
- Introduction of Managerial Economics
- Definition of Managerial Economics
- Characteristics of Managerial Economics
- Role in Business Decision-Making
- Micro vs Macro Aspects
- Normative vs Positive Approach
- Interdisciplinary Nature
- Tools and Techniques Used
- Relationship with Other Fields
- Limitations
- Conclusion
Introduction of Managerial Economics
Economics is an essential social science that plays a pivotal role in shaping decisions in business, policy-making, and personal financial planning. It studies how individuals, firms, and governments allocate limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants. Understanding economics is more crucial than ever in an age of rapid globalization, technological advancement, and evolving markets. The discipline provides insights into how economies function, why markets behave the way they do, and how various forces interact to influence the allocation of resources, pricing, and production. Economics is not merely about money or markets; it encompasses human behavior, decision-making, and societal welfare. Whether analyzing the performance of a national economy or understanding consumer purchasing patterns, economics provides the analytical tools necessary to interpret and respond to real-world phenomena. In business, economics forms the foundation for making strategic choices such as pricing products, investing in new ventures, or entering new markets. For policymakers, it guides decisions on taxation, interest rates, and social welfare programs.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Definition of Managerial Economics
Economics is often defined as the study of how people choose to use limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants. British economist Lionel Robbins offered one of the most cited definitions: “Economics is the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.” This definition highlights the core concern of scarcity and choice. The term “economics” is derived from the Greek words oikos (household) and nomos (law), meaning household management. Historically, it was closely associated with managing household resources, but over time, its scope has broadened to include everything from international trade to environmental sustainability. Economics is divided into various subfields, rapid globalization, including microeconomics, which deals with individual decision-makers, and macroeconomics, which examines the economy as a whole.
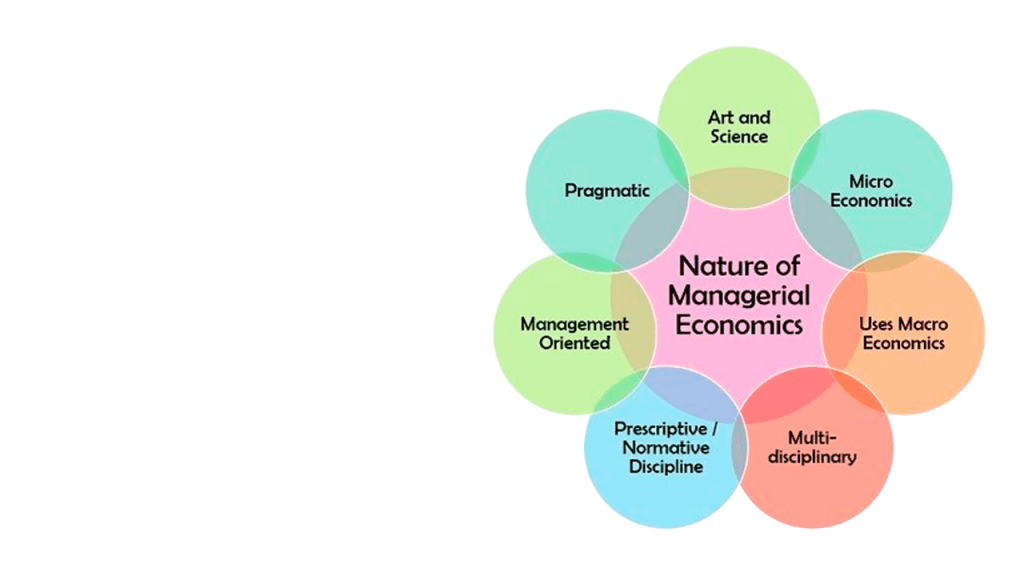
Characteristics of Managerial Economics
Several defining characteristics distinguish economics as a field of study:
- Scarcity and Choice: Economics is based on the reality that resources are finite. Choices must be made about how to allocate these resources efficiently.
- Efficiency: It seeks to optimize resource use to maximize output or societal welfare.
- Incentives Matter: Economic agents respond to incentives, whether they are monetary or non-monetary.
- Subjectivity: Economic behavior is influenced by individual preferences, culture, and psychology.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis is an economics blend of statistical methods with qualitative reasoning.
- Predictive Nature: Although not always exact, economics aims to predict future trends and outcomes.
- Value Neutrality: Especially in positive economics, the discipline strives to describe what is rather than what ought to be.
- Pricing Strategy: By understanding the elasticity of demand, companies can set optimal prices that maximize revenue.Cost-benefit analysis helps decide whether a project is worth pursuing by comparing its expected costs and benefits.
- Market Analysis: Economic tools help analyze customer preferences, competitor behavior, and potential barriers to entry.
- Resource Allocation: Firms make production decisions based on marginal analysis comparing the additional cost to the extra benefit.
- Risk Assessment: Economics helps firms evaluate investment decisions, labor choices, and market expansion risks.
- Mathematics: For modeling and statistical analysis.
- Psychology: Behavioral economics studies how cognitive biases affect decision-making.
- Sociology: Social norms and culture influence economic behavior.
- Political Science: Economic policy is shaped by political ideologies and institutions.
- Environmental Science: Environmental economics addresses sustainability and resource management. This interdisciplinary approach makes economics a powerful tool for solving complex real-world problems, from climate change to health care and education policy.
- Statistical Tools: Regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and econometrics help test economic theories.
