
- Introduction to Operations Manager Responsibilities
- Process Optimization
- Resource Allocation
- Supply Chain Management
- Inventory Management
- Vendor Management
- Quality Control
- Budgeting and Cost Control
Introduction to Operations Manager Responsibilities
An Operations Manager plays a crucial role in maintaining the seamless functioning of a business by overseeing its core operational activities and ensuring they align with the company’s strategic goals. The scope of Operations Manager Responsibilities includes managing supply chains, streamlining production processes, coordinating internal departments, and ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently. These professionals are responsible for supervising staff, developing operational policies, setting performance benchmarks, and ensuring that day-to-day activities contribute to long-term growth and efficiency. A key part of Operations Manager responsibilities is identifying areas for improvement, solving operational issues promptly, and driving continuous process enhancements skills that are further strengthened through PMP training. They also play a vital role in budgeting, forecasting, and maintaining quality standards across operations. Acting as a liaison between senior leadership and various departments, Operations Managers ensure smooth communication and implementation of organizational strategies. Strong leadership, problem-solving, and organizational skills are essential for excelling in this multifaceted role. This introduction provides a comprehensive overview of Operations Manager Responsibilities, offering insight into the strategic and operational tasks that define this key position in any organization.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Process Optimization
- Identify and Map Current Processes: The first step in business process optimization is to document and analyze existing workflows to understand how tasks are performed and where inefficiencies lie.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve, whether it’s reducing costs, improving turnaround time, or increasing output accuracy, to guide the optimization strategy effectively a principle often emphasized in curriculum discussions at top institutions featured in the Best MBA Colleges in India list.
- Eliminate Redundancies and Bottlenecks: Streamline operations by removing duplicate tasks and addressing points in the process that slow down progress or cause delays.
Process optimization is a strategic approach focused on improving the efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability of an organization’s operations. It involves analyzing existing workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing changes to streamline activities and reduce costs. A key goal of business process optimization is to enhance productivity while maintaining or improving quality and customer satisfaction. Below are key elements involved in effective process optimization:
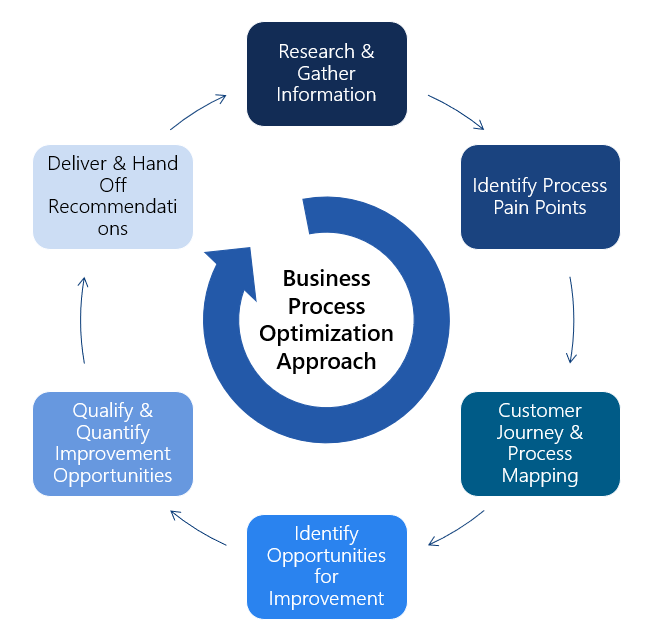
- Leverage Technology and Automation: Implement tools such as automation software or digital dashboards to reduce manual work and improve data accuracy.
- Monitor and Measure Performance: Continuously track key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the impact of changes and adjust strategies as needed.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage teams to regularly evaluate processes and suggest enhancements, reinforcing the principles of business process optimization throughout the organization.
- Strategic Sourcing and Procurement: Identifying reliable suppliers and negotiating favorable contracts is essential to maintain quality and cost-effectiveness in the supply chain.
- Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking is critical for operational efficiency and can be effectively managed using various Tools and Techniques in Management Accounting.
- Logistics and Distribution: Coordinating the movement of goods through warehouses, transportation channels, and delivery systems ensures timely and accurate order fulfillment.
- Demand Forecasting: Leveraging supply chain analytics helps predict future customer demand, allowing for better planning and resource allocation.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential disruptions, such as supply shortages or geopolitical issues, ensures supply chain resilience.
- Performance Monitoring: Using supply chain analytics to track key metrics enables continuous improvement, cost reduction, and greater responsiveness to market changes.
- Vendor Selection and Qualification: Choosing vendors based on clear criteria such as quality, reliability, compliance, and pricing ensures strong, long-term partnerships.
- Contract Negotiation and Agreement: Defined contracts that include service-level agreements (SLAs) help prevent misunderstandings and set performance expectations.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly evaluating vendor performance ensures they meet agreed-upon standards and contribute to business goals a key competency sought in candidates pursuing Top MBA Operations Management Jobs for Career advancement.
- Compliance and Documentation: Keeping proper documentation and ensuring vendors adhere to legal and regulatory standards is crucial for risk mitigation.
- Vendor Risk Management Integration: Incorporating vendor risk management into procurement strategies helps identify financial, operational, and reputational risks early on.
- Ongoing Communication and Improvement: Maintaining open communication and conducting regular reviews supports collaboration. continuous improvement and robust vendor risk management practices.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation is a critical component of effective operations management, involving the strategic distribution of an organization’s resources, such as manpower, time, money, and equipment to maximize productivity and achieve business goals. Proper resource allocation ensures that every department and project has the necessary assets to function efficiently without waste or shortage. This process requires careful planning, prioritization, and real-time adjustments based on changing demands and constraints, highlighting the Nature of Managerial Economics importance in effective decision-making and resource allocation. To streamline this process, many organizations rely on resource allocation tools, which provide data-driven insights and allow managers to track, adjust, and forecast resource usage accurately. These tools help identify underutilized assets, prevent overallocation, and improve decision-making by visualizing workloads and deadlines. By using resource allocation tools, businesses can respond quickly to shifts in project scope, client requirements, or market conditions. Moreover, these tools enhance cross-functional collaboration by ensuring transparency and equitable distribution of resources across teams. Effective resource allocation tools not only boost efficiency but also help reduce operational costs and improve project outcomes. As organizations grow and handle more complex operations, adopting smart and scalable resource allocation practices becomes essential for long-term success and sustainability.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) is the strategic coordination of activities involved in sourcing, producing, and delivering goods and services from suppliers to end customers. Effective SCM ensures that the right products reach the right place at the right time while minimizing costs and maximizing customer satisfaction. In today’s data-driven world, supply chain analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing visibility, efficiency, and decision-making throughout the entire supply chain. Below are six key components of successful supply chain management:
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Inventory Management
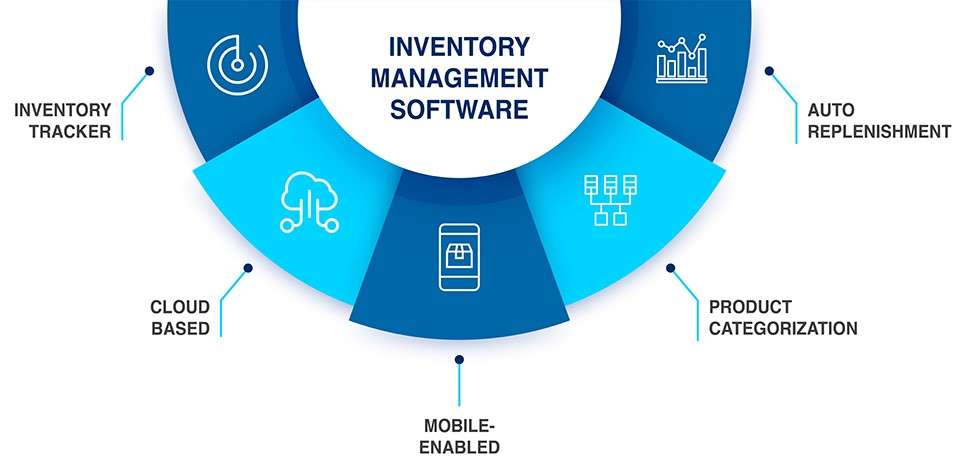
