
- PHP Data Objects in PHP
- Why Use PHP Data Objects Instead of MySQL?
- Connecting to a Database Using PHP Data Objects
- Executing SQL Queries with PDO
- Using Prepared Statements in PDO
- Fetching Data with PHP Data Objects
- Handling Errors in PHP Data Objects
- Security Best Practices in PHP Data Objects
- Using PDO with Multiple Databases
PHP Data Objects in PHP
The database access layer PHP Data Objects (PDO) offers a standardized and cohesive interface for communicating with different database systems in PHP applications. It provides a consistent method for connecting to and working with data in several databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and others, without necessitating major code modifications when alternating between them. To explore how intelligent frameworks and structured methodologies simplify database integration while supporting scalable web applications, explore Full Stack Developer Training a hands-on course that covers backend connectivity, frontend design, and advanced deployment strategies for career growth.
Principal attributes and benefits of PDO:
- Database Abstraction: By serving as an abstraction layer, PDO enables programmers to create code that is independent of databases. This makes maintenance and porting easier because the fundamental logic for database interactions is the same independent of the underlying database technology.
- Statements that have been prepared: Prepared statements are an essential security feature that aids in thwarting SQL injection attacks. PDO automatically cleans and escapes user input before to execution, separating the SQL query structure from the data. This lowers the possibility of malicious code injection considerably.
- Object-Oriented Interface: PDO makes use of an object-oriented methodology that offers classes and methods as a clear and organized means of interacting with databases.
- Error Handling with Exceptions: PDO provides a strong and organized method for identifying and controlling database-related issues by using exceptions for error handling. Debugging and application stability are enhanced as a result.
- Support for Several Database Systems: PDO’s particular drivers (such as PDO_MYSQL, PDO_PGSQL, and PDO_SQLITE) enable a broad range of database systems, enabling developers to take advantage of its advantages in a variety of database environments.
Basic usage example:
- <?php
- $dsn = ‘mysql:host=localhost;dbname=testdb’;
- $username = ‘root’;
- $password = ‘password’;
- try {
- $pdo = new PDO($dsn, $username, $password);
- $pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION); // Set error mode to exceptions
- // Prepare and execute a statement
- $stmt = $pdo->prepare(“SELECT name, email FROM users WHERE id = :id”);
- $stmt->bindParam(‘:id’, $userId);
- $userId = 1; // Example user ID
- $stmt->execute();
- // Fetch results
- $user = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
- if ($user) {
- echo “User Name: ” . $user[‘name’] . “, Email: ” . $user[’email’];
- } else {
- echo “User not found.”;
- }
- } catch (PDOException $e) {
- echo “Connection failed: ” . $e->getMessage();
- }
- ?>
Why Use PHP Data Objects Instead of MySQL?
For database interaction in PHP applications, PDO (PHP Data Objects) has been chosen over MySQLi for two main reasons: flexibility and security. To explore how structured paradigms like functional programming emphasize immutability and pure functions, while object-oriented programming focuses on encapsulation and reusability and how these approaches influence database handling and application design explore Functional Programming vs OOP a comprehensive comparison that covers core principles, practical use cases, and performance trade-offs for modern developers.
- Database Agnosticism: PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and various other database systems might all be handled using a single interface due to PDO. thereby requiring a full revision of the database interaction logic, this means that if a project’s database backend needs to change in the future, only the connection string along with a few database-specific queries would need to be replaced. By contrast, MySQLi is designed particularly for MySQL databases.
- Portability and Flexibility: PDO offers applications with better portability across numerous environments and database systems since it is database-agnostic. Such flexibility is an important benefit for projects that need to interact with different data sources or may change over time.
- Reduced Learning Curve and Unified API: PDO offers a standardized API for communicating with various databases. Developers may deal with numerous database systems without having to learn separate, vendor-specific libraries by mastering just one API.
- Error Handling: PDO makes it easier to identify and fix database-related problems by providing reliable and consistent error handling capabilities across various drivers.
For many PHP development scenarios, PDO is a more flexible and future-proof option due to its unified API and wider database support, even though MySQLi and PDO both include features like prepared statements to avoid SQL injection.
Interested in Obtaining Your Full Stack Developer Certificate? View The Full Stack Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Connecting to a Database Using PHP Data Objects
Creating instances of the PDO base class is how connections are made. The PDO class name is always used, regardless of the driver you choose. The constructor takes as inputs the database source (sometimes called the DSN) and optionally the password and username (if any). To explore how structured methodologies and intelligent frameworks simplify database connectivity while supporting scalable web applications, explore HTML Projects Guide a hands-on resource that covers PDO integration, backend connectivity, frontend design, and advanced deployment strategies for modern developers.
