
- What is PostgreSQL?
- Why PostgreSQL?
- Advantages of PostgreSQL
- Disadvantages of PostgreSQL
- Setting up PostgreSQL Environment
- How to create a database in PostgreSQL?
- Designing Database Tables and Schemas
- Adding Data to the Database
- Conclusion
What is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is a complicated open-supply object-relational database control machine for its robustness, extensibility, and compliance with enterprise requirements. Developed over numerous decades, PostgreSQL gives a wealthy set of functions, inclusive of guides for complicated facts kinds, superior indexing strategies, transactional integrity, and concurrent entry to control. It excels at coping with massive volumes of facts and gives an effective SQL question language and several extensions and plug-ins. Whether for small-scale tasks or enterprise-stage programs, Database Training PostgreSQL empowers builders with a bendy and dependable database answer.PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) known for its reliability, advanced features, queries and standards compliance. Often referred to as “Postgres,” it supports both SQL (relational) and JSON (non-relational) querying, making it a flexible choice for modern applications. Originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley, PostgreSQL has grown into one of the most popular databases in the world, trusted by developers, enterprises, and governments alike. What sets PostgreSQL apart is its strong emphasis on extensibility and robustness. It supports advanced data types, full-text search, custom functions, and indexing techniques that allow users to tailor the database to their needs. PostgreSQL is ACID-compliant, ensuring data integrity through features like transactional support, concurrency control, and point-in-time recovery. In addition to traditional database features, PostgreSQL is also capable of handling complex analytical queries, geospatial data (via PostGIS), and high-performance workloads. It runs on all major operating systems and is backed by a vibrant open-source community that actively contributes to its development and support.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Why PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an effective, open-supply relational database control machine (RDBMS) that is extensively praised for its robustness, characteristic richness, and requirements compliance. It helps with superior facts kinds and overall performance optimization functions, making it appropriate for each easy program and complicated enterprise-stage systems. One of the important motivations builders and businesses pick out PostgreSQL is its guide for extensibility: customers can outline their very own facts, kinds, functions, or even write code in specific programming languages like PL/pgSQL, Python, or Perl. This makes it particularly adaptable to a lot of use cases. Another robust motive to choose PostgreSQL is its ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance, which guarantees facts reliability and integrity, even withinside the occasion of a crash or machine failure. It gives superior indexing strategies inclusive of B-tree, GiST, and GIN, and helps full-textual content search, JSON/JSONB for file storage, and geospatial facts thru PostGIS. These functions make PostgreSQL now no longer only a conventional SQL relational database, however a hybrid machine able to cope with structured, semi-structured, and unstructured facts. Additionally, PostgreSQL boasts a robust network and common updates, because of this that it’s far constantly evolving with new functions, safety patches, Graph databases and overall performance improvements. Its open-supply nature additionally guarantees there aren’t any any licensing fees, making it a cost-powerful answer for startups, instructional tasks, and massive firms alike. Whether you`re constructing a small-scale net app or a facts-extensive analytics platform, PostgreSQL gives the flexibility, scalability, and reliability had to guide your improvement goals.
Advantages of PostgreSQL
- Open-source and free to use
- ACID-compliant for reliable transactions
- Highly extensible with custom functions and data types
- Supports both SQL ETL Process and JSON querying
- Strong security features and user access control
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Handles complex queries and large datasets efficiently
- MVCC for high concurrency without locking
- Supports full-text search and geospatial data (via PostGIS)
- Backed by an active, supportive open-source community

Disadvantages of PostgreSQL
- Steeper learning curve for beginners compared to simpler databases
- Slower performance for very simple read-heavy operations versus some NoSQL solutions
- Smaller developer and hosting ecosystem compared to MySQL
- Limited built-in tools for high availability Database Training and clustering (requires external setup)
- Can require more tuning and configuration for optimal performance in large-scale systems
- Less commercial support compared to proprietary databases like Oracle or SQL Server
- Backup and replication setup can be complex for new users
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Setting up PostgreSQL Environment
Setting up the PostgreSQL environment is a crucial first step before you can begin working with databases. PostgreSQL is available on all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. To get started, you need to download the latest stable version of PostgreSQL from the official PostgreSQL website . The installer typically includes key components such as the PostgreSQL server, command-line tools (psql), and a graphical interface like pgAdmin for easier management. After installation, you will be prompted to set a password for the default PostgreSQL user (postgres) and define the port for the server (default is 5432). Once installed, you can access PostgreSQL using pgAdmin for a GUI-based approach or use the psql terminal for command-line operations. On Linux, Object-Oriented Databases you may need to use package managers like apt or yum to install PostgreSQL and enable the service manually.
