
- Embedded Systems in Automobiles
- Types of Embedded Systems
- Role in Modern Vehicles
- Engine Control Units (ECU)
- Body Electronics
- Safety Systems (ABS, Airbags)
- Infotainment Systems
- Communication Protocols (CAN, LIN)
- Real-Time Operating Systems
- Power Management & Autonomous Driving Support
- Security and Reliability
- Conclusion
Embedded Systems in Automobiles
Embedded systems are specialized computing systems that perform dedicated functions within larger mechanical or electrical systems. Unlike general-purpose computers, embedded systems are task-specific and often operate under real-time constraints. To understand how intelligent systems enhance these task-specific operations through real-time decision-making and adaptive control, explore Artificial Intelligence Training a hands-on course that covers embedded AI, machine learning, and system optimization for high-performance, time-sensitive applications. In the automotive industry, they are integral to vehicle functionality, from basic operations like power windows to complex applications like autonomous driving. With advancements in microcontroller technologies and the need for smart, efficient, and safe vehicles, embedded systems have become the backbone of modern automotive design.
Types of Embedded Systems
Automotive embedded systems can be broadly classified into stand-alone, networked, real-time, and mobile embedded systems. To explore how these classifications integrate with advanced architectures and intelligent features in modern EVs, explore Tesla Electric Vehicles a comprehensive guide that explains Tesla’s embedded systems, autonomous driving technologies, battery integration, and the innovations redefining electric mobility.
- Stand-alone systems function independently, such as a digital dashboard display.
- Networked systems communicate with other systems via protocols like CAN or LIN (e.g., ECU networks).
- Real-time systems are crucial in functions requiring instant response, like ABS and airbag systems.
- Mobile embedded systems integrate with external devices or networks, such as GPS or Bluetooth systems.
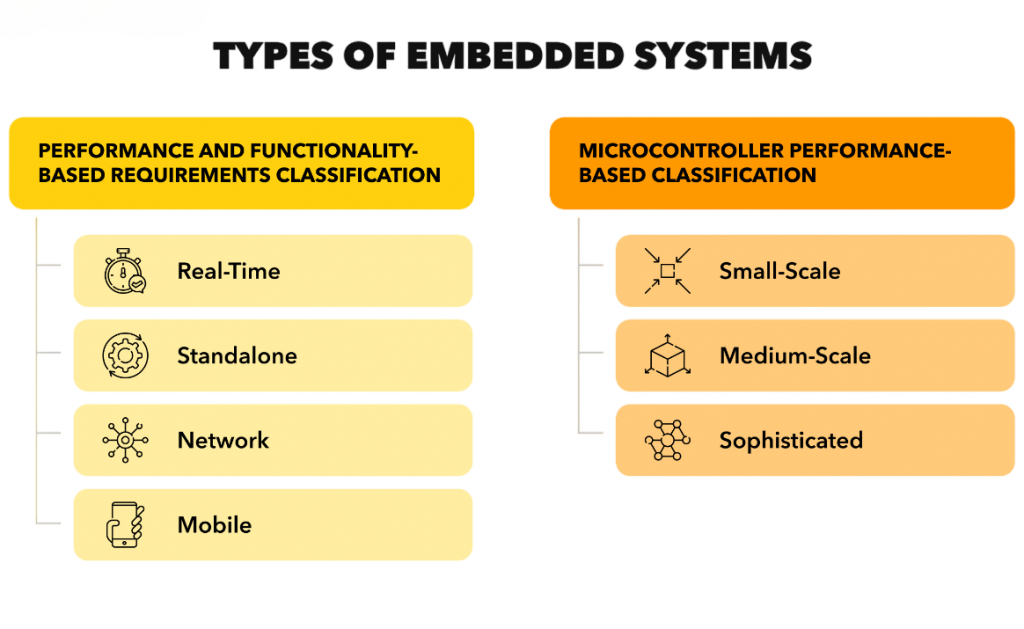
Each type plays a specific role in improving safety, performance, and user experience.
Ready to Get Certified in Artificial Intelligence ? Explore the Program Now Artificial Intelligence Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Role in Modern Vehicles
Embedded systems control most aspects of vehicle operation. From fuel injection timing, climate control, and lighting to advanced features like adaptive cruise control, they provide precision, efficiency, and automation. To explore how expertise in these technologies opens up opportunities for engineers, developers, and innovators, explore Career in Electric Vehicle Industry a comprehensive guide that highlights skill requirements, job roles, industry trends, and pathways to build a successful future in the EV sector. Their role is not limited to enhancing user comfort; they also enable regulatory compliance, reduce emissions, and improve fuel efficiency. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous technology, embedded systems are becoming even more critical, managing everything from battery systems to AI-based decision-making.
To Explore Artificial Intelligence in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Engine Control Units (ECU)
The Engine Control Unit is the brain behind engine operations. It continuously monitors inputs from sensors (e.g., oxygen sensor, throttle position sensor) and adjusts actuators (e.g., fuel injectors, spark plugs) to optimize engine performance. To explore how these monitoring and control mechanisms translate into modern EV architecture, explore Electric Vehicle Components a comprehensive guide that explains motors, controllers, batteries, inverters, and the integrated systems that drive efficiency and reliability in electric mobility. ECUs manage fuel-air mixtures, ignition timing, and idle speed to enhance power output, reduce emissions, and increase fuel efficiency. Modern vehicles can have 50+ ECUs working simultaneously, and advanced ECUs support adaptive algorithms for real-time learning and adjustments based on driving behavior.
