
- Introduction to GMAT & CAT
- Key Differences
- Exam Pattern Comparison
- Eligibility & Age Criteria
- Global vs Indian Acceptance
- Difficulty Level
- Preparation Strategy
- Cost and Fees
Introduction to GMAT & CAT
The GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) and CAT (Common Admission Test) are two of the most prominent and competitive entrance exams for aspiring business school candidates worldwide. Although both exams aim to evaluate a candidate’s aptitude for management education, they cater to distinct audiences and have different geographical focuses. The Graduate Management Admission Test is widely recognized by business schools internationally, particularly in North America, Europe, and many other regions. It serves as a standardized test to assess skills in analytical writing, quantitative reasoning, verbal reasoning, and integrated reasoning, making it a critical component of MBA and other graduate management program admissions across a broad spectrum of universities. In contrast, the CAT is predominantly an Indian entrance exam, primarily used for admission into prestigious Indian management institutes such as the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) and other top business schools within India. The CAT exam tests candidates on quantitative ability, verbal ability and reading comprehension, data interpretation, and logical reasoning. While the GMAT offers flexibility by allowing candidates to take the exam multiple times a year and is accepted by numerous schools globally, the CAT is conducted once annually and has a significant influence on the Indian management education landscape. Both tests, despite their differences in format, acceptance, and regional focus, play a pivotal role in shaping the future careers of business professionals by opening doors to top-tier management education. Ultimately, candidates choose between the GMAT and CAT based on their target institutions, career goals, and preferred study destinations.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Differences
One of the fundamental differences between the GMAT and the CAT exams is their target audience and global reach. The GMAT is internationally recognized and widely accepted by business schools across the world, especially in North America, Europe, and other global regions. This makes it an ideal choice for candidates aiming to pursue MBA programs or other graduate management studies outside India. In contrast, the CAT is specifically designed for candidates seeking admission to top Indian business schools, most notably the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs). While the CAT is crucial for aspirants targeting Indian institutions, some Indian schools also accept GMAT scores, especially for executive or specialized MBA programs. Another significant distinction lies in the exam structure and content. The GMAT assesses candidates through multiple sections, including Integrated Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, and the Analytical Writing Assessment, thus testing a broad range of skills from data analysis to critical thinking and written communication. On the other hand, the CAT emphasizes Quantitative Ability, Verbal Ability, Logical Reasoning, and Data Interpretation, with a strong focus on problem-solving speed and accuracy.
Additionally, the GMAT allows candidates to take the test multiple times throughout the year, providing flexibility in test planning, whereas the Common Admission Test is conducted once annually, making GMAT preparation and timing critical. Both exams require a thorough understanding of their respective formats, question types, and time management strategies. Ultimately, the choice between the Graduate Management Admission Test and CAT depends on a candidate’s career goals, preferred study destination, and the institutions they wish to target.
Exam Pattern Comparison
- Number of Sections: The GMAT consists of four main sections Analytical Writing Assessment, Integrated Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, and Verbal Reasoning. In contrast, the CAT has three sections Quantitative Ability, Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension, and Data Interpretation & Logical Reasoning.
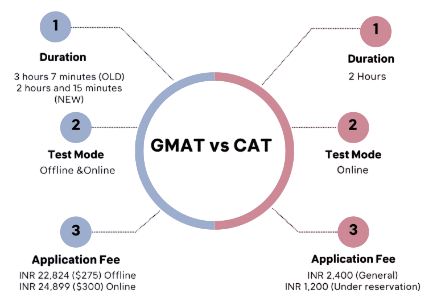
- Duration: The GMAT exam lasts about 3 hours and 7 minutes, including optional breaks, while the CAT exam is approximately 3 hours long, divided into three one-hour sections.
- Question Types: The GMAT features multiple-choice questions across all sections, with the Analytical Writing Assessment requiring an essay. The CAT primarily has multiple-choice questions but also includes non-MCQ questions, especially in the Quantitative and Data Interpretation sections.
