
- Introduction to Sorting
- Manual Sorting Logic
- Using Loops for Sorting
- Bubble Sort Algorithm
- Selection and Insertion Sort
- Using sorted() Function
- Writing Custom Sort Functions
- Sorting Lists of Tuples or Objects
- Sorting by Specific Conditions
- Time Complexity Analysis
- Code Examples
- Summary
Introduction to Sorting
Sorting is one of the most common operations in programming. It allows you to arrange data in a specific order, such as ascending or descending. In Python, the built-in sort() and sorted() functions make this task straightforward. However, understanding how sorting works under the hood is essential for learning algorithm design, improving problem-solving skills, and preparing for coding interviews. To apply these insights in real-world development, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how mastering Python’s core logic alongside React’s dynamic frontend empowers developers to build efficient, scalable applications where algorithmic thinking drives both performance and maintainability. That’s why exploring Python list sorting without sort function can be highly valuable for students and developers alike. By practicing Python list sorting without sort function, you strengthen your knowledge of algorithms such as bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, and quicksort, all of which form the backbone of computer science problem-solving.
To Earn Your Full Stack With Python Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Full Stack With Python Course Today!
Manual Sorting Logic
Manual sorting involves implementing an algorithm that can compare and arrange the elements in a list. To sort manually, one must understand the logic behind rearranging numbers or strings based on comparisons. To preserve and iterate on such logic efficiently across development cycles, exploring Git and Version Control reveals how developers can track changes, branch experiments, and collaborate seamlessly ensuring that sorting algorithms and other core logic evolve with clarity, accountability, and rollback safety throughout the software lifecycle. It includes checking elements pair by pair and swapping them if needed until the entire list is sorted.
Using Loops for Sorting
You can use loops like for or while to create a custom sorting routine. For example, by iterating through a list and comparing each element with the others, you can manually swap them to achieve a sorted order. This is a good way to simulate sorting for small datasets. To scale such logic across distributed systems, exploring What are Microservices reveals how modular services can independently handle tasks like sorting, filtering, and data transformation enabling flexible, maintainable architectures where each function operates as a standalone unit within a larger ecosystem.
- numbers = [5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6]
- for i in range(len(numbers)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(numbers)):
- if numbers[i] > numbers[j]:
- numbers[i], numbers[j] = numbers[j], numbers[i]
- print(numbers)
This basic form of nested loops can produce a sorted list in ascending order.
Would You Like to Know More About Full Stack With Python Course? Sign Up For Our Full Stack With Python Course Now!
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Bubble Sort Algorithm is one of the simplest sorting algorithms. It repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order.

To understand how such foundational logic fits into broader development workflows, exploring What is Python Programming reveals how Python’s simplicity and readability make it ideal for learning core algorithms empowering developers to build efficient solutions while mastering the principles of structured programming.
- def bubble_sort(arr):
- n = len(arr)
- for i in range(n):
- for j in range(0, n – i – 1):
- if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]:
- arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j]
- return arr
- print(bubble_sort([64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]))
Bubble Sort Algorithm is easy to understand but inefficient for large datasets (O(n^2) time complexity).
Selection and Insertion Sort
Selection Sort works by selecting the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion and moving it to its correct position. To understand how this algorithm interacts with data structures, exploring Need To Know About Python List reveals how Python lists support dynamic indexing, in-place modifications, and efficient iteration making them ideal for implementing sorting routines and mastering core algorithmic patterns.
- def selection_sort(arr):
- for i in range(len(arr)):
- min_index = i
- for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
- if arr[j] < arr[min_index]:
- min_index = j
- arr[i], arr[min_index] = arr[min_index], arr[i]
- return arr
Insertion Sort builds the sorted list one element at a time by inserting each new element into its correct position:
- def insertion_sort(arr):
- for i in range(1, len(arr)):
- key = arr[i]
- j = i – 1
- while j >= 0 and key < arr[j]:
- arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
- j -= 1
- arr[j + 1] = key
- return arr
Both algorithms are more efficient than bubble sort in some scenarios but still have a time complexity of O(n^2).
Using sorted() Function
Selection Sort works by selecting the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion and moving it to its correct position. To understand how this algorithm interacts with data structures, exploring Need To Know About Python List reveals how Python lists support dynamic indexing, in-place modifications, and efficient iteration making them ideal for implementing sorting routines and mastering core algorithmic patterns.
- original = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9]
- sorted_list = sorted(original)
- print(sorted_list)
However, since this is also a built-in Python method, it bypasses the goal of learning to sort manually. Use it only if required for comparison.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Full Stack With Python Course? Sign Up For Our Full Stack With Python Course Today!