Body Electronics
Body electronics manage non-drivetrain functions related to user comfort and convenience. These include systems like automatic climate control, central locking, power windows, interior/exterior lighting, and seat adjustments. To explore how intelligent systems enhance user comfort and operational efficiency across these features, explore Artificial Intelligence Training a hands-on course that covers embedded AI, sensor integration, and real-time control for smarter in-vehicle experiences. Embedded systems in body electronics are interconnected and often use a Body Control Module (BCM) that coordinates these functions. Intelligent lighting systems (adaptive headlights), keyless entry, and remote vehicle start are all powered by embedded controllers that ensure reliable and energy-efficient operation.
Safety Systems (ABS, Airbags)
Safety is a top priority in automotive design, and embedded systems are vital to active and passive safety mechanisms.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Uses embedded controllers to prevent wheel lock-up during sudden braking, improving vehicle control.
- Airbag Systems: Rely on embedded modules to instantly deploy airbags upon collision detection, triggered by accelerometers and crash sensors.
These systems must operate under strict real-time constraints to ensure immediate response within milliseconds, highlighting the importance of robust software and fail-safe design.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Artificial Intelligence Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems merge entertainment, navigation, and connectivity into a unified interface. Embedded systems enable voice control, touchscreen interfaces, smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto), and GPS navigation. To explore how these digital features integrate with the broader innovations shaping mobility, explore Electric Vehicle Technology a comprehensive guide that explains EV architecture, smart systems, battery innovations, charging infrastructure, and the role of embedded intelligence in modern electric vehicles. These systems also handle vehicle-to-driver communication through digital dashboards and driver-assist features. With advancements in user interface technologies, embedded systems now support gesture recognition, haptic feedback, and personalized profiles, greatly enhancing driver experience and safety.
Communication Protocols (CAN, LIN)
Communication between various embedded systems is crucial for synchronized operation.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): High-speed protocol used for real-time communication between ECUs (e.g., engine, transmission, brakes).
- LIN (Local Interconnect Network): Simpler functions like window controls and mirror adjustments.
These protocols reduce wiring complexity and enable diagnostic and fault-detection capabilities.
Preparing for Artificial Intelligence Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
An RTOS is essential in automotive embedded systems, especially where time-sensitive operations are involved. Unlike general-purpose OS, an RTOS ensures tasks are executed within predictable timeframes. To explore how these real-time controls synchronize with advanced braking and energy recovery systems, explore Electric vehicles with Regenerative Braking a comprehensive guide that explains braking energy capture, motor control, efficiency improvements, and the critical role of embedded systems in enhancing EV performance. Safety-critical systems like ABS, ESC, and powertrain control depend on RTOS for reliable, low-latency performance. Common automotive RTOS platforms include QNX, VxWorks, and AUTOSAR OS. These systems offer modularity, deterministic task handling, and fault tolerance, ensuring compliance with automotive safety standards like ISO 26262.
Power Management & Autonomous Driving Support
Power Management:
- Efficient power management is crucial, particularly for electric and hybrid vehicles. Embedded systems monitor and control energy distribution across various vehicle components to minimize wastage and maximize battery life. Systems like Battery Management Systems (BMS) ensure optimal battery charging, discharging, and thermal regulation. Embedded controllers also manage idle-stop systems, regenerative braking, and power recovery from accessories. These contribute to increased vehicle efficiency and compliance with emission regulations.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving heavily rely on embedded platforms for real-time processing of sensor data from cameras, LiDAR, radar, and GPS. These systems make decisions on braking, lane-keeping, obstacle avoidance, and speed control. Embedded platforms integrate with AI and machine learning algorithms to interpret complex scenarios and make predictive decisions. Real-time vision processing, sensor fusion, and decision logic must work flawlessly to ensure passenger safety and legal compliance.
Autonomous Driving Support:
Security and Reliability
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Embedded systems must be resilient against attacks that could compromise safety or user privacy. To explore how secure embedded systems integrate with propulsion technologies and speed management in EVs, explore Motor Types and Their Speed a comprehensive guide that explains induction motors, BLDC motors, PMSM motors, their speed control mechanisms, and the role of electronics in ensuring both performance and safety. Techniques like secure boot, encryption, and secure OTA updates are implemented. Functional safety is addressed through redundancy, self-check mechanisms, and compliance with standards like ISO 26262 and SAE J3061. Reliability also includes hardware durability, real-time system stability, and fault detection mechanisms that ensure fail-operational or fail-safe behaviors in critical systems.
Conclusion
Embedded systems have revolutionized the automotive industry, making vehicles smarter, safer, and more efficient. Their integration ranges from engine management to autonomous driving, requiring expertise in hardware-software co-design, real-time computing, communication protocols, and safety compliance. To explore how intelligent systems enable this integration across complex automotive domains, explore Artificial Intelligence Training a hands-on course that covers embedded AI, system architecture, and predictive control for high-performance, safety-critical EV applications. With the future heading toward electric and autonomous mobility, the demand for skilled embedded engineers and robust systems will continue to grow, shaping the next generation of intelligent vehicles.




