
- Introduction to Factorial Concept
- Use Cases of Factorial in Real Life
- Mathematical Definition of Factorial
- Factorial Using for Loop
- Factorial Using While Loop
- Factorial Using do-while Loop
- Factorial Using Recursion
- Conclusion
Introduction to Factorial Concept
The Factorial Program of a non-negative integer is a fundamental concept in mathematics and computer science. Represented by n!, it is defined as the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. Factorial calculations are common in algorithm design, permutations, combinations, and in solving recursive problems. Understanding how to compute factorials in C helps build a solid foundation in loops, recursion, and number handling.The factorial is a basic yet important concept in mathematics, especially in algebra, combinatorics, and probability Web Designing & Development Training. It is used to find the number of ways to arrange or choose items. The factorial of a number n is written as n!, and it represents the product of all positive integers from 1 to n. For example, 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120. Factorials grow very quickly. Even a small increase in n leads to a large jump in the value of n!. For example, 6! = 720, and 10! = 3,628,800. By definition, 0! is equal to 1, which may seem strange at first but is necessary for mathematical consistency, especially in formulas involving combinations. Factorials are most commonly used in problems involving permutations (arranging items) and combinations (choosing items). For instance, if you want to know how many ways you can arrange 4 books on a shelf, you would calculate 4! = 24. Understanding factorials is essential for building a strong foundation in mathematics, especially in topics involving probability, statistics, and algorithms in computer science.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Use Cases of Factorial in Real Life
Factorial in Real Life are used in a variety of real-world contexts such as:
- Combinatorics: Calculating permutations and combinations (e.g., arranging people, selecting items).
- Probability Theory: Computing probabilities in events.
- Mathematics and Algorithms: Reverse a String Dynamic programming, recursive algorithms, etc.
- Statistical Computing: Analyzing data sets in statistics.
- Computer Graphics: For transformations and animation sequences.
These practical applications highlight why factorials are an essential topic in programming.
Mathematical Definition of Factorial
Mathematically, the factorial of a number n is defined as:
n! = n × (n−1) × (n−2) × … × 1
Special cases include:
- 0! = 1 (by definition)
- 1! = 1
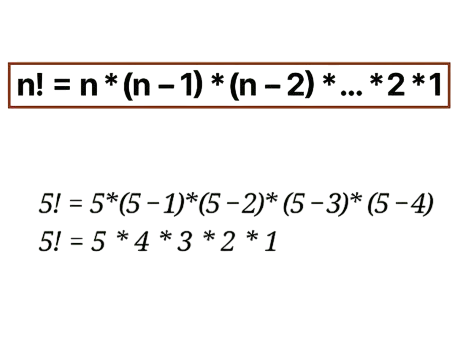
For example:
5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
This recursive nature of factorials makes them ideal for learning both iteration and recursion in programming Lambda Expression .
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Factorial Using for Loop
The most straightforward method of calculating factorial in C is by using a for loop Prim’s Algorithm Explanation.
- #include
- int main() {
- int n, i;
- unsigned long long factorial = 1;
- printf(“Enter a number: “);
- scanf(“%d”, &n);
- for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
- factorial *= i;
- }
- printf(“Factorial of %d = %llu\n”, n, factorial);
- return 0;
- }
The for loop iteratively multiplies each number from 1 to n, and stores the result. The use of unsigned long allows for larger storage.
Factorial Using While Loop
The same logic can be implemented using a while loop:
- #include
- int main() {
- int n, i = 1;
- unsigned long long factorial = 1;
- printf(“Enter a number: “);
- scanf(“%d”, &n);
- while (i <= n) {
- factorial *= i;
- i++;
- }
- printf(“Factorial of %d = %llu\n”, n, factorial);
- return 0;
- }
The while loop is useful when the number of iterations Web Designing & Development Training is not known in advance or when conditions are dynamically controlled.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
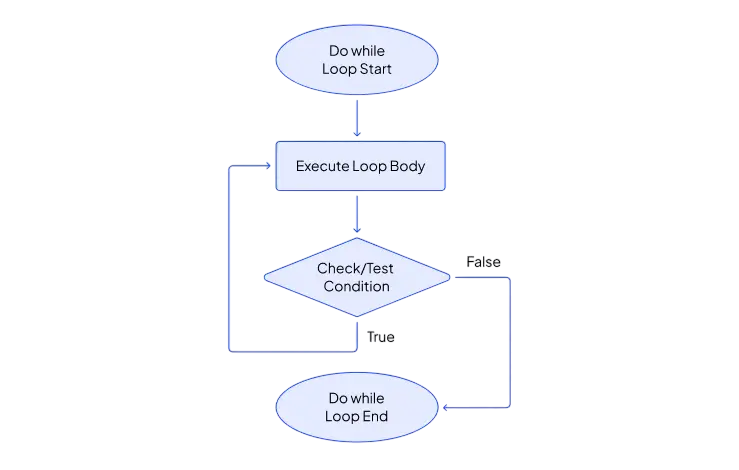
Factorial Using do-while Loop
A do-while loop can also be used and guarantees that the loop runs at least once Fibonacci Series in Python :
- #include
- int main() {
- int n, i = 1;
- unsigned long long factorial = 1;
- printf(“Enter a number: “);
- scanf(“%d”, &n);
- do {
- factorial *= i;
- i++;
- } while (i <= n);
- printf(“Factorial of %d = %llu\n”, n, factorial);
- return 0;
- }
This method is functionally similar to the whole version but structured differently.
Factorial Using Recursion
Factorial Using Recursion provides a more elegant and mathematical approach to computing factorials:
- #include
- unsigned long long factorial(int n) {
- if (n == 0 || n == 1)
- return 1;
- else
- return n * factorial(n – 1);
- }
- int main() {
- int n;
- printf(“Enter a number: “);
- scanf(“%d”, &n);
- printf(“Factorial of %d = %llu\n”, n, factorial(n));
- return 0;
- }
This method reflects the mathematical PPC Analyst Salary definition but can be memory-intensive for large n due to deep recursion stacks.
Conclusion
The Factorial Program concept is a vital mathematical idea that finds wide applications in various fields such as mathematics, computer science, statistics, and engineering. Represented by an exclamation mark (n!), the factorial of a number is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to that number. For example, 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120. This simple yet powerful concept helps in solving problems related to permutations and combinations, where the arrangement and selection of objects matter. In computer science, Web Designing & Development Training factorials are frequently used in algorithm design, recursion, and complexity analysis. Understanding how to compute factorials both manually and programmatically builds a solid foundation for tackling more advanced programming challenges. Common implementations in programming include iterative methods using loops and recursive approaches, which are excellent for illustrating key programming concepts. Factorials also play a crucial role in probability theory, where they are used to calculate the likelihood of different outcomes. They are essential in fields like data analysis, cryptography, and machine learning. In conclusion, mastering the factorial concept equips learners with the tools to approach a variety of mathematical and computational problems. It’s a small concept with a big impact, bridging the gap between theory and real-world applications.





