
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Frontend Frameworks (React, Angular)
- Backend Technologies (Node.js, Django, etc.)
- API Integration
- Database Knowledge (MongoDB, SQL)
- DevOps Basics
- Version Control
- Testing and Debugging
- Cloud Services (AWS, Azure)
- Security Principles
- Agile and Scrum Practices
- Conclusion
HTML, CSS, JavaScript
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the foundational technologies of web development. HTML (HyperText Markup Language) structures the content of web pages. It uses elements such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links to define the layout of a webpage. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to style and visually enhance the HTML elements core skills taught in Web Designing Training, where learners build structured layouts using semantic HTML and apply styling through CSS properties like typography, spacing, and color schemes. Mastering these fundamentals enables developers to create visually appealing, responsive websites that adapt seamlessly across devices. It controls aspects like fonts, colors, layouts, and responsiveness. JavaScript adds interactivity and functionality to websites. It enables tasks such as form validation, dynamic content updates, and event handling. Mastery of these three core technologies is considered one of the essential Full Stack Developer Skills, as they form the backbone of frontend development. Along with backend knowledge, practicing Full Stack Developer Skills ensures that developers can handle both client-side and server-side tasks efficiently. Ultimately, building expertise in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript lays a strong foundation for advancing broader Full Stack Developer Skills needed in today’s tech industry.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Frontend Frameworks (React, Angular)
Front-end frameworks like React and Angular simplify the process of building complex user interfaces. React, developed by Facebook, is a component-based library that allows developers to build reusable UI components core tools explored in Understanding the Role of a Full Stack Developer, where learners master both client-side frameworks and server-side technologies to create seamless, scalable web applications. Full Stack Developers leverage these tools to ensure cohesive design systems, efficient state management, and responsive user experiences across platforms.
It uses a virtual DOM to enhance performance and supports unidirectional data flow, making the code easier to debug and maintain. Angular, developed by Google, is a full-fledged framework offering two-way data binding, dependency injection, and a rich set of built-in tools. Understanding the differences between React and Angular helps developers choose the right tool for the job and enables them to build scalable and maintainable web applications.
Backend Technologies (Node.js, Django, etc.)
- Backend technologies power the server-side logic of applications. Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine. It allows developers to use JavaScript on the server side and is known for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, making it ideal for scalable applications.
- Django, a Python-based framework, follows the “batteries-included” philosophy and provides an admin panel, ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), and built-in security features. Other notable backend technologies include Express.js (used with Node.js) frameworks often paired with tools from IDE for Web Development, where developers streamline coding, debugging, and deployment across full-stack environments.
- Ruby on Rails, Flask, and Laravel. Proficiency in at least one backend framework enables developers to manage data, user authentication, server configuration, and application logic effectively.
- API integration is essential for connecting the frontend and backend of web applications. RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods and status codes, making them easy to use and understand.
- GraphQL is another approach to APIs that allows clients to request only the data they need, improving efficiency. API integration involves sending and receiving data, handling errors, and ensuring security.
- Developers must also understand authentication methods such as API keys, OAuth, and JWT (JSON Web Tokens). API documentation tools like Swagger or Postman are vital for testing and collaborating with APIs. Proper integration allows seamless communication between client-side interfaces and server-side data.
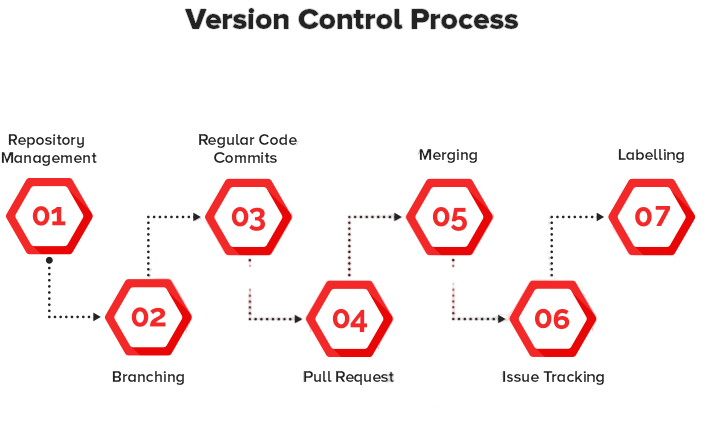
- Version control systems like Git are essential for tracking changes in code and collaborating with teams. Git allows developers to create branches, commit changes, and merge code efficiently.
- Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket provide hosting for Git repositories and offer collaboration tools such as pull requests, issue tracking, and code reviews. Understanding branching strategies (e.g., Git Flow, trunk-based development) and resolving merge conflicts are critical skills.
