
- What is Android Development
- Academic Qualifications Needed
- Programming Languages (Java/Kotlin)
- Android Studio and Tools
- UI/UX Design Principles
- Backend Integration
- APIs and Libraries
- Publishing Apps to Play Store
- Certifications and Courses
- Internships and Projects
- Resume and Portfolio
- Final Thoughts
What is Android Development
Android development involves creating applications for devices running the Android operating system. With over 2.5 billion active users globally, Android is the most widely used mobile platform. This popularity creates a strong demand for skilled Android developers, making it a highly rewarding career path. The Android development ecosystem provides tools, frameworks, and programming languages, as well as support for Java Training that simplify the process of designing, coding, testing, and deploying mobile applications. Scalability, security, and maintainability are also prioritised in Android development, allowing apps to support enormous user bases while still meeting contemporary requirements. Finally Android development is one of the most dynamic and significant areas of contemporary software development since it blends creativity, technological know-how, and problem-solving to create applications that affect millions of consumers worldwide.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Java? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
Academic Qualifications Needed
While there is no strict educational requirement to become an Android developer, a background in computer science, software engineering, or a related field is advantageous. Degrees like BCA, B.Sc in Computer Science, or B.Tech in IT/CS provide a strong foundation in programming, data structures, algorithms, and system design. However, many successful Android developers, by learning Android App Development Fundamentals , are self-taught, leveraging online courses, tutorials, and hands-on projects.
Programming Languages (Java/Kotlin)
Android applications are primarily built using Java and Kotlin. Java has been the traditional language for Android development, offering robust libraries and community support. Kotlin, now officially supported by Google, is a modern, concise, and safer alternative to Java. It reduces boilerplate code and is interoperable with Java, making it an ideal choice for new Android projects.
- Proficiency in either or both languages is crucial for success in Android development.
- Android Studio, Google’s official Integrated programming Environment (IDE), is usually used for Android programming.
A code editor, debugging tools, an emulator for testing apps, performance profilers, and resources to understand concepts like What is BYOD are just a few of the many tools available in Android Studio. Gaining proficiency with Android Studio’s capabilities greatly increases output and code quality. The Android developer’s toolkit must also include other essentials like ADB (Android Debug Bridge) for device connectivity and Gradle for build automation.
Android Studio and Tools
Android Studio is the official IDE for Android development. It provides comprehensive tools such as:
- Code Editor: Smart suggestions and syntax highlighting.
- Layout Editor: Drag-and-drop interface design.
- Emulator: Simulates devices for app testing.
- Debugger and Profiler: Helps in debugging and optimizing app performance.
Other important tools, as well as resources on How to Become an iOS Developer , include:
UI/UX Design Principles
Creating user-friendly and visually appealing interfaces is crucial in Android development. Key principles include:
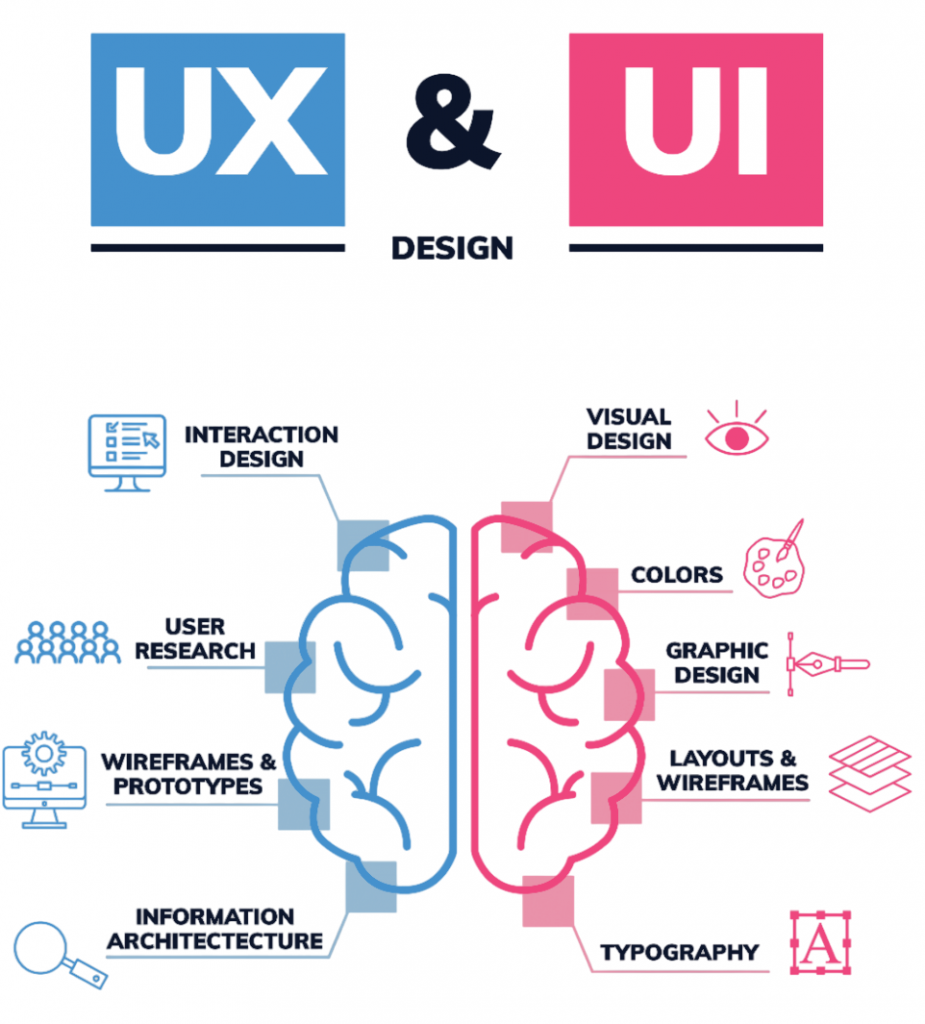
- Consistency: Use of Material Design guidelines for uniform look and feel.