- Scoring: GMAT scores range from 200 to 800 for the combined Quantitative and Verbal sections, with separate scores for Integrated Reasoning (1-8) and Analytical Writing (0-6). CAT scores are percentile-based, reflecting the candidate’s rank relative to others.
- Adaptive Nature: The GMAT is a computer-adaptive test at the section level, meaning question difficulty adjusts based on the candidate’s performance in real-time. The CAT is not adaptive but is known for its variable difficulty levels each year.
- Test Frequency: The GMAT is available throughout the year, and candidates can retake it multiple times with certain restrictions. The CAT is conducted once a year, typically in November or December.
- Section Order: The GMAT allows candidates to choose the order in which they take the sections, providing flexibility. The CAT follows a fixed section order that all candidates must adhere to.
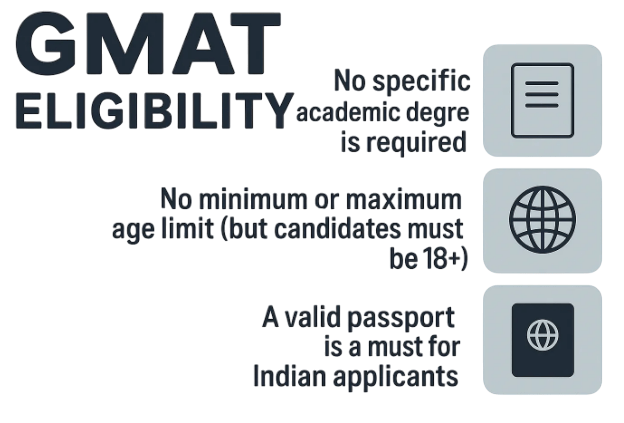
- Educational Qualification GMAT: There is no specific educational qualification required to take the GMAT. Candidates from any academic background, including fresh graduates, working professionals, and even those still pursuing their degrees, can register for the exam.
- Educational Qualification CAT: To be eligible for the CAT exam, candidates must hold a bachelor’s degree with at least 50% marks (45% for reserved categories) from a recognized university. Final-year students awaiting results can also apply.
- Age Limit GMAT: There is no upper or lower age limit to appear for the GMAT. Candidates of all ages can take the exam, making it accessible for freshers, mid-career professionals, and even senior executives.
- Age Limit CAT: Similarly, the CAT exam does not have any specific age limit. Aspiring candidates of any age can appear for the exam, provided they meet the educational qualifications.
- Work Experience GMAT: While work experience is not mandatory to take the GMAT, many top business schools prefer applicants with some professional experience. However, candidates can apply to many programs immediately after graduation.
- Work Experience CAT: Work experience is not a mandatory eligibility criterion for CAT either. However, some Indian institutes may give weightage to work experience during the selection process.
- Number of Attempts GMAT: Candidates can take the GMAT up to five times within a rolling 12-month period, with a maximum of eight attempts in total. This allows flexibility to improve scores.
- Overall Difficulty: Both the GMAT and Common Admission Test are challenging exams, but the CAT is often considered more difficult due to its unpredictable question patterns and intense competition.
- Exam Focus: The GMAT primarily tests logical reasoning, critical thinking, and verbal skills. It emphasizes the application of knowledge rather than rote learning, which can make it somewhat more approachable for well-prepared candidates.
- Question Design: GMAT questions are designed to evaluate analytical thinking and problem-solving skills. The test adapts to the test-taker’s ability level, providing a more personalized challenge.
- CAT Complexity: The CAT exam features sections like Logical Reasoning and Quantitative Ability that tend to be more complex and nuanced, demanding faster problem-solving skills and deeper conceptual clarity.
- Predictability: The GMAT has a fairly standardized structure and question types, making preparation more straightforward. The CAT, however, is known for its unpredictability in question types and difficulty level, adding to the challenge.
- Competition Level: The CAT sees a massive number of test-takers every year, with a highly competitive selection process for a limited number of seats in prestigious Indian management institutes, increasing the exam’s overall difficulty.
