
- Overview of Retail Management
- Role of Retail Manager
- Types of Retail Stores
- Retail Marketing Strategies
- Challenges in Retail Management
- Inventory Management
- Store Layout and Design
- Retail Supply Chain Management
- Technology in Retail
- Career Opportunities in Retail
- Conclusion
Overview of Retail Management
Retail management is the process of delivering goods from manufacturers to customers effectively and profitably. It involves planning, organizing, staffing, coordinating, and supervising retail operations. Today, retail management guide goes beyond traditional brick-and-mortar methods due to the growth of online platforms and changes in buying habits. It now includes inventory software management, customer interaction, strategic planning, and using technology to improve customer experiences. The goals are to ensure smooth store retail operations, maintain customer satisfaction, and ultimately increase profits in Data analytics training.
Role of Retail Manager
The retail manager is essential for the daily retail operations of a retail store. They oversee staff, ensure customer satisfaction, manage inventory, and meet sales targets. Retail managers need strong leadership and communication skills, as they connect upper management with the store team. Their responsibilities include scheduling shifts, training new employees, addressing customer complaints, and making sure the store follows health and safety guidelines. They also analyze sales reports to predict demand, handle budgets, and effectively run promotional campaigns.
Types of Retail Stores
Retail stores come in many varieties and formats. Some common types include:
- Department Stores: Large retailers offering various goods in departments like clothing, electronics, and home goods.
- Supermarkets: Self-service Retail stores offering food, beverages, and household items in one location.
- Specialty Stores: Focused on a specific product category like shoes, books, or electronics, providing extensive product knowledge and variety.
- Convenience Stores: Smaller outlets with limited products, typically open for longer hours and located near residential areas.
- Discount Stores: Retailers that sell products at lower prices by reducing operating costs and offering fewer services.
- E-commerce Stores: Online platforms where customers can shop anytime, anywhere.
- Warehouse Retailers: Bulk sellers like Costco, focusing on high volume and low prices.
- Merchandising: Organizing products to maximize sales.
- Promotions and Discounts: Offering seasonal sales, discounts, loyalty programs, and special deals.
- Omnichannel Marketing: Combining online and offline channels for a consistent customer experience.
- Branding: Building a strong, recognizable brand identity that connects with the target audience.
- Personalization: Using customer data to customize recommendations and communications.
- Social Media Marketing: Engaging with customers on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok to build community and drive traffic.
- Location-based Marketing: Using GPS and mobile data to send relevant offers to nearby customers.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Rapid shifts in customer behavior require quick adjustments in marketing and inventory software strategies.
- High Competition: The growth of e-commerce stores has made the market more competitive, pushing retailers to stand out.
- supply chain in retail Disruptions: Delays or shortages can hurt sales and impact customer satisfaction.
Each store type needs a different management strategy to ensure effective operations and meet customer expectations.
Retail Marketing Strategies
Retail marketing strategies are crucial for attracting and keeping customers. Common strategies include:
Effective retail marketing boosts foot traffic and online visits while also strengthening customer loyalty and brand value.
