
- Global EV Market Trends
- Technological Advancements
- Government Policies and Incentives
- Battery Innovations
- Charging Infrastructure
- Autonomous EVs
- Impact on Oil and Gas
- Climate and Environmental Benefits
- Industry Challenges
- EV and Renewable Energy Integration
- Urban Mobility Solutions
- Final thoughts
Global EV Market Trends
The global electric vehicle (EV) market has seen a remarkable transformation over the past decade. From niche technology to mainstream transportation, EVs are now at the forefront of the automotive and energy revolution. As nations strive for sustainability and reduced carbon emissions, the EV market is poised to reshape the future of mobility. In 2024, global EV sales crossed over 14 million units, driven by strong demand in China, Europe, and the U.S., supported by advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and Artificial Intelligence Training that optimized production and performance. Analysts project that EVs could account for over 50% of global car sales by 2035. Growing environmental concerns, technological breakthroughs, and supportive policies are accelerating this adoption rate. Over the past ten years, the worldwide electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced a spectacular transition, going from a niche innovation to a mainstream method of transportation.
Technological Advancements
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) is largely driven by technological developments, which enhance performance, efficiency, and user experience. In order to increase economy, manufacturers are switching from conventional induction motors to permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) in powertrain development, one significant area of innovation. Regenerative braking systems, which enable EVs to recover and repurpose energy during deceleration and increase their range, have also become commonplace, alongside emerging innovations such as Battery Swapping in EV technology that further enhance efficiency and convenience. Additionally, a number of original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are creating specialised EV platforms, like Volkswagen’s MEB and GM’s Ultium, which enable scalable designs and modular battery packs. When taken as a whole, these developments are advancing electric vehicles into the next phase of automotive excellence by improving their accessibility, dependability, and comfort.
Government Policies and Incentives
Through well-designed regulations and incentive schemes, governments all over the world significantly contribute to the acceleration of the adoption of electric cars (EVs). In an effort to lower carbon emissions and advance sustainable mobility, many countries have set aggressive EV targets.
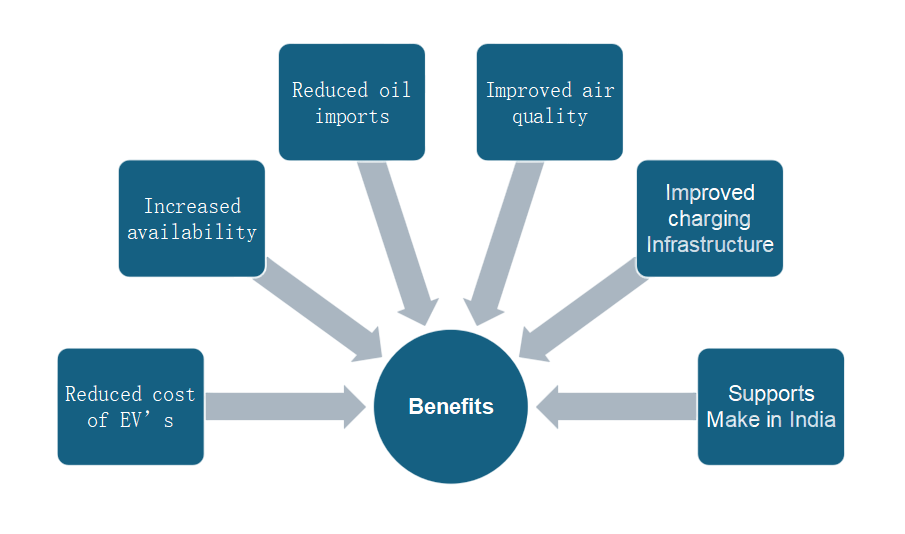
Infrastructure for charging is another important area of emphasis. To guarantee safety and network compatibility, governments are financing the construction of public charging stations, modernising power systems, and encouraging the creation of EV supply equipment (EVSE) standards and testing facilities, while also promoting EV Industry Career opportunities to support the growing workforce needs of this evolving sector. Lastly, the global automobile landscape is changing due to legislative mandates. In addition to enforcing strict CO2 fleet emission regulations, a number of nations have declared their intention to outlaw the sale of new internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles by 2035. The expansion of EVs and the global shift to a cleaner, electrified future are being accelerated by this policy alignment at both the national and municipal levels.
Ready to Get Certified in Artificial Intelligence ? Explore the Program Now Artificial Intelligence Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Battery Innovations
Battery technology is the linchpin of EV performance. The race to create safer, cheaper, and longer-lasting batteries, led in part by advancements in Tesla EV Battery Tech has driven several key innovations:
- Lithium-Ion Improvements
- Higher energy densities and faster charging rates.
- NMC (Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt) and LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) chemistries dominate. Solid-State Batteries
- Promise of greater safety, energy density, and lifecycle.
- Toyota, BMW, and QuantumScape are investing heavily. Silicon Anodes and Graphene
- Higher capacity materials replacing traditional graphite.
- Enable ultra-fast charging and better range.
These innovations will define the next generation of EVs.
Charging Infrastructure
Over the past ten years, the worldwide electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced a spectacular transition, going from a niche innovation to a mainstream method of transportation. EVs are currently at the vanguard of the energy and automotive revolutions, revolutionising the global transition to greener and more sustainable modes of transportation, while ongoing discussions around EV’s Advantages and Disadvantages continue to shape consumer perception and policy development. Electric vehicles have become a crucial component in accomplishing global sustainability targets as nations around the world step up efforts to cut carbon emissions and fight climate change.
