
- Introduction
- History and Background
- Cost and Licensing
- User Interface
- System Architecture
- Security Features
- Command-Line Capabilities
- Software Compatibility
- Hardware Support
- Performance and Speed
- Use Cases (Enterprise, Personal, Servers)
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of operating systems, Linux and Windows are among the most commonly compared options. Each has its own philosophy, strengths, and users. Choosing between them involves more than just picking an interface it requires understanding the full development stack, user experience goals, and platform capabilities, as covered in Web Developer Training. This program equips learners with hands-on skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and responsive design, enabling them to craft intuitive, high-performance websites that adapt seamlessly across devices and user contexts. It reflects your needs, security priorities, customization preferences, and budget. This guide explores Linux and Windows in depth, helping you find the best operating system for personal, professional, or enterprise use.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
History and Background
Windows
Windows, created by Microsoft, first appeared in 1985 as a graphical shell for MS-DOS. It quickly gained popularity, especially in consumer and business markets, eventually owning over 70% of the desktop computing market. Windows has evolved over the decades with major versions like Windows 95, XP, 7, 10, and the current Windows 11, all offering user-friendly interfaces and solid software support an evolution that parallels the development of modern frameworks like What is Angular, where learners explore how Angular’s component-based architecture, CLI tooling, and SPA capabilities streamline web development across platforms. Understanding these parallels helps developers build responsive, scalable applications that align with user expectations and system capabilities.
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like open-source operating system that Linus Torvalds introduced in 1991. Rather than being a single product, Linux is a collection of distributions (distros) such as Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, and Debian. These distros are developed by communities or organizations that share the same Linux kernel at their core. Linux has become a favored choice for developers, system administrators, and businesses seeking a flexible and secure platform.
Cost and Licensing
Cost is one major difference between the two.
Windows
Windows is a proprietary operating system that requires users to buy a license. Though OEM licenses often come with new PCs, standalone licenses can be costly, especially for businesses that need volume licenses.
Linux
Linux, however, is open-source and free to use. Most distributions can be downloaded and installed without any charge. Even enterprise versions like Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) or SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) offer free versions or low-cost subscriptions for support and maintenance. For organizations looking to reduce software expenses, Linux is an appealing option.
User Interface
- Windows has long been known for its user-friendliness. Its consistent graphical user interface (GUI), familiar layout, and ease of use make it suitable for everyday consumers and office settings. Features like the Start Menu, taskbar, and straightforward settings allow even non-technical users to navigate the system with little trouble.
- Linux has made significant progress in user interfaces despite its traditional association with command-line interfaces (CLI). Desktop environments like GNOME, KDE Plasma, and Cinnamon provide polished experiences that can compete with Windows or macOS an example of user-centric design principles echoed in Basics of Service Design, where learners explore how IT services are architected to meet business objectives, user expectations, and operational standards.
- By aligning functionality, usability, and continuity, service designers can deliver consistent value across platforms and environments. However, the GUI differs among distributions, and setting up or customizing it may require more technical know-how.
- Windows has a monolithic but closed-source architecture. This means the core system is tightly integrated and not open to public modification. This setup supports compatibility with a broad range of hardware and software but limits customization and transparency.
- In comparison, Linux has a modular and open-source architecture that offers great flexibility. Users can modify nearly every aspect of the operating system, from the kernel to system services. This flexibility is particularly valuable in enterprise and development settings where tailored performance or security features are essential.
- When it comes to software availability, Windows is clearly the leader for desktop applications. It supports a vast array of software, including Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Suite, gaming platforms like Steam, and many business-specific applications yet even robust platforms can encounter runtime issues like Python KeyError Exceptions, which occur when a dictionary key is accessed but not found.
- Understanding how to handle these exceptions using `.get()` methods or `try-except` blocks helps developers build resilient applications that gracefully manage missing data and prevent crashes. Developers often prioritize Windows compatibility because of its large user base.
