
- Introduction to React
- Component-Based Architecture
- JSX Syntax and Structure
- Virtual DOM Concept
- Unidirectional Data Flow
- Props and State Management
- Lifecycle Methods and Hooks
- React Router Overview
- Redux and Context API
- Code Splitting and Optimization
- Integration with Backend APIs
- Project Structure and Folder Organization
- Conclusion
Introduction to React
React is a popular open-source JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building user interfaces, particularly for single-page applications (SPAs). It allows developers to build reusable UI components and manage the state of web applications efficiently. React has revolutionized frontend development with its declarative syntax and efficient rendering approach. Its core objective is to enable the creation of fast, scalable, and simple applications through a component-based design. To integrate this frontend power with robust backend capabilities, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how developers can master both client-side interactivity and server-side logic using Python frameworks like Django or Flask alongside React to build dynamic, end-to-end web applications. Understanding React JS Architecture is essential for grasping how components, props, state, and the virtual DOM work together to deliver efficient performance. By mastering React JS Architecture, developers can design applications that are both maintainable and optimized for real-world use cases.
To Earn Your Full Stack With Python Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Full Stack With Python Course Today!
Component-Based Architecture
One of the foundational concepts of React is its component-based architecture. In React, the UI is divided into independent, reusable pieces called components. These components are either class-based or function-based and can manage their own state. Components can be nested within each other, allowing for a hierarchical tree structure. To build and maintain such dynamic interfaces effectively, exploring Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers reveals how proficiency in frontend frameworks, state management, and component architecture is essential alongside backend integration, database handling, and deployment workflows that complete the full development cycle. This modular approach promotes code reusability, easier maintenance, and improved testability. A typical React component includes:
- Render logic: Describes what the UI looks like.
- State management: Handles dynamic data.
- Props handling: Accepts external inputs to customize behavior.
- function Greeting(props) {
- return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
- }
This component takes the name as a prop and returns a greeting message.
JSX Syntax and Structure
JJSX (JavaScript XML) is a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows writing HTML-like code in React components. It simplifies UI creation by letting developers use familiar HTML syntax within JavaScript. JSX is transpiled to standard JavaScript using tools like Babel. To connect these components with external data sources, exploring What is Axios in React reveals how Axios simplifies HTTP requests, enabling seamless data fetching, error handling, and integration with React’s state-driven architecture.
- const element = <h1>Welcome to React</h1>;
- // Behind the scenes, JSX is compiled into:
- const element = React.createElement(‘h1’, null, ‘Welcome to React’);
JSX enhances readability and maintains the closeness of HTML and logic, making it easier to manage components.
Would You Like to Know More About Full Stack With Python Course? Sign Up For Our Full Stack With Python Course Now!
Virtual DOM Concept
React utilizes a Virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to improve rendering efficiency. The Virtual DOM is an in-memory representation of the real DOM. Whenever a component’s state changes, React creates a new Virtual DOM and compares it with the previous one using a process called “diffing.” Only the parts of the DOM that changed are updated, reducing unnecessary re-renders and improving performance. To understand how such frontend efficiency fits into full-stack development, exploring What is MEAN Stack reveals how MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js work together to deliver dynamic, scalable web applications where optimized rendering complements robust backend logic.
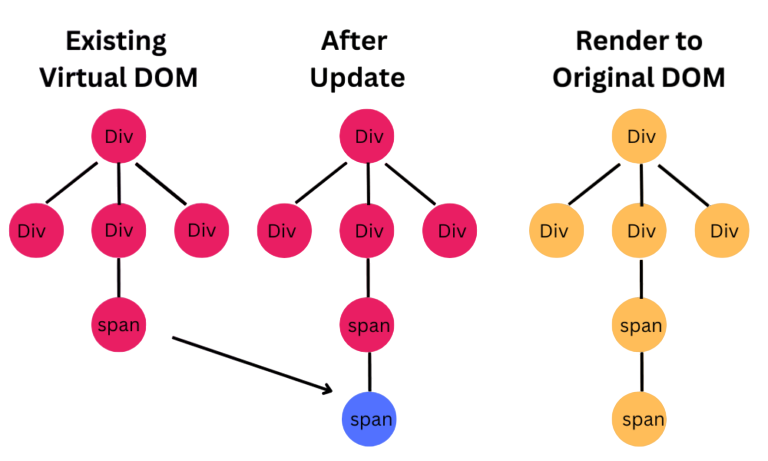
This approach provides:
- Fast UI updates
- Efficient memory usage
- Enhanced performance for complex interfaces
- class Counter extends React.Component {
- constructor(props) {
- super(props);
- this.state = { count: 0 };
- }
- increment = () => {
- this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
- };
- render() {
- return <button onClick={this.increment}>{this.state.count}</button>;
- }
- }
- Mounting: constructor, componentDidMount
- Updating: componentDidUpdate
- Unmounting: componentWillUnmount
- useState: For local state
- useEffect: For side effects (similar to componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate)
- useContext, useReducer, useMemo: For advanced needs
- <BrowserRouter>
- <Routes>
- <Route path=”/home” element={<Home />} />
- <Route path=”/about” element={<About />} />
- </Routes>
- </BrowserRouter>
- Single source of truth
- State is read-only
- Changes through pure functions (reducers)
- const ThemeContext = React.createContext(‘light’);
- function App() {
- return (
- <ThemeContext.Provider value=”dark”>
- <Toolbar />
- </ThemeContext.Provider>
- );
- }
- Memoization: React.memo, useMemo, useCallback
- Avoid unnecessary renders
- Efficient rendering keys and component reuse
- useEffect(() => {
- fetch(‘https://api.example.com/data’)
- .then(res => res.json())
- .then(data => setData(data));
- }, []);
- /src
- /components
- /pages
- /services
- /hooks
- /contexts
- /assets
- /utils
- App.js
- index.js
- components: Reusable UI components
- pages: Route-specific components
- services: API handlers
- hooks: Custom React hooks
- contexts: Context API implementations
- assets: Images, styles, etc.
