
- Introduction to psycopg2
- Setting Up PostgreSQL with psycopg2
- Installing psycopg2
- Connecting to PostgreSQL Database
- Executing SQL Commands
- Parameterized Queries
- Transactions in psycopg2
- Conclusion
Introduction to psycopg2
psycopg2 is a popular PostgreSQL adapter for the Python programming language. It allows developers to connect, query, and interact with PostgreSQL databases using Python scripts. As one of the most reliable and widely used libraries for PostgreSQL in the Python ecosystem, psycopg2 adheres to the Python DB API 2.0 specification. Its performance, robustness, Python Training and advanced features like transaction control and connection pooling make it a go-to solution for database-driven Python applications . psycopg2 is a popular PostgreSQL adapter for the Python programming language. It allows Python developers to interact with PostgreSQL databases easily and efficiently. Built on the PostgreSQL libpq library, psycopg2 is known for its stability, performance, and full compliance with the Python DB API 2.0 specification. This library enables you to perform all standard database operations—such as connecting to a PostgreSQL server, executing SQL queries, inserting records, updating tables, and managing transactions—directly from your Python code. Whether you’re building data-driven applications, performing data analysis, or working on backend services, psycopg2 provides the tools needed to work with PostgreSQL in a clean and Pythonic way. psycopg2 also supports advanced PostgreSQL features, such as server-side cursors, asynchronous notifications, and automatic type conversion between Python and PostgreSQL data types. Additionally, it supports parameterized queries, which help prevent SQL injection attacks and make your applications more secure. Overall, psycopg2 is a robust and essential tool for any Python developer working with PostgreSQL databases. Its ease of use, Complete Guide on System Software extensive features, and strong community support make it the go-to choice for database interaction in Python projects.
Do You Want to Learn More About Python? Get Info From Our Python Online Training Today!
Installing psycopg2
You can install psycopg2 using Python’s package manager, pip. There are two main variants:
- psycopg2 (binary package with native C dependencies):
- psycopg2 (source package, requires compilation):
pip install psycopg2-binary
pip install psycopg2
The binary version is easier for most users, especially those who want to avoid dealing with native PostgreSQL development libraries Polymorphism in C++. However, for production environments, the non-binary version is often recommended for greater stability and flexibility.
Connecting to PostgreSQL Database
To connect a Python application to a PostgreSQL database, you can use the psycopg2 library, which provides a simple and efficient way to establish and manage database connections. First, ensure that psycopg2 is installed in your environment using pip install psycopg2-binary. Then, you can connect to your PostgreSQL database using the connect() function by providing essential parameters C++ Vectors such as the database name, user, password, host, and port.Once installed, connecting to a PostgreSQL database is straightforward. psycopg2 provides the connect() method, which requires parameters like database name, username, password, host, and port.
- import psycopg2
- conn = psycopg2.connect(
- dbname=”mydb”,
- user=”postgres”,
- password=”mypassword”,
- host=”localhost”,
- port=”5432″
- )
This returns a connection object, which can be used to create cursors and perform SQL operations. It’s good practice to manage connections using with statements or proper try/finally blocks to ensure they are closed after use.
Executing SQL Commands
After establishing a connection, SQL queries can be executed using cursor objects. Cursors represent a database session where SQL commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE are executed Python Training.
- cur = conn.cursor()
- cur.execute(“SELECT * FROM employees”)
- rows = cur.fetchall()
- for row in rows:
- print(row)
- cur.close()
- conn.close()
Cursors should be explicitly closed after use to release database resources.
Want to Pursue a Python Master’s Degree? Enroll For Python Master Program Training Course Today!
Parameterized Queries
Parameterized queries in psycopg2 allow you to safely insert user input into SQL statements without risking SQL injection attacks. Instead of directly embedding values into SQL strings, you use placeholders (%s) and pass the actual values as a separate tuple or list. psycopg2 automatically escapes and formats the inputs, Backtracking Programming ensuring database security and cleaner code. To prevent SQL injection, psycopg2 supports parameterized queries using placeholders. Instead of concatenating strings, values are passed as parameters to the execute() method.
cur.execute(“SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s”, (user_id,))
psycopg2 automatically escapes values and converts data types properly. Note that placeholders use %s regardless of the underlying data type—do not use Python’s string interpolation (% or f””) with SQL queries directly.
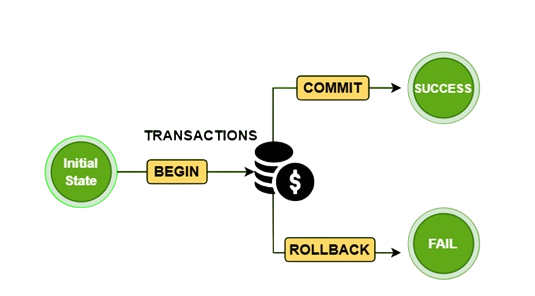
Transactions in psycopg2
psycopg2 automatically starts a new transaction upon connection and commits it only when conn.commit() is explicitly called. If an error occurs, conn.rollback() is used to undo the transaction. C Programming Examples This allows for precise control over database consistency.
- try:
- cur.execute(“INSERT INTO orders VALUES (%s, %s)”, (order_id, amount))
- conn.commit()
- except Exception as e:
- conn.rollback()
- print(“Transaction failed:”, e)
This transaction control mechanism is critical in banking, inventory, and multi-step update scenarios.
Error Handling
psycopg2 provides robust error handling by throwing exceptions from the psycopg2 namespace. These include:
- psycopg2.Error – base class for all exceptions
- psycopg2.OperationalError
- psycopg2.ProgrammingError
- psycopg2.IntegrityError
- try:
- cur.execute(“SELECT * FROM non_existing_table”)
- except psycopg2.Error as e:
- print(“Database error:”, e)
You can catch specific exceptions or Height of a Tree use the generic Exception to handle all errors:
Using specific exceptions provides better insight and debugging.
Preparing for a Python Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Python Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Setting up PostgreSQL with psycopg2 is a straightforward process that forms the foundation for integrating Python applications with powerful relational databases. By installing PostgreSQL, creating a database, and configuring psycopg2 in your Python environment, you’re ready to perform robust data operations Python Training directly from your code. This setup enables seamless interaction with your database, allowing you to write, read, and manage data efficiently. Once connected, you can begin building data-driven applications with the full power of Python and PostgreSQL combined.