- Preparation Impact: Due to these factors, candidates often find that success in the CAT requires intense preparation and practice with diverse question types, while the GMAT rewards consistent logical reasoning and verbal skills practice.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Eligibility & Age Criteria
Global vs Indian Acceptance
The GMAT and CAT exams differ significantly in their global acceptance and the range of institutions that recognize their scores. The GMAT is a globally accepted test, recognized by over 7,000 business schools in more than 115 countries. It is especially prominent in countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, and across Europe. Prestigious universities such as Harvard Business School, Stanford Graduate School of Business, INSEAD, and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania require or highly recommend Graduate Management Admission Test scores for admission into their MBA programs. This widespread acceptance makes the GMAT the preferred choice for candidates aspiring to study management at top institutions worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. The exam’s international reputation adds considerable value to a candidate’s profile when applying globally. In contrast, the CAT is primarily accepted by Indian business schools, most notably the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), which are among the country’s most prestigious management institutes. Other top Indian business schools like XLRI, Faculty of Management Studies (FMS), SP Jain Institute of Management and Research, and the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT) also accept CAT scores for their MBA admissions. Although the Common Admission Test does not have a broad global presence, a few international institutions, mainly in Singapore and Dubai, occasionally consider CAT scores. However, this acceptance is relatively rare compared to the GMAT. Therefore, the choice between these exams often depends on a candidate’s geographical and institutional preferences for pursuing management education.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Difficulty Level
Preparation Strategy
Preparing for the GMAT and CAT exams requires focused strategies tailored to the unique demands of each test. For the GMAT, it is essential to build strong skills in analytical writing, integrated reasoning, and verbal reasoning. Since the GMAT is a computer-adaptive test, managing time effectively and practicing under realistic test conditions are crucial. Taking multiple practice tests helps candidates become familiar with the adaptive nature of the exam and improves their pacing across sections. Utilizing official GMAT preparation materials ensures exposure to authentic question types and exam patterns. Many candidates also benefit from enrolling in coaching classes or online courses that offer structured guidance, expert tips, and personalized feedback. On the other hand, CAT preparation demands a thorough and disciplined approach, especially in areas like quantitative aptitude, data interpretation, and logical reasoning. Given the intense competition for admission to premier Indian business schools, joining a reputable coaching program or online course can provide a solid foundation and systematic preparation schedule. Regularly taking mock tests is vital for the CAT, as it helps candidates develop speed and accuracy while honing time management skills under exam-like conditions. Mock tests also reveal strengths and weaknesses, allowing aspirants to focus their efforts on areas needing improvement. Overall, both exams require consistent practice, strategic planning, and familiarity with the exam formats. Success depends not only on mastering content but also on building test-taking endurance and confidence through repeated practice.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Cost and Fees
The cost of taking the GMAT and CAT exams varies significantly, influenced by geographic location and any additional services candidates may require. The GMAT exam fee is generally around $275 (USD), which includes sending official score reports to up to five business schools. This fee reflects the global nature and extensive administrative support behind the exam. However, candidates should also be aware of potential additional charges. For example, requesting extra score reports beyond the initial five schools incurs an extra fee, as does rescheduling or canceling a test appointment. These additional costs can add up, especially if a candidate needs to retake the exam or make changes to their testing plans. On the other hand, the CAT exam, primarily held in India, is much more affordable, making it accessible to a larger pool of candidates. The fee for the CAT exam typically ranges between INR 2,000 to 2,500, which translates to roughly $25 to $35 USD. This significantly lower fee is appealing to aspirants who may have budget constraints but still want to pursue a top management education in India. While the CAT fee does not include extra services like sending score reports internationally, the overall cost-effectiveness of the CAT exam makes it an attractive option for many Indian students. In summary, while the GMAT offers global recognition at a higher cost, the CAT provides a more budget-friendly alternative tailored to the Indian management education ecosystem.