- utils: Utility functions and helpers
Unidirectional Data Flow
React follows a unidirectional data flow model, meaning data flows from parent components to child components via props. This predictable flow simplifies debugging and ensures data consistency across the application. State is usually managed at higher-level components and passed down to child components. To support such structured development environments, exploring Install Node.JS on Ubuntu reveals how setting up Node.js correctly enables seamless backend integration, efficient package management, and scalable component-based architecture especially when building full-stack applications with React or similar frameworks. Any changes in data must be propagated upwards through callbacks or handled by state management tools like Redux.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Full Stack With Python Course? Sign Up For Our Full Stack With Python Course Today!
Props and State Management
Props (short for properties) are used to pass data from one component to another. They are immutable and define the static configuration of components. State, on the other hand, is mutable and local to the component. It holds dynamic data that can change over time due to user interaction or network responses. To explore how these concepts align with functional and object-oriented paradigms, exploring What is Scala Programming reveals how Scala blends immutability, state management, and reactive design making it a powerful choice for building scalable, component-driven applications.
State management becomes complex in larger applications, where external libraries like Redux or Context API are often used.
Preparing for Full Stack With Python Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Full Stack With Python Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Lifecycle Methods and Hooks
Lifecycle methods in class components allow developers to hook into different phases of a component’s life: such as mounting, updating, and unmounting. To integrate these frontend dynamics with backend proficiency, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how React’s lifecycle control pairs seamlessly with Python frameworks like Django and Flask empowering developers to build responsive, full-featured applications with synchronized client-server interactions.
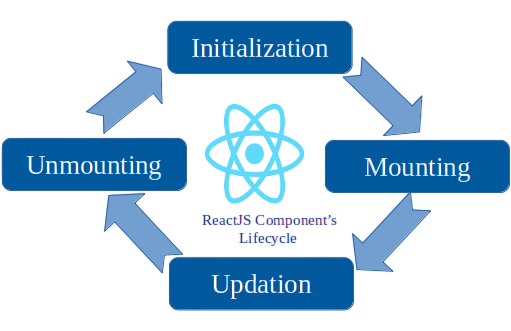
With the introduction of React Hooks in functional components, developers can now use state and lifecycle features without writing class components. Common hooks include:
Hooks promote cleaner, more functional programming patterns and have become the standard in modern React development.
React Router Overview
Python handles edge cases robustly: from type mismatches to unexpected input formats, its built-in error handling and flexible syntax make it ideal for resilient programming. To explore how developers interact with programs dynamically, exploring What Is User Input in Python reveals how the `input()` function captures runtime data, enabling personalized workflows, conditional logic, and real-time decision-making in Python applications.
React Router helps in building SPAs that feel like multi-page apps by updating the browser history and DOM without a full page reload.
Redux and Context API
Redux is a state management library that provides a single source of truth for the application’s state. It works on three principles: a single immutable state tree, actions that describe state changes, and pure functions called reducers. To understand how these principles align with object-oriented design, exploring Interface vs Abstract Class reveals how both constructs define contracts and shared behavior helping developers architect predictable, maintainable systems whether in frontend state logic or backend service layers.
Redux is useful for large-scale applications with complex state interactions. It includes middleware like redux-thunk or redux-saga for async operations. The Context API, introduced in React 16.3, allows for global state sharing without prop drilling. It’s simpler than Redux and is ideal for moderate complexity state management like themes or user authentication.
Code Splitting and Optimization
Code splitting is the practice of dividing code into smaller bundles that are loaded on demand. React supports code splitting with React.lazy() and Suspense. It improves performance by reducing initial load time. To explore how mastering such optimization techniques can shape your career path, exploring What to do after B.Tech reveals how skills in frontend performance, modular architecture, and modern frameworks can open doors to roles in full-stack development, DevOps, and scalable system design.
Performance Optimization Techniques in React:
These practices ensure scalable and performant applications.
Integration with Backend APIs
React integrates seamlessly with backend APIs using tools like fetch or libraries like axios. Data is fetched asynchronously and used to update state or props. To turn such real-time data handling into impactful academic work, exploring Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas reveals how concepts like API integration, state management, and asynchronous workflows can be transformed into innovative projects ranging from dynamic dashboards to intelligent recommendation systems.
React components can also manage form inputs, validate user data, and submit forms to APIs, making it a complete frontend solution.
Project Structure and Folder Organization
A well-organized folder structure is critical for scalability and maintainability. A common structure might include: separating components, services, assets, and utilities into clearly defined directories. To understand how such architectural discipline impacts long-term project success, exploring Technical Architect reveals how experts design scalable systems, enforce coding standards, and guide development teams ensuring that every layer of the application remains modular, efficient, and future-proof.
A modular structure simplifies onboarding, testing, and collaboration across teams.
Conclusion
React JS Architecture offers a powerful and flexible framework for building modern web applications. From its component-based structure and Virtual DOM to efficient routing, state management, and API integration, React continues to empower developers to build high-performance, scalable, and maintainable user interfaces. To extend these frontend capabilities into full-stack mastery, exploring Full Stack With Python Course reveals how combining React with Python frameworks like Django or Flask enables seamless development of dynamic web applications bridging client-side interactivity with robust backend logic. By mastering the principles of React JS Architecture, developers can ensure robust frontend solutions that meet industry standards while delivering seamless user experiences.