- Graphical Analysis: Supply-demand curves, production possibility frontiers, and cost diagrams.
- Surveys and Field Studies: Gathering data directly from economic agents to understand behavior.
- Software Tools: Applications like STATA, R, Python, and Excel are commonly used for data analysis.
- Simulations: To predict economic outcomes under various scenarios.
- Finance: Both deal with resource allocation, risk, and value over time. Business Management: Economic analysis supports strategic planning and resource management.
- Law: Economic principles guide antitrust cases, regulatory frameworks, and contract analysis.
- Political Science: Economics informs policy decisions, election outcomes, and governance.
- Engineering: Economic feasibility studies are crucial in infrastructure and technological development.
- Urban Planning: Uses economic models to determine zoning, housing policy, and transportation planning.
- Assumptions vs Reality: Many economic models rely on unrealistic assumptions such as perfect information or rational behavior.
- Prediction Challenges: Economic outcomes are influenced by multiple variables, making accurate forecasting difficult.
- Value Judgments: Normative economics involves subjective opinions that may differ across cultures and ideologies.
- Data Limitations: Reliable and timely data is not always available, particularly in developing countries.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Cost-benefit analyses may ignore moral and social considerations.
- Dynamic Nature of Economy: Economic behavior evolves, making static models obsolete quickly. Acknowledging these limitations is crucial for applying economic insights responsibly and realistically.
These characteristics make economics versatile and widely applicable across various disciplines, including finance, marketing, politics, and sociology.
Role in Business Decision-Making
In the business context, economics provides a vital framework for decision-making. Managerial economics a specialized branch uses microeconomic principles to make strategic and operational business decisions. Business leaders use economic models to forecast demand, set prices, assess competitive strategy, and evaluate market trends.
Economic principles help businesses operate efficiently and make informed, data-driven decisions.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Micro vs Macro Aspects
Economics is broadly divided into two major branches: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
MicroeconomicsThis field examines the behavior of individual economic agents—consumers, firms, and workers. It explores how prices are determined, resources are allocated, and consumers make choices. Key concepts include demand and supply, elasticity, market structures (like monopoly and perfect competition), and game theory.
MacroeconomicsIn contrast, macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies aggregate indicators such as GDP, unemployment, inflation, interest rates, and fiscal policies. Macroeconomics also examines how economies grow over time and what causes business cycles. Policymakers rely on macroeconomic theories to implement monetary and fiscal policies that stabilize the economy. Both branches are interconnected. For instance, microeconomic behavior (such as increased consumer spending) can influence macroeconomic outcomes (such as GDP growth).
Normative vs Positive Approach
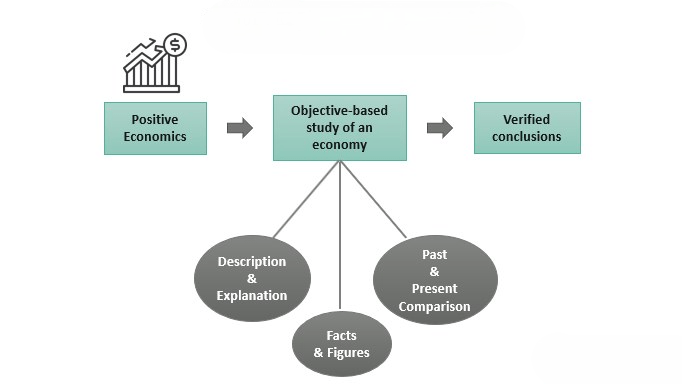
Economics employs two different analytical approaches: positive economics and normative economics.
Positive EconomicsThis approach is objective and fact-based. It deals with what is and can be tested through data and empirical research. For example, “An increase in the minimum wage leads to a reduction in employment” is a positive economic statement. It can be validated or refuted through statistical analysis.
Normative EconomicsThis is subjective and value-based. It deals with what ought to be. Statements like “The government should increase the minimum wage to reduce poverty” reflect normative economics because they are based on opinions and societal values. Understanding the distinction helps policymakers and business leaders distinguish between data-driven insights and value judgments.
Interdisciplinary Nature
Economics does not operate in a vacuum. It is deeply interdisciplinary and draws from various other fields:
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Tools and Techniques Used
Economists use a wide array of tools and techniques to analyze and interpret data: Mathematical Modeling: Representing economic relationships through equations and formulas.
These tools allow economists to build models, interpret trends, and offer data-backed recommendations.
Relationship with Other Fields
Economics has a strong symbiotic relationship with several academic and professional fields:
These connections enhance the applicability and relevance of economics in solving real-world challenges.
Limitations
Despite its broad utility, economics has limitations:
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Conclusion
Economics is a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that offers powerful tools for understanding how societies manage their resources. From its core principles of scarcity and choice to its modern applications in global trade, health, education, and environmental sustainability, Role in business decision-making economics remains deeply relevant to our daily lives and long-term development.Its dual nature—micro and macro, positive and normative—allows for a comprehensive analysis of individual and societal decisions. The interdisciplinary essence of economics ensures that it continues to evolve and adapt to rapid globalization, integrating insights from psychology, data science, politics, Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis and more.Whether you are a business professional, a policymaker, or simply a curious citizen, a solid understanding of economics equips you with the analytical skills to interpret the world more clearly, make informed business decision-making , and contribute meaningfully to discussions that shape our collective future.