- Responsiveness: Design adaptable layouts using ConstraintLayout, other responsive techniques, and tools like Xamarin Studio .
- Accessibility: Ensure app usability for users with disabilities.
- Intuitive Navigation: Clear and easy-to-use navigation patterns.
Tools like Figma and Adobe XD are often used for UI/UX prototyping before actual development.
Backend Integration
Most Android apps need to communicate with a server or database. Backend integration involves:
- RESTful APIs: Enable client-server communication using HTTP methods.
- Retrofit/Volley: Libraries for making API calls.
- Firebase Realtime Database/Firestore: Cloud databases for storing and syncing app data.
- Authentication Services: Login and user management through Firebase or OAuth providers like Google, Facebook, etc.
Understanding JSON parsing, network handling, and security protocols is vital for seamless backend integration.
APIs and Libraries
Utilizing external APIs and libraries, including those for Java Training enhances app functionality and reduces development time. Some commonly used ones include:
- Google Maps API: Location and navigation features.
- Glide/Picasso: Image loading and caching.
- Room: Local database management.
- WorkManager: For background tasks and job scheduling.
- LiveData and ViewModel: For managing UI-related data and lifecycle.
Choosing the right libraries and understanding their documentation is an essential skill.
Looking to master Java? Sign up for ACTE’s Java Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
Publishing Apps to Play Store
Deploying your Android app involves several steps:
- App Signing: Use a secure key to sign the APK.
- Testing: Ensure the app is bug-free on multiple devices.
- Preparing Store Listing: Include app name, description, screenshots, and promotional graphics.
- Submission: Upload the APK or AAB file to the Google Play Console.
- Review and Release: Google reviews the app before it becomes publicly available.
Understanding Google Play policies and adhering to privacy guidelines ensures smooth app publication, especially when developing in Swift vs Objective C environments.
Certifications and Courses
Certifications validate your skills and improve employability. Some notable ones include:
- Google Associate Android Developer Certification.
- Udacity Android Developer Nanodegree.
- Coursera Specializations by University of Maryland or Vanderbilt University.
Popular platforms offering Android development courses:
- Udemy
- Pluralsight
- LinkedIn Learning
- Codecademy
These courses cover basic to advanced topics, often including capstone projects.
Preparing for Java interviews? Visit our blog for the best Java Interview Questions and Answers
Internships and Projects
Practical experience is crucial for skill enhancement. Internships provide exposure to real-world development scenarios, team collaboration, and industry practices. Look for opportunities in startups, tech firms, or freelance platforms, especially if you have experience working with AlertDialog in Android development.
Building a variety of personal projects is equally important. Examples include:
- To-Do List App
- Weather App using API
- Chat App using Firebase
- Fitness Tracker
- E-commerce App
- Summary: Brief about your skills and interests.
- Technical Skills: Programming languages, tools, and libraries.
- Projects: Describe your role, technologies used, and outcomes, such as explaining How to create a Background Services In Android to demonstrate your technical expertise.
- Certifications: List relevant courses and achievements.
- GitHub Link: Showcase code quality and collaboration.
Such projects demonstrate your understanding of development concepts and problem-solving ability.
Resume and Portfolio
A strong resume and portfolio significantly improve your job prospects. Include:
Create a personal website or blog to further showcase your work and understanding of Android development.
Final Thoughts
Android development is a dynamic and lucrative career path. With the right educational foundation, mastery of tools like Android Studio, strong programming skills in Kotlin or Java, hands-on experience through projects, and Java Training you can build a successful career. Continuous learning, industry exposure, and an impressive portfolio will set you apart in the competitive job market. Furthermore, it’s critical to keep up with the newest developments in Android development trends and technology. This entails becoming acquainted with Jetpack libraries, contemporary architecture paradigms like MVVM, and cutting-edge tools for declarative UI creation like Jetpack Compose. Gaining knowledge of best practices for app security, testing, and performance optimization will also help you become more credible as a professional developer.