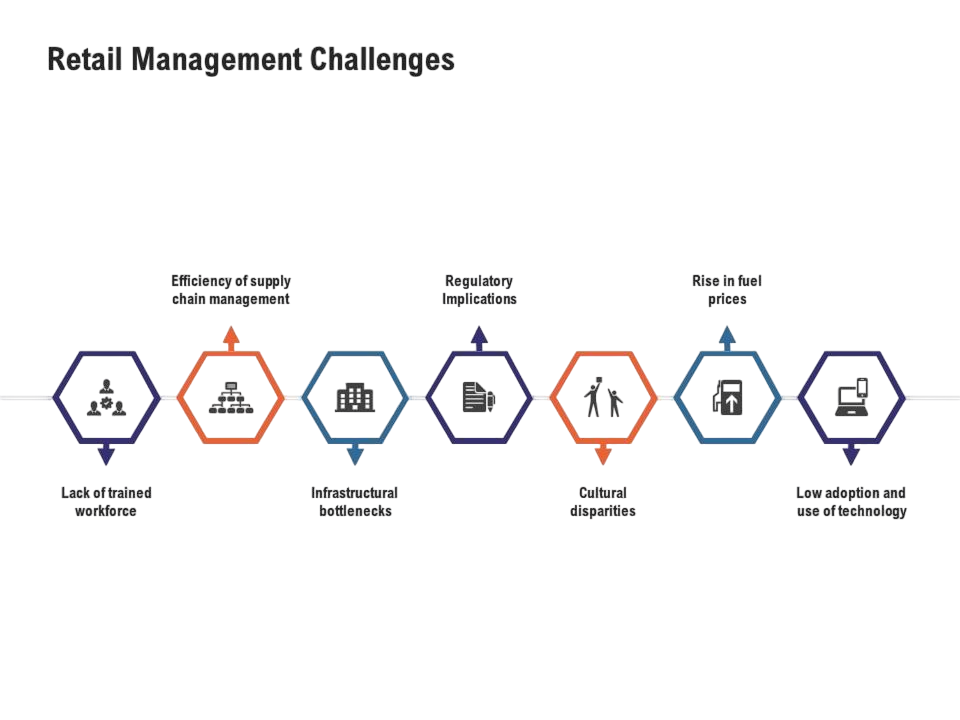
Challenges in Retail Management
Retail managers face various challenges in a fast-paced market. These include:
Inventory Management
Inventory management is crucial to retail operations. It tracks retail stock control levels, forecasts demand, and replenishes products to meet customer needs without overstocking. Effective inventory management ensures product availability, minimizes holding costs, and reduces losses due to theft or obsolescence. Techniques like Just-In-Time (JIT), ABC analysis, and automated retail stock control replenishment help optimize inventory. Technology such as barcode scanners, RFID, and inventory management software makes real-time monitoring easier. Accurate inventory tracking builds customer trust by ensuring popular items are always available.
Store Layout and Design
Store layout and design greatly impact customer experience and sales. A well-planned layout directs customers through the store, encourages browsing, and highlights high-margin products. Common layouts include grid, loop, and free-flow designs, each suited to different types of stores. Elements like lighting, colors, signage, and music shape the overall atmosphere and influence buying behavior. Proper placement of checkout counters, promotional displays, and necessary items can increase impulse purchases. The aim is to create a visually appealing, comfortable, and user-friendly shopping environment that maximizes time spent in-store and conversion rates.
Retail Supply Chain Management
Retail Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves coordinating the flow of goods from suppliers to customers. It covers procurement, warehousing, transportation, inventory retail stock control, and distribution. Efficient supply chain in retail Management (SCM) lowers expenses, minimizes delays, and guarantees timely delivery of products to their intended locations. Retailers often use technology like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and supply chain analytics to track performance and make smart choices. Data Analytics Training Working closely with suppliers, real-time inventory tracking, and demand forecasting are key to a responsive supply chain in retail. A well-run supply chain enhances service levels and customer satisfaction.
Technology in Retail
Technology is changing the retail landscape by improving efficiency and customer experience. Point-of-sale (POS) systems make transactions and inventory tracking easier. e-commerce stores platforms and mobile apps provide convenience and broaden access. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning help with demand forecasting, personalized marketing, and chatbots for customer service. Augmented Reality (AR) allows for virtual try-ons, while Internet of Things (IoT) devices monitor shelf stock in real-time. Payment methods like digital wallets and contactless payments ensure quick and secure checkouts. Embracing technology is vital for staying competitive and meeting changing customer needs.
Career Opportunities in Retail
Retail offers many career paths for people with various skills. Entry-level roles include sales associates and cashiers, while experienced workers can become store managers, visual merchandisers, and inventory software analysts. Strategic positions include retail stock control buyers, supply chain in retail managers, and marketing specialists. With the rise of e-commerce, there is also demand for digital marketing experts, data analysts, and UX designers.
retail management guide courses and certifications can improve job prospects and lead to leadership roles in national and international chains. The industry values individuals who are customer-focused, flexible, and innovative.
Conclusion
Retail management is a dynamic field that plays a critical role in connecting products with customers. From managing store retail operations and marketing to using technology and handling supply chain in retail, effective retail management guide requires a mix of strategic thinking, customer insight, and operational skill. As customer expectations change and competition grows, the role of retail stock control managers becomes increasingly complex and important. Data Analytics Training With many career opportunities and ongoing industry advancements, retail management continues to be an exciting and rewarding field for aspiring professionals.