- Version control ensures that changes can be tracked, bugs can be fixed efficiently, and multiple developers can work on the same project without interfering with each other’s work.
- Agile is a software development methodology that focuses on iterative development, customer collaboration, and flexibility. Scrum is a popular Agile framework that organizes work into sprints, usually lasting two to four weeks.
- Key roles include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. Scrum practices include sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. Agile tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana help manage tasks and track progress collaborative workflows that rely heavily on HTTP Request Methods to enable seamless client-server communication. Methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE ensure that Agile platforms can retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently across distributed teams and iterative development cycles.
- Agile emphasizes continuous feedback and improvement, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements. Understanding Agile and Scrum principles enhances team collaboration and project management.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
API Integration
Database Knowledge (MongoDB, SQL)
Databases are used to store and retrieve data for applications. SQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite are relational and use structured schemas with predefined tables and columns. Queries are written in SQL (Structured Query Language) to manipulate and retrieve data an essential backend skill often paired with Web Designing Training, where developers learn to integrate structured layouts with dynamic data sources. By combining HTML/CSS for presentation and SQL for data operations, learners build full-stack applications that are both visually engaging and functionally robust. NoSQL databases like MongoDB use flexible, JSON-like documents and are better suited for unstructured or semi-structured data. Understanding the differences between relational and non-relational databases helps developers choose the right tool based on the application requirements. Additionally, knowledge of indexing, normalization, and data modeling is crucial for building efficient and scalable database solutions.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
DevOps Basics
DevOps is a set of practices that bridges the gap between development and operations. It emphasizes automation, continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and monitoring. Basic knowledge of DevOps tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes can greatly enhance a developer’s workflow.CI/CD pipelines automate the testing and deployment process, allowing code to be released more quickly and reliably an essential workflow highlighted in Web Development Tools, where developers explore platforms like GitHub Actions, Netlify, and Vercel to streamline continuous integration and delivery. These tools reduce manual errors, accelerate release cycles, and ensure consistent performance across environments, making them indispensable in modern web development. Containerization tools like Docker ensure consistency across development and production environments. Understanding versioning, configuration management, and cloud deployment is also part of DevOps practices. These skills help improve collaboration and streamline the software development lifecycle.
Version Control
Cloud Services (AWS, Azure)
Cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure provide infrastructure and services for hosting, deploying, and scaling applications. Developers can use services like EC2 (virtual machines), S3 (storage), Lambda (serverless computing), and RDS (databases) to build powerful applications without managing physical hardware. Azure offers similar services such as Azure Functions, Blob Storage, and Virtual Machines. Familiarity with cloud concepts like scalability, elasticity, load balancing, and security is important principles covered in What Is Web Development, where learners explore how modern web applications integrate with cloud platforms to ensure performance, reliability, and global accessibility. Understanding these foundational concepts empowers developers to architect resilient, scalable solutions across both frontend and backend layers. Knowledge of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation is also valuable. Cloud computing skills enable developers to deploy resilient and scalable applications.
Security Principles
Security is a critical aspect of software development. Developers must follow secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities like SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). Authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as OAuth2, JWT, and session management, must be properly implemented. HTTPS, data encryption, and secure storage of sensitive information are essential for protecting user data security practices emphasized in MEAN Stack vs Full Stack, where learners compare how different stacks handle user identity, access control, and data protection. Whether using Angular with MongoDB or React with PostgreSQL, secure implementation across the stack is critical for building trustworthy, scalable web applications. Security headers, input validation, and regular security audits help maintain a secure application environment. Understanding the OWASP Top Ten vulnerabilities is a good starting point for developing secure web applications.
Agile and Scrum Practices
Conclusion
A strong portfolio and an active GitHub presence are vital for showcasing Full Stack Developer Skills to potential employers. Portfolios should highlight completed projects, the technologies used, and the developer’s role, while GitHub repositories should include clear documentation, README files, and commit history to demonstrate coding practices best practices emphasized in Web Designing Training, where learners showcase responsive layouts, structured HTML/CSS, and interactive UI components. A well-crafted portfolio paired with a clean GitHub history reflects both technical proficiency and professional discipline. Projects can range from simple to complex, such as to-do lists, e-commerce websites, REST APIs, or full-stack applications. Contributing to open-source projects is another way to demonstrate collaboration and coding abilities. By consistently building and maintaining a portfolio and GitHub profile, developers can effectively exhibit their Full Stack Developer Skills, leaving a strong impression on employers and significantly enhancing their career prospects in the tech industry.