- Linux has solid alternatives like LibreOffice, GIMP, and VLC, but compatibility with proprietary software can be limited. Tools such as Wine or virtual machines can run Windows applications on Linux, but the experience may not always be smooth. However, for programming, web development, and server-based applications, Linux is often the preferred choice.
- Windows usually has broader hardware support right out of the box, particularly for consumer-grade peripherals like printers, scanners, webcams, and gaming accessories. Hardware manufacturers typically focus on creating drivers for Windows due to its large user base.
- Linux has made significant strides in hardware compatibility, especially with popular distributions like Ubuntu and Fedora. However, some specialized or newer hardware may still experience delays in support, requiring manual driver installation or kernel updates. Many server-grade components are designed with Linux in mind.
- Windows is commonly used for personal computing, business desktops, and enterprise environments that rely on Microsoft products like Office, SharePoint, and Active Directory.
- Its compatibility with enterprise software, ease of use, and vendor support make it a natural choice for corporate IT qualities that align with the structured logic taught in Control Statements in Java, where learners explore how decision-making, looping, and branching statements shape program flow. Mastering these constructs enables developers to build reliable, scalable applications that meet enterprise-grade performance and maintainability standards.
- Linux dominates the server market, running a majority of web servers, cloud infrastructure, and supercomputers. Its stability, security, and scalability are ideal for hosting services, databases, and large-scale applications. On the personal side, Linux is popular among developers, cybersecurity experts, and users who value privacy and customization.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
System Architecture
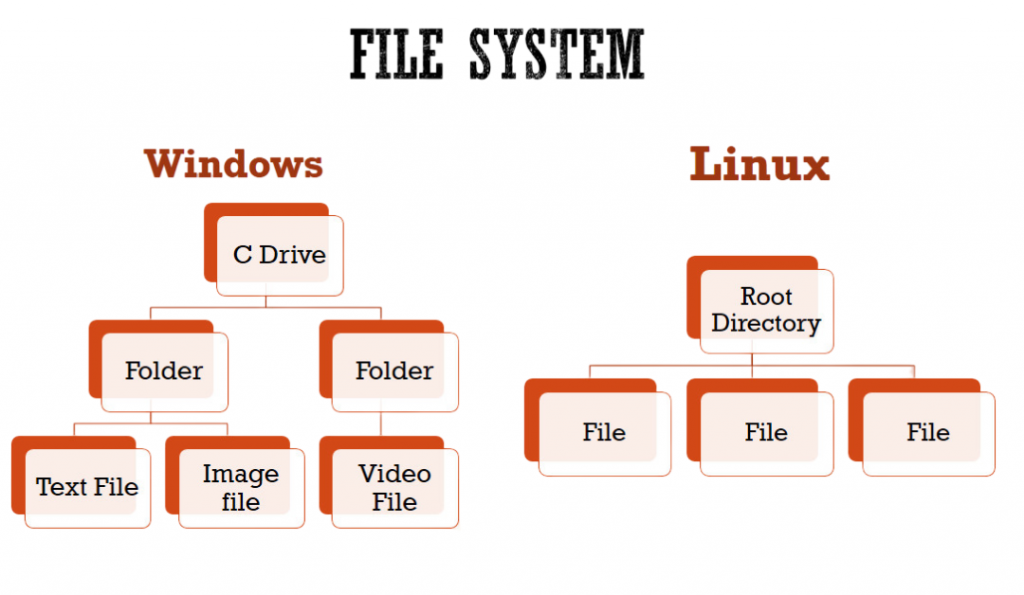
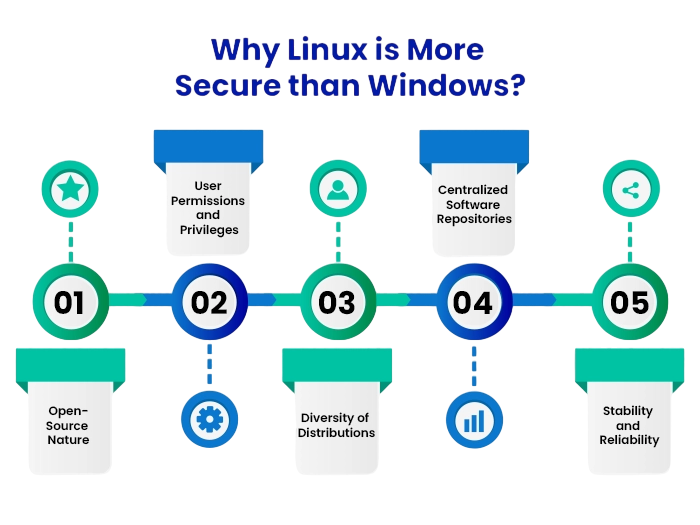
Security Features
Linux
Security is a vital concern, and Linux usually has the advantage. Its architecture, user permission model, and community oversight make it generally more secure. Most Linux distros do not automatically grant administrative privileges, which lowers the risk of accidental or harmful changes. The open-source code allows the community to identify and fix vulnerabilities quickly.
Windows
Windows has made notable improvements lately, introducing features like Windows Defender, SmartScreen, and secure boot. However, its popularity also makes it a frequent target for malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks risks that underscore the importance of secure coding practices taught in Web Developer Training, where learners master front-end and back-end development with an emphasis on performance, accessibility, and cybersecurity. By understanding platform vulnerabilities, developers can build resilient websites that protect user data and maintain trust. Regular updates and third-party security software are typically necessary to keep a secure environment.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Command-Line Capabilities
