
As we see, numerous frameworks are emerging day by day in the Web Development field. Most of these get updated on a regular basis. In the case of Angular, various updates have already come within a few years. The first version of AngularJS was developed by Google, which was released in 2009. Angular is leading the world of JavaScript frameworks, supported and adopted by both individuals and enterprises alike. Hence, Angular has enhanced its versions, such as AngularJS 1.0, Angular 2.0, Angular 4, etc., to cater to the widening user base.
Angular is considered one of the best open-source JavaScript frameworks. Google’s Angular team released Angular 2 as a complete makeover of its original Angular 1 framework. For those of you who are still learning Angular frameworks, this blog will offer a comparison of Angular 1 (AngularJS), Angular 2, and Angular 4
Architecture
The architecture of Angular 1 is based on the Model View Controller.
Angular 2 comprises a significant change in structure as compared to Angular 1. Angular 2 is based on a Components structure, like what we see in React.js.
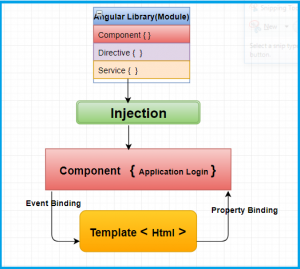
Angular 2 was focused on mobile apps development. Angular 4 is much faster and reduces the file generated code of components; it also allows the developer to generate code you can use in debug mode and production mode.
Angular JS
AngularJS was created by Misko Heavery. He had built a framework to handle the downfalls of HTML and also taking ideas and best practices of the libraries which were never done earlier.
This first version of the framework known as AngularJS was launched in the year 2009. It laid the foundation of the present-day front-end application development. Angular JS was one of the best single-page application development solution. Gradually, it wide adoption and become very popular.
Features of Angular JS
- A JavaScript MVW Framework
- Extends HTML support by adding tags, attributes, and expressions
- Allows easy event Handling
- Supports for Data Binding
- Built-In Template Engine and Routing
- Form Validations and Animations
- Dependencies Injection
Following are some of the pros and cons of AngularJS.
Pros:
- AngularJS supports both unit testing and integration testing.
- It provides a routing facility, which is making a move from one view to another.
- It provides two-way binding, which keeps the presentation layer and data in sync.
- It provides directives that help the functionality of HTML elements, which provide more power to a web application.
Cons:
- AngularJS is less secure because it doesn’t provide server authentication and authorization.
- It might lead to a memory leak, which causes various issues such as high latency, crashing, and slowing down of the process.
- It has various ways to perform the same task, so it is hard to predict which is the best way to perform the task.
- It is not supported everywhere, and it is totally based on JavaScript.
Angular 2
After, releasing Angular JS, Angular team released Angular 2 which is complete rewrite of its original Angular 1 or AngularJS. Angular 2 version is built around the concept of the component. It was rewritten from scratch by the Angular team using Typescript. It offers better performance to web developers. There are many new features along with other improvements and tweaks.
Features of Angular 2 are:
- Modern, faster, and highly scalable framework
- Equally useful framework for web, mobile, and desktop apps
- Web components based architecture
- Supports Hierarchical Dependency Injection
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of Angular 2.
Advantages:
- Angular 2 provides simpler routing, and it is mobile-oriented.
- It provides various languages to choose from, such as TypeScript, Dart, ES6, and ES5.
- It has enhanced modularity and dependency injection.
Disadvantages:
- Angular 2 is tough to set up when compared to AngularJS.
- It is not effective in building small and simple web applications.
Angular 4
Angular 4 is unlike Angular 2 (which is completed rewritten version of Angular 1). There are in fact only few minor changes and new features added in it. Angular 4 supports TypeScript, which compiles to JavaScript and displays the same in the browser.
Some other features of Angular 4 are:
- Reduce the size of the generated bundled code up to 60%
- Animation moved out to a separated package @angular/animations
- Supports for if/else statement
- Supports for email validator
Following are some of the pros and cons of Angular 4.
Pros:
- It allows faster application development processes and also easy-to-write tests.
- It provides a modular animation package.
- It is used for single-page web applications with an improved view engine.
- It supports TypeScript and also helps in developing large applications.
Cons:
- The processing is slow when displaying a huge amount of data.
- Testing is challenging in Angular 4.
- It doesn’t support the older versions of browsers.