- <?php
- $dsn = ‘mysql:host=localhost;dbname=testdb’;
- $username = ‘root’;
- $password = ‘password’;
- try {
- $pdo = new PDO($dsn, $username, $password);
- $sql = “INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES (‘John Doe’, ‘john.doe@example.com’)”;
- $affectedRows = $pdo->exec($sql);
- echo “Rows affected: ” . $affectedRows;
- } catch (PDOException $e) {
- echo “Error: ” . $e->getMessage();
- }
- ?>
Connecting to a database using PHP Data Objects (PDO) is a secure and flexible way to manage database interactions. PDO supports multiple database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite using the same set of functions. It provides built-in methods for error handling and prepared statements, which help prevent SQL injection attacks. To connect, you create a new PDO object with the database credentials and connection string. Overall, PDO makes database connections in PHP more efficient, portable, and safer to use.
To Explore Full Stack Developer Course in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Full Stack Developer Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Using Prepared Statements in PDO
One essential technique for improving database interaction security and performance is to use prepared statements in PDO (PHP Data Objects). To explore how intelligent frameworks and structured methodologies strengthen backend development with secure database handling, query optimization, and scalable application design, explore Full Stack Developer Training a hands-on course that covers PHP, PDO, frontend integration, and advanced deployment strategies for career success.
- Getting the Statement Ready: To build a prepared statement object, use the PDO::prepare() function. Using placeholders rather than explicitly embedding values, this approach accepts your SQL query as an input.
- Parameters for binding bindParam() and execute(), For placeholders without names: With an array of values, use PDOStatement::bindParam() or PDOStatement::execute(). While supplying an array to execute() attaches values directly, bindParam() enables you to bind variables by reference.
- Statement Execution:PDOStatement::execute(): After binding the parameters, use PDOStatement::execute() to run the prepared statement.
- Results Fetching (for SELECT queries):PDOStatement::fetch(), fetchAll(), fetchColumn(),If your prepared statement is a SELECT query, you can use these methods to retrieve the results.
Fetching Data with PHP Data Objects
Creating a database connection, crafting a SQL query, running the query, and then receiving the results are the stages involved in fetching data with PHP’s PDO. To explore how structured styling techniques like internal CSS enhance web projects by keeping design rules within the same HTML file while supporting cleaner layouts, better readability, and faster development explore Explain Internal CSS in HTML a practical guide that covers syntax, use cases, and integration with backend workflows for modern developers.
- <?php
- $dsn = ‘mysql:host=localhost;dbname=your_database’;
- $username = ‘your_username’;
- $password = ‘your_password’;
- try {
- $pdo = new PDO($dsn, $username, $password);
- $pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION); // Set error mode
- } catch (PDOException $e) {
- die(“Database connection failed: ” . $e->getMessage());
- }
- ?>
Create and Run the Query:
Prepared statements are advised for safe and effective data retrieval, particularly when working with user input.
- <?php
- // Example: Fetching all users
- $stmt = $pdo->prepare(“SELECT id, name, email FROM users WHERE status = :status”);
- $stmt->bindParam(‘:status’, $status, PDO::PARAM_STR); // Bind parameters if needed
- $status = ‘active’; // Example value for the bound parameter
- $stmt->execute();
- ?>
Results Fetching:
PDO provides a number of ways to retrieve results from the statement that was executed, including:
- while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)) {
- echo “ID: ” . $row[‘id’] . “, Name: ” . $row[‘name’] . “, Email: ” . $row[’email’] . “<br>”;
- }
- $results = $stmt->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
- foreach ($results as $row) {
- echo “ID: ” . $row[‘id’] . “, Name: ” . $row[‘name’] . “, Email: ” . $row[’email’] . “<br>”;
- }
A common task in programming and database management involves using a FETCH command in SQL or a similar function. This command retrieves one row from a cursor or query result and stores it in variables for the application to use. This process is important for managing large result sets by processing them one row at a time.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Full Stack Developer by Enrolling in Our Full Stack Developer Training Course Now!
Handling Errors in PHP Data Objects
Set the error mode to PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION and encapsulate your database operations in try-catch blocks to capture PDOException objects in order to manage problems with PDO. To explore how structured exception handling improves application stability, error reporting, and debugging efficiency in PHP, explore Dive into What is PHP a practical guide that covers try-catch implementation, PDO error modes, and advanced exception handling strategies for modern developers. You can re-throw the exception to allow a higher-level handler to handle it, or you can use methods like getMessage() or errorInfo() to collect full error information for logging and debugging within the catch block. In production settings, refrain from showing end users comprehensive error messages.
