
- Node.js
- Node.js Architecture
- Event-Driven Model
- Node.js vs Traditional Servers
- Setting Up Environment
- NPM and Packages
- Core Modules
- File System and Streams
- Asynchronous Programming
- Use Cases of Node.js
- Popular Frameworks
- Node.js in Modern Development
Node.js
Node.js is a cross-platform, open-source runtime environment that enables the execution of JavaScript code outside a web browser. Developed by Ryan Dahl in 2009, Node.js revolutionized web development by enabling JavaScript previously confined to the browser to run on the server side. It uses the V8 JavaScript engine built by Google, which compiles JavaScript into native machine code for high performance. A skilled node.js developer leverages this power to build efficient, scalable server-side applications that respond quickly to user demands. Node.js is renowned for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, which allows it to handle multiple requests simultaneously. This makes it an ideal choice for building fast, scalable network applications like APIs, real-time chat servers, data streaming services, and single-page applications (SPAs). The ability to write both front-end and back-end code in JavaScript makes the node.js developer’s workflow more streamlined and productive, contributing to the platform’s widespread adoption.
Key reasons for What is Node.js adoption include:
- High performance due to V8 engine
- Unified development language (JavaScript)
- Active community and rich ecosystem (npm)
- Support for modern web standards
- Scalable architecture for real-time applications
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Node.js Architecture
Node.js operates on a single-threaded, non-blocking architecture based on the event loop. Unlike traditional multi-threaded models, Node.js does not create a new thread for each request. Instead, it uses an event loop to manage concurrent operations efficiently. To learn Node.js from scratch, it’s essential to understand how this event-driven model works and why it enables high-performance, scalable applications.
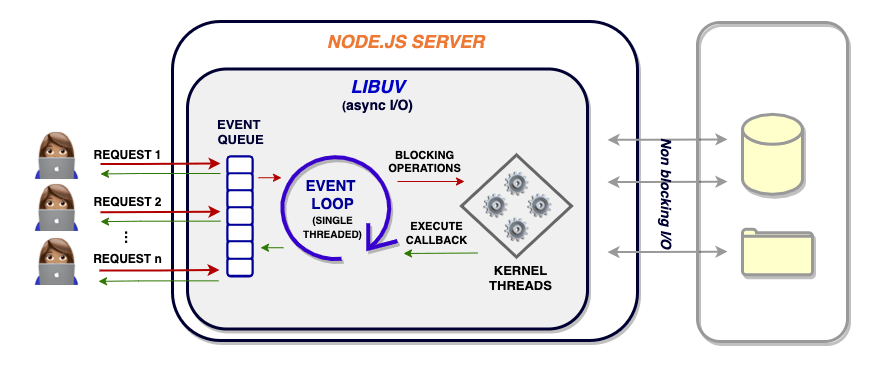
Main architectural components:
- Event Loop: The core component that continuously checks the event queue and executes callback functions when events are ready.
- Callbacks and Promises: Used for asynchronous task handling.
- Libuv Library: Handles thread pooling and low-level OS operations.
- Worker Pool: Background threads for executing expensive or blocking operations.
- V8 Engine: Executes JavaScript code with high efficiency.
Node.js is particularly efficient at I/O-bound tasks such as reading/writing files, database operations, and API calls.
Event-Driven Model
Node.js follows an event-driven, asynchronous model of programming. This allows it to perform non-blocking operations and continue executing other code while waiting for operations like file reads or API calls to complete. EventEmitter is a built-in module in Node.js that facilitates this pattern. Node.js developer can create custom events and listeners using it:
- const EventEmitter = require(‘events’);
- const emitter = new EventEmitter();
- emitter.on(‘data’, (data) => {
- console.log(‘Received:’, data);
- });
- emitter.emit(‘data’, ‘Hello, Node.js!’);
This event-driven nature is essential for creating highly responsive applications.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Node.js vs Traditional Servers
Traditional web servers such as Apache or IIS use a multi-threaded model where each incoming request spawns a new thread. While effective, this model consumes significant system resources under heavy load.
| Feature | Node.js | Traditional Servers (Apache) |
|---|---|---|
| Threading Model | Single-threaded, non-blocking | Multi-threaded, blocking |
| Resource Usage | Low | High |
| Real-Time Apps | Excellent | Limited |
| Complexity | Simpler for small apps | More complex |
| Use Case | APIs, real-time, microservices | Static sites, monolith apps |
Node.js uses a single-threaded model with a non-blocking event loop, enabling it to handle thousands of concurrent requests with minimal overhead.