- It is difficult to maintain server templating
Differences between Angular JS and Angular 2
When the first version of AngularJS was released in 2010 than it was referred as Angular 1, while Angular 2 was released in 2016 that was not an update but a completely transformed version of Angular which was written from the scratch only. This is why when someone writes a code in Angular and Angular 2, it looks completely different. Here, in this section, we are going to highlight the major differences between both of these versions that make them unique from each other.
Angular JS vs. Angular 2 – Components
Here, Angular JS wins the race among too.
- When AngularJS and Angular 2 are compared on the basis of communication between components then Angular JS will be found smooth and fast in message processing between various components. Therefore, it is considered as highly supportive and convenient interface for the developers.
- AngularJS is controller based in which $scope is used to set up communication among Views, while a component-based approach is followed in Angular 2 and there is no existence of controllers in Angular2. In Angular 2 the controllers are only used assorted building blocks that makes the code reusability easier.
- Unit testing is done in quite less time in Angular 2 and it is usually done by using components that promotes smoothness and consistency. Due to this feature, they can be tested for the use of resources, event execution, and the component flow.
| Angular 2 | Angular JS |
|---|---|
| Released in 2016 | Released in 2010 |
| Follows a component-service architecture Service/Control architecture | Follows Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture |
| Was created to build mobile-based applications | Was created to build web-based applications |
| Runs on both server-side and client-side | Runs only on client-side |
| To initialize bootstrap, the module() function is used | To initialize AngularJS bootstrap, ng-app functions are used |
Differences Between Angular 2 And Angular 4
Angular 2 was released in 2016 and Angular 4 in 2017, but both are different in terms of the performance values. Angular 4 can be said and treated as an enhanced version of Angular 2 because it comes with better performance values, better resources, better user-interaction features, smoother results, least commotions, and the faster reflexes etc. Both of these versions have below-listed differences:
- Angular 2 is not an extended version of Angular JS instead it is written from scratch. A little bit changes are made in core libraries rest of the services are completely re-written. Still, if you have earlier worked on Angular 2, then you will find Angular 4 quite easy to use.
- Approaches and concepts of both Angular 2 and Angular 4 are the little bit same, so the developers can easily work on the Angular 4 and find it easy.
- Angular 2 and Angular 4 both are the enhanced size of AoT or ahead-of-time and have compiler generated code. Due to compiler generated code, Angular 4 has become smoother and swift than the Angular JS 2.
- Angular 2 supports TypeScript 1.8 version, whereas Angular 4 supports typescript 2.1 and 2.2 versions.
- In Angular 4, user can use “else” block along with “*ngif” block, example is given below how it works actually:
| Angular 2 | Angular 4 |
| The size of a file generated by Angular 2 is large, hence the performance is slow | The size of a file generated by Angular 4 is reduced by 60% so that the performance is fast |
| The animation package is not present | The animation package is present |
| Angular 2 is compatible with TypeScript and Dart | Angular 4 is compatible with the enhanced versions of TypeScript 2.1 and TypeScript 2.2 |
| It doesn’t have a specific phase to adjust code | It has a proper phase to adjust code for developers |
| Instance scope controller is present | Instance scope controller is not present |
AngularJS vs Angular 2 vs Angular 4: A Complete Comparison
| Parameters | AngularJS | Angular 2 | Angular 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | It is an open-source front-end framework used for developing dynamic web apps | Angular 2 is an open-source front-end web application framework | Angular 4, an enhanced version of AngularJS, is an open-source web application platform |
| Architecture | AngularJS follows the Model-View-Controller architecture | Angular 2 is based-on the component-service architecture | Angular 4 is based on structural-directives |
| Language used | AngularJS uses JavaScript | Angular 2 uses Microsoft’s TypeScript | Angular 4 uses the latest versions of TypeScript |
| Expression syntax | In AngularJS, we need to remember the accurate ng directive to add images, property, and events | Angular 2 follows parentheses () for event binding and square brackets [] for property binding | Angular 4 follows advanced syntax, i.e., ngIf and ngFor directives |
| Performance | Slow performance | Faster performance | Improved performance by dependency injection |
| Routing | The $routeProvider.when() method is used for routing configuration | @RouterConfig{(….)} is used by Angular 2 for routing configuration | It uses two routing methods: RouterModuleforRoot () and RouterModuleforChild () |