- try {
- // Establish a new PDO connection
- $pdo = new PDO(‘mysql:host=localhost;dbname=mydatabase’, ‘user’, ‘password’);
- $pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION); // Set to exception mode
- // Execute a database operation
- $stmt = $pdo->prepare(“SELECT * FROM non_existent_table”);
- $stmt->execute();
- } catch (PDOException $e) {
- // Error handling logic here
- // For example, log the error or display a user-friendly message
- error_log(“Database error: ” . $e->getMessage());
- echo “An error occurred. Please try again later.”;
- }
Are You Preparing for Full Stack Developer Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Full Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Security Best Practices in PHP Data Objects
PDO automatically reverses any work done in a transaction if you issue SQL queries within it and the script terminates without specifically committing or rolling back the transaction. To explore how iterative risk analysis and controlled development cycles mirror this rollback-and-recovery approach in software projects, explore Spiral Lifecycle Model in Software Engineering a comprehensive guide that covers phased development, risk management, and adaptive design strategies for building resilient applications. PDO automatically switches the database connection back to autocommit mode once you commit or rollback the transaction.
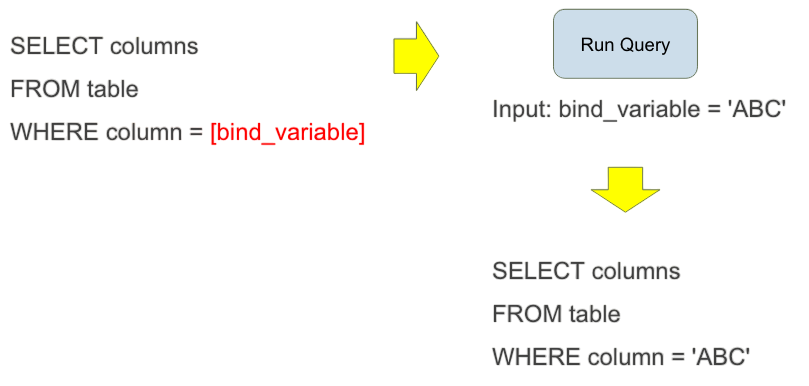
- $stmt = $pdo->prepare(“SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = :username”);
- $stmt->[bindParam](guide://action?prefill=Tell%20me%20more%20about%3A%20bindParam)(‘:username’, $username);
- $stmt->[execute](guide://action?prefill=Tell%20me%20more%20about%3A%20execute)();
Properly Bind Parameters:
Best practices for secure and efficient PDO usage include:
- Named Placeholders: For improved readability and maintainability, particularly in complex queries, utilize named placeholders (:username).
- Indicate the Data Types: When using bindParam() or bindValue() to bind parameters, always specify the right data type (e.g., PDO::PARAM_INT, PDO::PARAM_STR). This provides an additional degree of security and guarantees that the database handles the data appropriately.
- Verify and Clean User Input Before Processing: Verify and clean all user input, even when using prepared statements. By doing this, other vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) are avoided.
- Securely Address Errors: Disable display_errors in Production: To avoid giving consumers important information about your application or database structure, never show them comprehensive error messages in a production environment.
Details of a Secure Connection:
- Keep Credentials Safe: Avoid immediately hardcoding database credentials into your code. A secure configuration management system or environment variables can be used.
- Employ HTTPS: To encrypt data while it’s being transferred between your application and the database, always utilize HTTPS.
- Principle of Least Privilege: You should only provide your database user the access they need to do their assigned job. A highly empowered user should not be used for routine tasks.
- Update your software: To take advantage of security patches and bug fixes, update PHP, PDO drivers, and your database server on a regular basis.
Using PDO with Multiple Databases
There are several ways to use PHP’s PDO with multiple databases, depending on whether the databases are on the same server or separate servers, as well as if the database user has cross-database rights. To explore how intelligent frameworks and structured methodologies simplify multi-database connectivity while ensuring secure queries, optimized performance, and scalable application design, explore Full Stack Developer Training a hands-on course that covers PHP, PDO, backend integration, frontend design, and advanced deployment strategies for career success.
- <?php
- try {
- // Connection to Database 1
- $db1 = new PDO(“mysql:host=localhost;dbname=database1”, “user1”, “pass1”);
- $db1->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
- // Connection to Database 2
- $db2 = new PDO(“mysql:host=remote_host;dbname=database2”, “user2”, “pass2”);
- $db2->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
- // Perform operations on Database 1
- $stmt1 = $db1->prepare(“SELECT * FROM users”);
- $stmt1->execute();
- $users = $stmt1->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
- // Perform operations on Database 2
- $stmt2 = $db2->prepare(“INSERT INTO logs (message) VALUES (:msg)”);
- $stmt2->execute([‘:msg’ => ‘Data inserted into database2’]);
- } catch (PDOException $e) {
- echo “Connection or query failed: ” . $e->getMessage();
- }
- ?>
Things to think about:
- Security: By restricting access in the event that one connection is compromised, using distinct connections with distinct user accounts for every database improves security.
- Performance: Although establishing a single connection may appear easier, it is frequently required to open many connections for various databases on various servers, and this does not always result in noticeable performance problems.
- Portability: If you ever need to relocate databases to various servers, separate connections are more portable.
- Clarity: Code readability and maintainability can be enhanced by clearly describing connections for every database.




