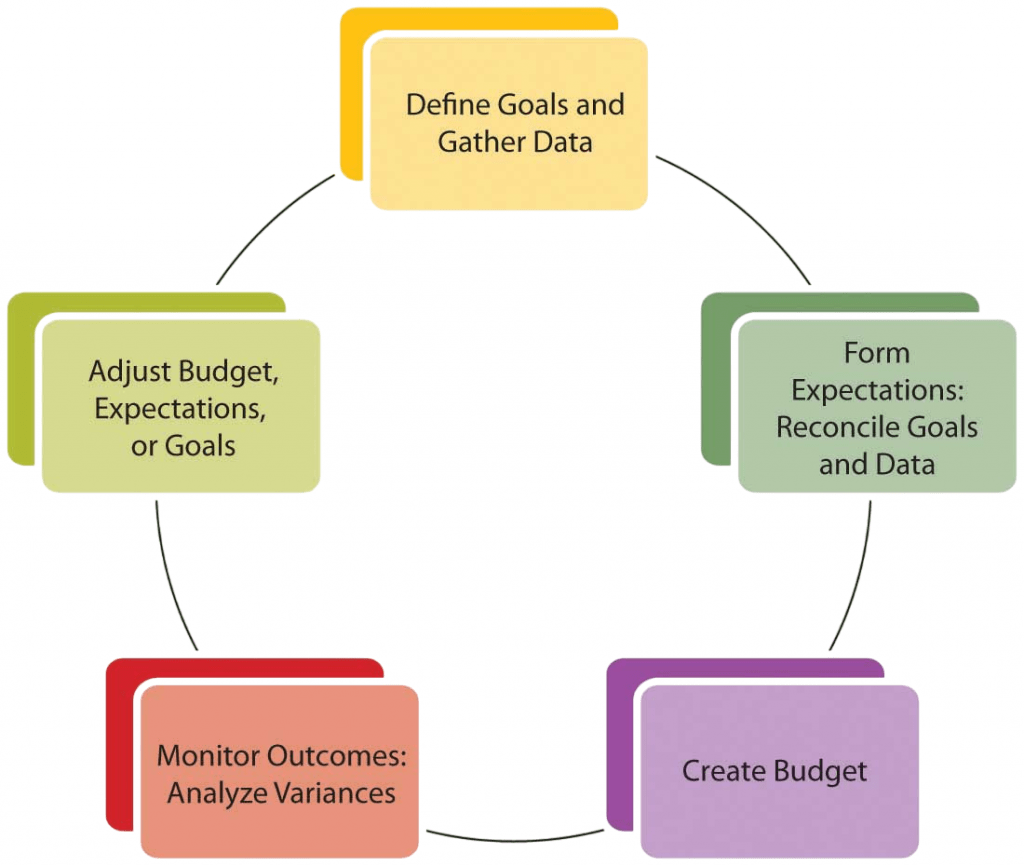
Budget preparation is the process of creating a financial plan that outlines expected revenues and expenditures over a specific period, typically one fiscal year. It is a collaborative effort that involves input from various departments and aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives. The process usually begins with setting assumptions based on historical data, market conditions, and internal projections. Departments then submit their budget requests, which are reviewed and adjusted to ensure alignment with organizational goals. A finalized budget serves as a benchmark for evaluating performance, managing costs, finance manager duties and ensuring that funds are allocated efficiently. Key elements of effective budget preparation include:
- Realistic forecasting
- Clear communication with stakeholders
- Incorporating contingencies
- Regular review and adjustments
- Assessing profitability and operational efficience
- Supporting investment and certificate in ifrs
- Ensuring regulatory compliance
- Facilitating internal controls and audits
- Conducting thorough market and financial analysis
- Evaluating risk and return trade-offs
- Aligning investments with strategic goals
- Monitoring and reviewing investment performance
- Accelerating receivables collection
- Delaying payables strategically
- Maintaining an adequate cash reserve
- Monitoring cash flow regularly
- Understanding applicable tax laws
- Timing income and expenses
- Utilizing tax credits and incentives
- Structuring transactions efficiently
- Creating a risk management framework
- Regularly updating risk assessments
- Implementing internal controls
- Engaging in insurance and hedging strategies
- Conducting cost-benefit analysis
- Benchmarking against industry standards
- Streamlining processes
- Monitoring savings and reinvesting gains
- Using accurate and up-to-date data
- Engaging stakeholders in the planning process
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting forecasts
- Integrating forecasting with budgeting and strategy
- Improved resource allocation
- Enhanced decision-making
- Better risk management
- Stronger organizational cohesion
Financial Reporting
Financial reporting involves the systematic preparation and presentation of financial statements that reflect the financial position and performance of an organization. These reports, which include the income statement, Responsibilities Of A Finance Manager balance sheet, and cash flow statement, market risk provide vital information to stakeholders such as investors, regulators, and management. Accurate financial reporting ensures transparency, builds trust, and supports informed decision-making. It also enables compliance with regulatory requirements and accounting standards such as GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) or certificate in ifrs(International Financial Reporting Standards). The importance of financial reporting lies in:
Investment Decisions
Investment decisions are strategic choices related to the allocation of capital to long-term assets or projects that generate future returns. These decisions are critical to the growth and profitability of an organization. Financial managers use tools such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period to evaluate investment opportunities. These metrics help assess the feasibility, risks, and potential returns associated with each project. Effective investment decision-making involves:
Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management refers to the monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing of the cash inflows and outflows within an organization. It is essential for maintaining liquidity, Responsibilities Of A Finance Manager, meeting financial obligations, and avoiding insolvency. Good cash flow management ensures that a company can pay its suppliers, employees, finance manager roles and responsibilities and creditors on time while also investing in growth opportunities. Tools such as cash flow forecasts and working capital analysis are commonly used to manage cash effectively. Strategies for effective cash flow management include:
Tax Planning
Tax planning is the analysis and arrangement of a financial situation to minimize tax liability within the legal framework. It involves understanding current tax laws and taking advantage of deductions,Finance manager duties exemptions, and credits to reduce the overall tax burden. Tax planning is not just about saving money; it’s about strategic decision-making that impacts business growth and compliance. Businesses often engage tax professionals to ensure that they are compliant and are using tax-efficient strategies. Elements of effective tax planning include:
Risk Management
Risk management in financial management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks that could adversely affect an organization’s assets, income, or operations. These risks include market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk. A structured risk management process includes risk identification, measurement, response planning, and monitoring. Tools like scenario analysis, sensitivity analysis, and financial derivatives (e.g., options, futures) help organizations hedge against potential financial losses. Best practices in risk management include:
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is the practice of lowering expenses to improve profitability without compromising product or service quality. It is a continuous process that involves analyzing operations, certificate in ifrs identifying inefficiencies, and implementing cost-saving measures. Common areas for cost reduction include procurement, production, labor, and administrative expenses. Techniques like lean management, best practices finance manager ,automation, and outsourcing are often employed. Key steps in cost reduction include:
Auditing and Compliance
Auditing and compliance are critical for ensuring that an organization adheres to internal policies, legal regulations, and financial standards. Internal audits assess the effectiveness of internal controls, risk management, and governance processes. External audits provide independent verification of financial statements. Compliance ensures that the organization operates within the legal and regulatory framework. Non-compliance can result in penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Forecasting and Planning
Forecasting and planning are forward-looking financial activities that help organizations set goals, allocate resources, and prepare for future scenarios. Forecasting uses historical data, market trends, best practices finance manager and statistical models to predict future financial performance. Planning involves setting objectives, developing strategies, and creating action plans to achieve financial targets. Together, forecasting and planning support decision-making and enhance organizational agility. Effective forecasting and planning require:
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Coordination with Other Departments
Financial management is not isolated; it requires active coordination with other departments such as operations, marketing, human resources, and IT. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that financial strategies align with operational needs and organizational goals. For example, coordination with marketing helps in aligning budgets with campaign goals, while collaboration with operations ensures cost efficiency and resource optimization. Benefits of cross-departmental coordination include:
Conclusion
Effective financial management encompasses a broad range of activities—from budgeting and reporting to investment decisions and compliance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the financial health and strategic success of an organization. By adopting Finance manager duties, embracing transparency in financial reporting, Finance manager making informed investment decisions, and fostering collaboration across departments, best practices finance manager, organizations, market risk can build a strong financial foundation that supports sustainable growth and resilience in a dynamic business environment.