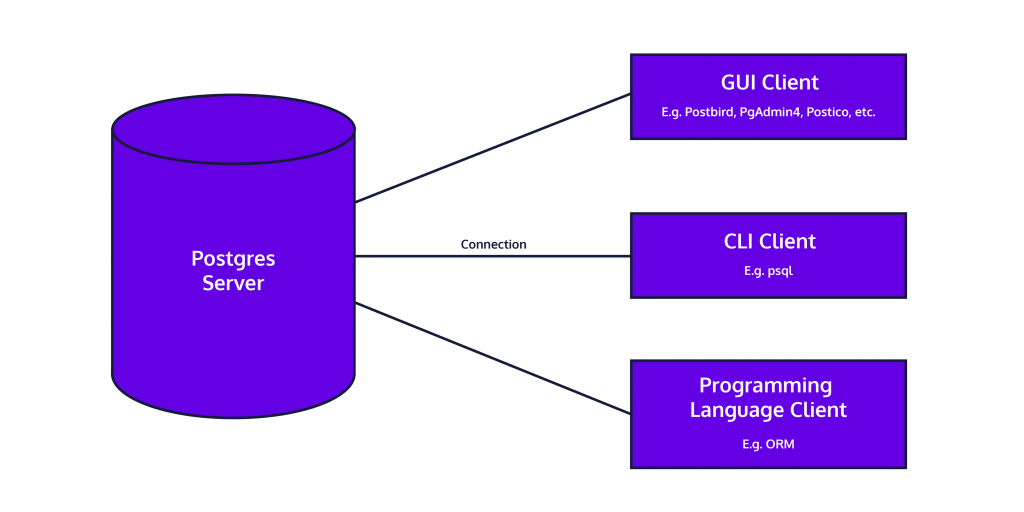
It’s also recommended to configure environment variables and ensure the PostgreSQL binary path is added to your system’s PATH. Once everything is set up, you can create users, assign roles, create databases, and start building your database structure. A properly set up PostgreSQL environment ensures smooth development, testing, and production workflows.
How to Create Database in PostgreSQL?
Creating a database in PostgreSQL is a straightforward process that can be done using SQL commands or command-line tools. The most common way is to use the CREATE DATABASE SQL statement, which allows you to define a new database with a specific name. Before creating a database, you need to connect to the PostgreSQL server using a client like psql, the interactive terminal. Once connected, you simply execute the command CREATE DATABASE database_name; replacing database_name with your desired name. PostgreSQL also allows you to specify additional options, such as the owner of the database, the encoding type, and the template database to use as a base. Alternatively, you can create a database from the command line using the createdb utility, Nosql Databases Explained which is a wrapper around the SQL command and offers a quick way to create a database without logging into the psql shell. After creation, you can connect to the new database to start creating tables, inserting data, and running queries. This process gives developers and administrators full control over organizing and managing data efficiently within PostgreSQL.
Designing Database Tables and Schemas
In Designing Database Tables, tables and schemas offer an established manner to prepare and shop information. Follow those steps to layout tables and schemas:
- Plan: Identify the entities and relationships on your information model. Find the attributes of every entity and outline relationships among them.
- Create Schemas: Schemas offer a logical grouping for tables and assist prepare your database. Use the CREATE SCHEMA announcement to create schemas.
- Define Tables: Create tables inside your schemas the use of the CREATE TABLE announcement. Specify the desk call and outline columns at the side of their information kinds and constraints.
- Establish Relationships: Use overseas keys to set up relationships among tables. Ensure referential integrity with the aid of using implementing constraints.
- Fine-song the Design: Consider overall performance optimizations together with indexing, partitioning, NoSQL vs SQL and denormalization primarily based totally for your utility`s requirements.
- Refine and Iterate: Database layout is an iterative process. Continuously examine and refine your schema and desk layout as you benefit insights into your information and alertness usage.
Adding Data to the Database
To upload information to a database in PostgreSQL, you could use the INSERT announcement. Here`s an PostgreSQL instance of a way to do it:
- Step 1: Connect to the PostgreSQL server the use of a purchaser utility or the command-line interface.
- Step 2: Select a database in which you need to feature information the use of subsequent command.
- Step 3: Execute the INSERT announcement to feature information to a desk withinside the database.Replace “table_name” with the call of the desk you need to insert information into. Specify the column names in parentheses after the desk call and offer the corresponding values withinside the VALUES clause.For instance, let`s say you’ve got got a desk named “employees” with columns “id,” “call,” and “salary.”
- Step 4: Execute the INSERT announcement, Top SQL Optimization and PostgreSQL will upload the information to the desired desk withinside the database.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Well, you’ve got got journeyed via the necessities of making and coping with Databases in PostgreSQL. From putting in place the surroundings to designing tables and schemas and populating the database, you currently own a strong basis in PostgreSQL Database Management. Remember to devise your database layout carefully, thinking about relationships, overall performance optimizations, and statistics integrity. With PostgreSQL`s reliability and versatility, you may construct robust, Database Training scalable, and green databases that empower your applications. At last, you need to welcome the energy of PostgreSQL and release infinite opportunities for statistics-pushed success!