Linux
Linux really excels in its command-line interface. The terminal in Linux allows users to automate tasks, install packages, manage users, control services, and access system internals precisely. Advanced scripting with Bash and tools like awk, sed, grep, and cron make Linux the preferred platform for system administrators and developers a versatility echoed in Web Development Languages To Learn, where learners explore how languages like Python, JavaScript, and PHP integrate with Unix-based environments to power scalable web applications. Understanding shell scripting alongside modern web stacks enhances automation, deployment, and system-level control in full-stack development.
Windows
Windows has enhanced its command-line tools with PowerShell and the newer Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), allowing users to run a Linux environment natively. Nonetheless, Linux still offers a more developed and flexible CLI experience, especially for advanced system tasks and server management.
Software Compatibility
Hardware Support
Performance and Speed
Linux
Linux is known for its lightweight and efficient use of resources, making it excellent for older hardware, embedded systems, and performance-critical applications. Its minimal overhead and customizable nature allow it to be optimized for specific tasks, such as web servers or scientific computing.
Windows
Windows tends to use more resources because of its graphical effects, background services, and bundled features. While modern PCs manage Windows well, older hardware users may find it sluggish compared to Linux. For high-performance computing or server deployments, Linux generally provides better throughput and reliability.
Use Cases (Enterprise, Personal, Servers)
Conclusion
Choosing between Linux and Windows is not about determining which is better universally but about finding which one meets your specific needs. Windows excels in user-friendliness, software support, and hardware compatibility, making it great for general users, gamers, and businesses tied to Microsoft’s ecosystem skills that align with modern interface design principles taught in Web Developer Training, where learners master HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and responsive UI/UX techniques. Understanding platform behavior helps designers create seamless, cross-device experiences that cater to diverse user needs. Linux, with its strong security, performance, and customization options, is preferred in server environments, development, and tech-savvy circles. For newcomers to computing, Windows provides an easier learning curve, while Linux offers unmatched flexibility for those seeking control, open-source options, or cost-effective scalability. Many professionals now use dual-boot or virtual machine setups to enjoy the benefits of both. As both ecosystems continue to develop, the choice between Linux and Windows ultimately depends on your goals, technical skill, and intended use.