To Explore Artificial Intelligence in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Autonomous EVs
The synergy between EVs and autonomous driving is reshaping mobility, with Artificial Intelligence Training playing a crucial role in enhancing vehicle perception, decision-making, and overall driving efficiency.
- Autonomous Tech Development
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and LiDAR integration.
- Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Cruise pioneering autonomy. Urban Mobility Integration
- Robo-taxis and autonomous shuttle services in testing.
- Potential for reduced traffic congestion and pollution. AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive maintenance, route optimization, and adaptive cruise.
- Enhancing vehicle efficiency and user experience.
- Zero emissions during operation.
- Significant contributor to urban air quality improvement. Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Cleaner electricity sources further reduce the carbon footprint, especially as the Electric Vehicles List continues to expand with more efficient and eco-friendly models from major automakers.
- Lifecycle emissions lower than ICE vehicles, even with battery production. Resource Optimization
- Efficient use of renewable energy for charging.
- Integration with smart grids and decentralized energy systems.
- Rooftop solar and EV charging integration.
- Reduces dependence on grid and enhances sustainability. Energy Storage Systems
- EV batteries as grid-balancing tools during demand peaks.
- Stationary storage from second-life batteries, repurposed from worn out Electric Vehicle Parts offers an innovative way to extend battery life and support renewable energy integration. Microgrids and Decentralized Networks
- Community-based energy and EV sharing models.
- Resilient energy infrastructure during outages. Demand Response and Smart Charging
- Aligns EV charging with grid capacity and renewable output.
Autonomous EVs represent the future of shared and individual transportation.
Impact on Oil and Gas
The conventional oil and gas sector is being significantly impacted by the quick uptake of electric vehicles (EVs), which is radically altering the dynamics of the world energy market. The demand for oil is predicted to gradually decrease over the next ten years as EVs rely on energy instead of fossil fuels, with advancements in the Types of Motors in Electric Vehicles further improving efficiency and performance across different models. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that by 2030, the widespread usage of EVs might replace around 5 million barrels of oil per day, signifying a dramatic departure from petroleum-based transportation. The global energy market is undergoing an economic realignment as a result of this change. As electricity starts to take over as the primary energy source for transportation, traditional trading patterns and refining sectors are changing. Once heavily dependent on oil exports, these nations are currently investigating alternative economic models centred on sustainable technologies and renewable energy.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Artificial Intelligence Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Climate and Environmental Benefits
EVs play a pivotal role in achieving global climate targets:
- Reduced Tailpipe Emissions
These benefits reinforce EVs as central to sustainability strategies.
Industry Challenges
Another significant issue is charging accessibility, particularly for city dwellers who don’t have designated parking spots for home charging. Furthermore, the distribution of infrastructure is still unequal, frequently underserving low-income and rural communities. For a significant portion of potential consumers, this imbalance restricts the practicality and ease of owning an EV, making a Hybrid Electric Vehicle an appealing alternative for those seeking both electric efficiency and traditional fuel flexibility.
Another issue with EVs is their cost. The initial cost of purchasing an electric vehicle is still higher than that of an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle, despite a consistent decline in battery prices. Additionally, there aren’t many affordable EV options in some areas, which limits middle-class and lower-class consumers’ access.
Preparing for Artificial Intelligence Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
EV and Renewable Energy Integration
The future of EVs is deeply linked with the energy sector’s transition:
- Solar-Powered EV Charging
EVs will not only consume energy but become part of the energy solution.
Urban Mobility Solutions
Cities’ approaches to urban mobility are being revolutionised by electric vehicles (EVs), which are spurring innovation in shared mobility, public transportation, and traffic control. The emergence of electric public transportation, such as e-buses and e-rickshaws, which are gaining popularity in both developed and developing countries, has been one of the biggest changes in the EV vs Fuel Vehicle debate, highlighting the environmental and operational advantages of electric mobility over traditional fossil-fuel-powered options. These electric fleets, which have minimal operating costs and are supported by government subsidies, are assisting cities in lowering emissions, lowering fuel prices, and improving air quality. Additionally, the development of small urban EVs, such as mini-electric vehicles and two-seaters, primarily addresses packed urban settings. Due to their energy-efficient and highly manoeuvrable design, these cars are perfect for short journeys and parking spots.
Summary
Electric vehicles are more than a trend; they represent a fundamental shift in how we think about mobility, energy, and the environment. From battery innovations to government policy, and from renewable integration to urban transformation, the EV landscape is dynamic and expansive. With sustained support, continued innovation, and advancements in Artificial Intelligence Training EVs will lead the charge into a sustainable, connected, and electrified future. People from various areas and socioeconomic backgrounds will have more access to electric vehicles as infrastructure grows and technology advances. Overcoming lingering issues like grid capacity, battery recycling, and charging accessibility will require cooperation between manufacturers, legislators, and consumers. In the end, the widespread use of EVs will change urban planning, economic opportunities, and our relationship with the environment in addition to lowering emissions. The move towards electrification is more than just a change in technology; it is a shared commitment to a future that is smarter, cleaner, and more robust for future generations.




