
- Introduction
- Consumer Behavior Study
- Product and Brand Management
- Marketing Strategy Development
- Sales and Distribution Management
- Advertising and Promotion
- Digital Marketing
- Market Research
- International Marketing
- Ethics in Marketing
- Career Opportunities
- Conclusion
Introduction
Marketing Management is an essential component of any business that aims to create, communicate, and deliver value to customers. It encompasses various strategies and practices to understand consumer needs, influence purchasing decisions, and maintain customer relationships. In the modern dynamic business environment, marketing is more than just selling; it is about understanding Marketing Management, positioning a brand, and developing a competitive edge, much like how PMP Training equips professionals with structured project management skills to stay competitive. As organizations strive to stay ahead of the competition and cater to increasingly informed consumers, the role of Marketing Management has become even more significant. From traditional practices to digital innovation, marketing continues to evolve with the times. This document explores the major facets of marketing, including a deep dive into consumer behavior, strategic planning, brand management, sales operations, promotions, digital transformation, global marketing approaches, ethical considerations, and the diverse career opportunities the field offers.
Consumer Behavior Study
Consumer behavior is the study of how individuals or groups select, purchase, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or ideas. It involves understanding psychological, personal, social, and cultural factors influencing consumer decisions. Marketers analyze buying behavior to tailor marketing strategies accordingly. Factors like motivation, perception, learning, beliefs, and attitudes play critical roles. Social influences such as family, friends, and reference groups, along with cultural aspects, also shape consumer behavior, making it essential to understand Training Process Steps for effective behavioral alignment. Marketers also consider the decision-making process, which includes need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Understanding this journey allows marketers to align messages, offers, and brand positioning effectively. Technological advancements have added another layer of complexity to consumer behavior. Today’s customers rely on online reviews, social media, and influencer endorsements. Thus, digital behavior tracking tools and analytics have become essential in gaining insights and predicting trends. Insights from consumer behavior help in segmenting the market, targeting the right audience, and positioning products effectively, ultimately contributing to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Product and Brand Management
- Product management deals with the planning, forecasting, and production of a product at all stages of the product lifecycle. It includes identifying customer needs, developing product strategy, and coordinating with multiple departments to deliver value. Product managers work on concept development, prototyping, testing, and launching products, as well as managing iterations based on market feedback, all while aligning with principles of Financial Management in Business to ensure sustainability and profitability.
- Brand management, on the other hand, focuses on building, maintaining, and improving a brand’s reputation. It includes defining brand identity, managing brand equity, and ensuring consistency in messaging across all channels. Elements such as brand name, logo, tagline, and overall personality are carefully designed and managed to resonate with the target audience.
- Strong brand management can increase customer loyalty, differentiate products from competitors, and command premium pricing. Tools like brand audits, customer perception studies, and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) help track brand performance. A well-positioned brand fosters emotional connections and drives long-term business success.

Marketing Strategy Development
- Marketing strategy refers to a business’s overall game plan to reach prospective consumers and turn them into customers of their products or services. It involves market segmentation, targeting, positioning (STP), and developing a marketing mix (4Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion). A well-crafted strategy aligns marketing goals with business objectives, understands the competitive landscape, and addresses customer needs effectively.
- Segmentation helps divide the market into distinct groups with similar needs or behaviors. Targeting selects which segments to focus on, while positioning defines how the product should be perceived in the minds of the consumers. Strategic planning also incorporates situational analysis tools like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal).
- Marketers use data analytics, customer journey mapping, and competitive benchmarking to create informed strategies. A sound marketing strategy ensures long-term sustainability and helps businesses navigate market fluctuations and evolving consumer preferences.
- Digital marketing refers to the use of digital channels, platforms, and technologies to promote products and services. It includes search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, email marketing, social media marketing, pay-per-click advertising, affiliate marketing, and influencer marketing. Digital marketing allows businesses to reach a global audience, personalize messages, and measure campaign effectiveness in real time.
- With the rise of smartphones and internet penetration, digital marketing has become a cornerstone of modern marketing strategy. Tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and HubSpot help track user behavior and optimize campaigns. Social media platforms like Instagram, LinkedIn, and TikTok offer diverse ways to engage audiences.
- Video marketing, voice search optimization, and AI-powered chatbots are some of the emerging trends. Personalization, data privacy, and omnichannel presence are key focus areas. Successful digital marketing enhances brand visibility, drives conversions, and fosters long-term relationships with customers.
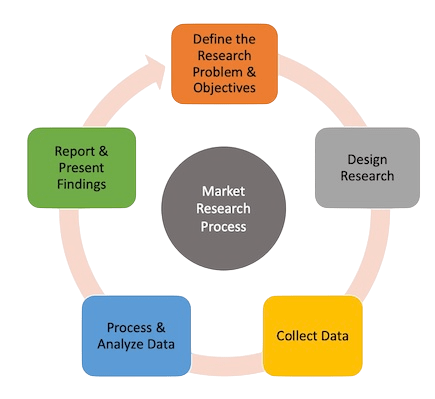
- Market research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of data about customers, competitors, and the market, forming a vital part of the Core Operations Manager Responsibilities. It helps businesses understand market needs, evaluate market size, analyze competition, and make informed decisions. There are two types of market research: primary (collecting new data) and secondary (analyzing existing data).
- Methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, observational techniques, and experimental research. Quantitative research provides measurable insights, while qualitative research explores attitudes and motivations. Online panels, AI-driven sentiment analysis, and big data analytics have revolutionized market research.
- Market research is critical for product development, pricing strategies, and customer satisfaction improvement. It reduces business risks, identifies market gaps, and supports innovation. Well-conducted research enables data-driven decisions that align with market realities.
- Marketing offers diverse career paths across industries. Key roles include marketing manager, brand manager, digital marketing specialist, market research analyst, sales manager, advertising executive, and public relations officer. With the growth of digital technologies, new roles like social media manager, SEO specialist, and content strategist have emerged.
- Professionals can specialize in B2B marketing, B2C marketing, retail, services, healthcare, or technology sectors. Skills in data analytics, creativity, strategic thinking, and communication are essential. Certifications like Google Ads, HubSpot, and Hootsuite enhance job prospects.
- Marketing roles offer both creative and analytical challenges, with opportunities to influence brand growth and customer experiences. Whether working in multinational corporations, startups, agencies, or as entrepreneurs, marketing professionals play a vital role in business success.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Sales and Distribution Management
Sales management involves planning, directing, and controlling an organization’s sales force and activities. It includes setting sales goals, analyzing data, creating sales strategies, training the sales team, and evaluating performance. Sales managers also focus on pipeline management, territory allocation, and incentive plans to drive performance, skills that can be further enhanced through PMP Training. Distribution management ensures the efficient movement of goods from producers to consumers. It involves logistics, warehousing, inventory control, and choosing the right distribution channels, whether direct-to-consumer, retailers, wholesalers, or e-commerce platforms. An effective distribution strategy balances cost-efficiency and customer satisfaction. Technology has transformed sales and distribution functions. CRM systems, sales automation tools, and supply chain analytics offer real-time visibility and efficiency. Strategic alignment between sales goals and distribution capabilities ensures product availability, market penetration, and revenue growth.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Advertising and Promotion
Advertising is a paid form of communication that promotes a product, service, or brand.It aims to inform, persuade, and remind customers through various media channels such as TV, radio, print, digital, and outdoor. Promotion includes advertising but also covers other marketing activities like sales promotions, public relations, sponsorships, events, and personal selling, all of which are influenced by the Levels of Management in Business. The promotional mix helps businesses create awareness, generate interest, and drive sales. Creativity, consistency, and relevance are vital to effective advertising and promotion. Emotional appeals, storytelling, and celebrity endorsements are common advertising techniques. Measuring ad effectiveness through metrics such as reach, impressions, CTR (Click Through Rate), and ROI is crucial. Promotions like discounts, contests, and loyalty programs help boost short-term sales and customer engagement. Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) ensures that all promotional activities are unified and reinforce the brand message across all touchpoints.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Digital Marketing
Market Research
International Marketing
International marketing involves planning and executing marketing strategies in more than one country. It requires understanding diverse cultural, economic, legal, and political environments. Companies must adapt their products, pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies to fit local preferences and regulatory conditions, which are often overseen through the Roles and Responsibilities of a General Manager. Entry strategies include exporting, licensing, franchising, joint ventures, and wholly owned subsidiaries. Standardization versus adaptation is a key strategic decision. Cultural sensitivity, language differences, and currency fluctuations must be addressed. Global brands like Coca-Cola and McDonald’s have succeeded by balancing global consistency with local customization. Technology and e-commerce have simplified cross-border marketing, but regulatory compliance and geopolitical risks remain critical. International marketing opens avenues for growth, economies of scale, and brand recognition.
Ethics in Marketing
Marketing ethics refers to the moral principles that guide marketing practices. It includes issues such as truth in advertising, fair pricing, respecting consumer privacy, avoiding manipulative tactics, and being socially responsible. Ethical marketing builds trust with consumers, enhances brand reputation, and prevents legal issues. Companies often adopt codes of ethics and engage in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives to align business goals with societal values. Examples include environmentally friendly packaging, cause-related marketing, and diversity in advertising, all of which fall under the Responsibilities of a General Manager. Transparency, honesty, and accountability are core to ethical marketing. In the digital age, data protection and responsible use of consumer data are pressing concerns. Ethical lapses can lead to consumer backlash, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Career Opportunities
Conclusion
Marketing Management is a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that plays a vital role in business success. From understanding consumer behavior to managing brands and strategizing market entry, marketing encompasses a wide range of activities. Digital transformation and globalization have added new dimensions to marketing practices, and professionals who pursue PMP Training can strengthen their ability to manage these complex projects effectively. Ethical considerations, customer-centric strategies, and data-driven decision-making are becoming increasingly important. As markets evolve, so do the tools and techniques marketers use. For students and professionals, marketing offers exciting opportunities to innovate, influence, and grow in a rapidly evolving global marketplace. With a strong foundation in marketing management principles and a willingness to adapt, individuals can build successful careers and contribute meaningfully to organizational goals.