Setting Up Environment
To start developing with Node.js:
- Download Node.js from https://nodejs.org
- Install Node.js and verify with: node -v
- npm -v
- Create Project Folder: mkdir my-node-app && cd my-node-app
- Initialize Project:
npm init -y
Create Entry File (index.js) and write a basic server:
- const http = require(‘http’);
- const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
- res.writeHead(200, { ‘Content-Type’: ‘text/plain’ });
- res.end(‘Hello World from Node.js!’);
- });
- server.listen(3000); Run it with node index.js and navigate to http://localhost:3000.
Do You Want to Learn More About Web Developer? Get Info From Our Web Developer Courses Today!
NPM and Packages
Node.js comes bundled with npm (Node Package Manager), which is used to manage dependencies and install packages.
Useful npm commands:
- npm install package-name – Install locally
- npm install -g package-name – Install globally
- npm uninstall package-name – Remove package
- npm update – Update all dependencies
Popular packages:
- Express – Web framework
- Mongoose – MongoDB ORM
- Dotenv – Environment variables
- Cors – Cross-origin resource sharing.
Core Modules
Node.js includes several core modules that offer out-of-the-box functionality:
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
| fs | File system operations |
| http | HTTP server/client |
| path | File and directory path tools |
| os | System-level information |
| events | Event-driven programming |
| util | Utility functions |
File System and Streams
Streams are abstract interfaces for working with streaming data in Node.js.
Types of streams:
- Readable: For reading data
- Writable: For writing data
- Duplex: Both read and write
- Transform: Modify data during read/write
- fs.readFile(‘file.txt’, (err, data) => {
- if (err) throw err;
- console.log(data.toString());
- });
- const { readFile } = require(‘fs’).promises;
- readFile(‘file.txt’, ‘utf8’)
- .then(data => console.log(data))
- .catch(err => console.error(err));
- async function readMyFile() {
- try {
- const data = await readFile(‘file.txt’, ‘utf8’);
- console.log(data);
- } catch (err) {
- console.error(err);
- }
- }
- Real-time applications (chat, gaming)
- REST APIs and microservices
- Data streaming apps (audio/video)
- IoT and sensor-based systems
- Single Page Applications (SPAs)
- Serverless functions
- Faster time to market
- Cost efficiency
- Unified language across stack
- High skill for node.js developer productivity
- Rich community support
Asynchronous Programming
Asynchronous code prevents blocking and improves performance.
1. Callbacks:
2. Promises:
3. Async/Await:
Use Cases of Node.js
Node.js is versatile and can be used for:
Popular Frameworks
Frameworks help simplify development with Node.js:
| Framework | Description |
|---|---|
| Express.js | Fast, minimal web framework |
| NestJS | Scalable and modular TypeScript-based |
| Koa | Lightweight and expressive |
| Fastify | Low overhead, high performance |
Each provides routing, middleware support, and enhanced security features.
Node.js in Modern Development
What is Node.js and answer is central in modern full-stack development. With support for microservices, real-time applications, and cloud-native architectures, it empowers scalable and efficient web systems. For those looking to learn Node.js from scratch, understanding its event-driven, non-blocking architecture is key to building responsive applications. Its ability to unify front-end and back-end development using JavaScript makes it especially appealing to developers. Many beginners who learn Node.js from scratch find that mastering its core modules and asynchronous patterns opens the door to building powerful APIs and real-time services.
Key benefits:
Node.js is also widely adopted in DevOps pipelines and containerized environments using Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD tools. To learn Node.js from scratch, it’s helpful to explore how it integrates with these modern development workflows, especially in automation and deployment scenarios.