Writing Custom Sort Functions
Python allows you to write custom functions that define how sorting should occur. For example, you can sort numbers by their absolute value. To apply such flexible logic in full-stack development, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how Python’s customizable sorting techniques integrate with React’s dynamic frontend enabling developers to build responsive applications that handle complex data operations with precision and control across both layers.
- def custom_sort(lst):
- for i in range(len(lst)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(lst)):
- if abs(lst[i]) > abs(lst[j]):
- lst[i], lst[j] = lst[j], lst[i]
- return lst
- print(custom_sort([3, -1, -7, 4]))
This demonstrates how to embed specific logic into the sorting process.
Preparing for Full Stack With Python Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Full Stack With Python Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Sorting Lists of Tuples or Objects
Sorting more complex data like tuples or custom objects requires accessing internal elements or attributes. To understand how this skill translates into professional development workflows, exploring What Is a Software Developer reveals how mastering data manipulation, algorithmic logic, and object-oriented principles equips developers to build scalable solutions where sorting isn’t just a coding exercise but a core part of designing efficient, real-world applications.
- data = [(“Alice”, 25), (“Bob”, 20), (“Charlie”, 30)]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(data)):
- if data[i][1] > data[j][1]:
- data[i], data[j] = data[j], data[i]
- print(data) # Sorted by age
This method is useful when dealing with structured data where you need to sort based on one specific field.
Sorting by Specific Conditions
You can add logic to sort based on custom conditions. For example, sort even numbers first, then odd numbers. To implement such sorting strategies across different programming ecosystems, exploring Kotlin vs Java reveals how both languages handle functional constructs like lambdas and comparators enabling developers to write expressive, condition-based sorting routines while comparing syntax, performance, and interoperability in real-world applications.
- def custom_even_odd_sort(lst):
- for i in range(len(lst)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(lst)):
- if lst[i] % 2 != 0 and lst[j] % 2 == 0:
- lst[i], lst[j] = lst[j], lst[i]
- return lst
- print(custom_even_odd_sort([5, 3, 2, 8, 1, 4]))
This allows for tailored sorting based on business or application needs.
Time Complexity Analysis
Basic sorting algorithms are simple but inefficient for large datasets: they often involve repeated comparisons and swaps that don’t scale well. To understand how such logic can be encapsulated and reused effectively, exploring What is Abstraction in Java reveals how abstraction allows developers to hide implementation details while exposing essential behavior making it easier to manage sorting logic, optimize performance, and maintain clean, modular code across large-scale applications.
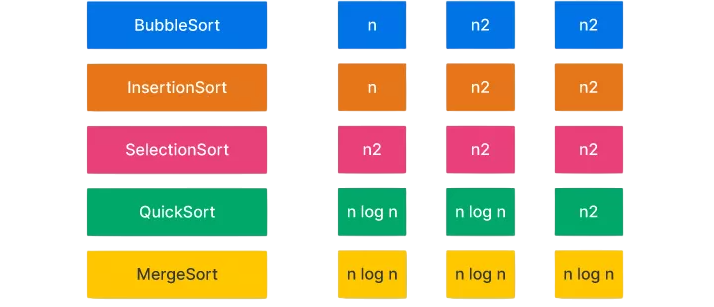
- Bubble Sort: O(n²)
- Selection Sort: O(n²)
- Insertion Sort: O(n²)
- Custom Sorts: Depends on logic, usually O(n²)
These algorithms are inefficient for large datasets. More advanced algorithms like Merge Sort (O(n log n)) and Quick Sort (O(n log n) average case) are recommended for performance-critical applications.
Code Examples
- Sorting in descending order:
- def descending_sort(lst):
- for i in range(len(lst)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(lst)):
- if lst[i] < lst[j]:
- lst[i], lst[j] = lst[j], lst[i]
- return lst
- print(descending_sort([3, 6, 1, 8]))
- Sorting strings:
- def sort_strings(lst):
- for i in range(len(lst)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(lst)):
- if lst[i].lower() > lst[j].lower():
- lst[i], lst[j] = lst[j], lst[i]
- return lst
- print(sort_strings([“banana”, “Apple”, “cherry”]))
Summary
Python list sorting without sort function provides a deeper understanding of how data can be organized and manipulated manually. By practicing different techniques and exploring algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort, developers gain insights into computational thinking and algorithm design. While learning these methods, the concept of Python list sorting without sort function helps programmers strengthen their problem-solving skills and prepare for technical interviews. To apply these algorithmic foundations in real-world development, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how Python’s sorting logic integrates with frontend workflows in React empowering developers to build efficient, interactive applications with optimized data handling across the full stack. Although manual sorting is not recommended for production use due to inefficiency, the practice of Python list sorting without sort function remains a valuable exercise for building strong programming fundamentals.