Inventory management is a vital function in operations that involves overseeing the ordering, storage, and use of a company’s inventory, ranging from raw materials to finished products. An efficient inventory management process helps businesses maintain optimal stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and prevent issues such as stockouts or overstocking. A well-organized inventory system is essential for tracking inventory in real-time, enabling accurate forecasting, and improving order fulfillment rates. By leveraging a modern inventory system, businesses can automate stock tracking, generate detailed reports, and integrate with other operational tools like sales and supply chain platforms capabilities that professionals with PMP training are well-equipped to manage and optimize. This leads to better decision-making, reduced human error, and improved overall efficiency. In fast-paced industries, an agile inventory system also enhances responsiveness to market demand and minimizes losses from obsolete or expired stock. Ultimately, strong inventory management ensures that products are available when and where they’re needed, directly impacting customer satisfaction and profitability. Whether a business is large or small, having a robust inventory management strategy supported by a reliable inventory system is key to maintaining smooth operations and supporting long-term growth.
Vendor Management
Vendor management is the process of selecting, onboarding, monitoring, and maintaining productive relationships with third-party suppliers to ensure quality, compliance, and cost-efficiency. Effective vendor management not only improves service delivery but also strengthens business continuity and strategic partnerships. A critical part of this process is vendor risk management, which involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with working with external vendors. Below are six key aspects of successful vendor management:
Quality Control
Quality control is a fundamental aspect of operations management that ensures products and services meet established standards of excellence and customer expectations. It involves systematic processes for inspecting, testing, and evaluating output at various stages of production to detect and correct defects. A strong quality control system helps maintain consistency, reduce waste, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance brand reputation. In today’s competitive market, many organizations rely on quality control software to streamline and automate these processes. This technology enables real-time monitoring, data collection, and analysis, making it easier to identify issues quickly and take corrective actions activities closely aligned with the core Functions of Product Management By using quality control software, companies can track quality metrics, generate compliance reports, and maintain detailed records for audits and continuous improvement efforts. It also helps enforce standard operating procedures and ensures that teams adhere to industry regulations and internal policies. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or service industries, quality control software plays a critical role in maintaining high-performance standards while minimizing human error. Investing in efficient quality control practices, supported by advanced software tools, is essential for delivering reliable products, reducing operational costs, and staying ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Budgeting and Cost Control
Budgeting and cost control are essential financial practices that help organizations plan, monitor, and manage their financial resources effectively. Budgeting involves setting financial goals, forecasting revenues and expenses, and allocating funds to various departments or projects to ensure that spending aligns with strategic objectives. Cost control, on the other hand, focuses on monitoring actual expenses against the budget, identifying variances, and implementing corrective actions to avoid overspending. Together, these practices enable businesses to make informed decisions, improve profitability, and ensure financial stability. By regularly reviewing budgets and tracking expenditures, organizations can identify inefficiencies, cut unnecessary costs, and reallocate resources to high priority areas practices that are reinforced through PMP training. Accurate budgeting and disciplined cost control also support better cash flow management, enhance accountability, and provide a clear financial roadmap for both short-term operations and long-term growth. Modern tools and software solutions further streamline these processes, allowing real-time tracking, analysis, and reporting of financial data. Ultimately, effective budgeting and cost control are not just about limiting expenses but about maximizing value, improving operational efficiency, and ensuring that every dollar spent contributes to the organization’s overall success.





